Summary
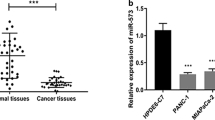
Previous studies have shown that miRNAs participate in a wide range of biological functions and play important roles in various human diseases including cancer. We found miR-146b-5p significantly dysregulated in human pancreatic cancer cells by qRT-PCR. To demonstrate its function and regulation mechanism, we overexpressed miR-146-5p by transfecting the mimics. Our data showed that miR-146b-5p overexpression significantly reduced the abilities of migration and invasion of MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells. Furthermore, we found that matrix metalloproteinase 16 (MMP16) was a downstream target of miR-146b-5p by dual-luciferase reporter assay. Altogether, our findings suggest that miR-146b-5p may be involved in pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting MMP16, and miR-146b-5p may be a potential therapeutic target for the pancreatic cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li D, Xie K, Wolff R, et al. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet, 2004,363(9414):1049–1057
Postier RG. The challenge of pancreatic cancer. Am J Surg, 2003,186(6):579–582
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs — microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 2006,6(4):259–269
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer, 2006,6(11):857–866
Sevignani C, Calin GA, Siracusa LD, et al. Mammalian microRNAs: a small world for fine-tuning gene expression. Mamm Genome, 2006,17(3):189–202
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, et al. microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol, 2007,302(1):1–12
Bhatti I, Lee A, James V, et al. Knockdown of microRNA-21 inhibits proliferation and increases cell death by targeting programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg, 2011,15(1):199–208
Zhao WG, Yu SN, Lu ZH, et al. The miR-217 microRNA functions as a potential tumor suppressor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by targeting KRAS. Carcinogenesis, 2010,31(10):1726–1733
Hanoun N, Delpu Y, Suriawinata AA, et al. The silencing of microRNA 148a production by DNA hypermethylation is an early event in pancreatic carcinogenesis. Clin Chem, 2010,56(7):1107–1118
Gironella M, Seux M, Xie MJ, et al. Tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 expression is repressed by miR-155, and its restoration inhibits pancreatic tumor development. PNAS, 2007,104(41):16 170–16 175
Rausch V, Liu L, Kallifatidis G, et al. Synergistic activity of sorafenib and sulforaphane abolishes pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics. Cancer Res, 2010,70(12):5004–5013
Nakada M, Nakamura H, Ikeda E, et al. Expression and tissue localization of membrane-type 1, 2, and 3 matrix metalloproteinases in human astrocytic tumors. Am J Pathol, 1999,154(2):417–428
He H, Jazdzewski K, Li W, et al. The role of microRNA genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005,102(52):19 075–19 080
Wang X, Tang S, Le SY, et al. Aberrant expression of oncogenic and tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer is required for cancer cell growth. PLoS One, 2008,3(7):e2557
Lin SL, Chiang A, Chang D, et al. Loss of mir-146a function in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. RNA, 2008,14(3):417–424
Nakasa T, Miyaki S, Okubo A, et al. Expression of microRNA-146 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum, 2008,58(5):1284–1292
Yamasaki K, Nakasa T, Miyaki S, et al. Expression of MicroRNA-146a in osteoarthritis cartilage. Arthritis Rheum, 2009,60(4):1035–1041
Xia H, Qi Y, Ng SS, et al. microRNA-146b inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion by targeting MMPs. Brain Res, 2009,1269():158–165
Bhaumik D, Scott GK, Schokrpur S, et al. Expression of microRNA-146 suppresses NF-kappaB activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast cancer cells. Oncogene, 2008,27(42):5643–5647
Hurst DR, Edmonds MD, Scott GK, et al. Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 up-regulates miR-146, which suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res, 2009,69(4):1279–1283
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
This project was supported by grants from the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 81071775, and No. 81001068).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, F., Wang, X., Jie, Z. et al. Inhibitory effects of miR-146b-5p on cell migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer by targeting MMP16. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 31, 509–514 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0481-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0481-5