Abstract
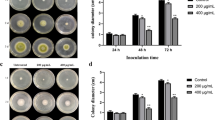
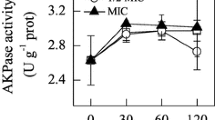
The objective of this work was to investigate antifungal actions of glycinin basic peptide (GBP), a natural preservative derived from soybean, against Aspergillus niger (A. niger). GBP exhibited the antifungal activity against A. niger with minimum inhibitory concentration of 1.5 mg/mL. The analysis of FSC and SSC manifested that GBP treatment could cause A. niger cells to shrink to become small and their granularity to complicate. And observations of electron microscopy directly showed more than 1.5 mg/mL GBP obviously destructed membrane, morphology, and organelles of mycelia and spores. The K+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ leakage further verified the disruptive region of GBP was membrane of A. niger. Moreover, the mitochondrial dysfunction by GBP was elucidated by the increase of intracellular reactive oxygen species and decrease of mitochondrial membrane potential. Taken together, GBP induced cellular damage and death of A. niger by collaborative action on cell membrane and mitochondria.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Sokmen, M. Gulluce, H.A. Akpulat, D. Daferera, B. Tepe, M. Polissiou, M. Sokmen, F. Sahin, The in vitro antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of the essential oils and methanol extracts of endemic Thymus spathulifolius. Food Control 15(8), 627–634 (2004)
V.C.H. Wu, X.J. Qiu, B.G. de los Reyes, C.S. Lin, Y.P. Pan, Application of cranberry concentrate (Vaccinium macrocarpon) to control Escherichia coli O157:H7 in ground beef and its antimicrobial mechanism related to the downregulated slp, hdeA and cfa. Food Microbiol. 26(1), 32–38 (2009)
S. Marín, M.E. Guynot, V. Sanchis, J. Arbonés, A.J. Ramos, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus niger, and Penicillium corylophilum spoilage prevention of bakery products by means of weak-acid preservatives. J. Food Sci. 67(6), 2271–2277 (2002)
G.F. Mehyar, H.M. Al-Qadiri, H.A. Abu-Blan, B.G. Swanson, Antifungal effectiveness of potassium sorbate incorporated in edible coatings against spoilage molds of apples, cucumbers, and tomatoes during refrigerated storage. J. Food Sci. 76(3), M210–M217 (2011)
S.C. Park, J.Y. Kim, J.K. Lee, I. Hwang, H. Cheong, J.W. Nah, K.S. Hahm, Y. Park, Antifungal mechanism of a novel antifungal protein from pumpkin rinds against various fungal pathogens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57(19), 9299–9304 (2009)
H.J. Kim, H.J. Suh, C.H. Lee, J.H. Kim, S.C. Kang, S. Park, J.S. Kim, Antifungal activity of glyceollins isolated from soybean elicited with Aspergillus sojae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58(17), 9483–9487 (2010)
Y.Q. Li, Q. Han, J.L. Feng, W.L. Tian, H.Z. Mo, Antibacterial characteristics and mechanisms of ɛ-poly-lysine against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 43, 2507–2515 (2014)
L. Zhang, A. Rozek, R.E.W. Hancock, Interaction of cationic antimicrobial peptides with model membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 276(38), 35714–35722 (2001)
S. Damodaran, J.E. Kinsella, Effect of conglycinin on the thermal aggregation of glycinin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 30(5), 812–817 (1982)
S. Hu, H. Liu, S. Qiao, P. He, X. Ma, W. Lu, Development of immunoaffinity chromatographic method for isolating glycinin (11S) from soybean proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 61(18), 4406–4410 (2013)
M.Z. Sitohy, S.A. Mahgoub, A.O. Osman, In vitro and in situ antimicrobial action and mechanism of glycinin and its basic subunit. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 154(1), 19–29 (2012)
Y.Q. Li, X.X. Sun, J.L. Feng, H.Z. Mo, Antibacterial activities and membrane permeability actions of glycinin basic peptide against Escherichia coli. Innovative Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 31, 170–176 (2014)
J. Yang, G.J. Sun, Y.Q. Li, K.Y. Cui, H.Z. Mo, Antibacterial characteristics of glycinin basic polypeptide against Staphylococcus aureus. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 25(5), 1477–1483 (2016)
J. Hou, Y.Q. Li, Z.S. Wang, G.J. Sun, H.Z. Mo, Applicative effect of glycinin basic polypeptide in fresh wet noodles and antifungal characteristics. LWT-food. Sci. Technol. 83, 267–274 (2017)
T. Nagano, M. Hirotsuka, H. Mori, K. Kohyama, K. Nishinari, Dynamic viscoelastic study on the gelation of 7S globulin from soybeans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 40(6), 941–944 (1992)
G. Ruchi, S. Sheela, Antifungal effect of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs LR14) derived from Lactobacillus plantarum strain LR/14 and their applications in prevention of grain spoilage. Food Microbiol. 42, 1–7 (2014)
Y.Z. Wang, X.B. Zeng, Z.K. Zhou, K. Xing, A. Tessemac, H. Zeng, J. Tiana, Inhibitory effect of nerol against Aspergillus niger on grapes through a membrane lesion mechanism. Food Control 55, 54–61 (2015)
K.D. Choi, H.Y. Kim, I.S. Shin, Antifungal activity of isothiocyanates extracted from horseradish (Armoracia rusticana) root against pathogenic dermal fungi. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 26(3), 847–852 (2017)
J. Tian, Y.Z. Wang, Z.Q. Lu, C.H. Sun, M. Zhang, A.H. Zhu, X. Peng, Perillaldehyde, a promising antifungal agent used in food preservation, triggers apoptosis through a metacaspase-dependent pathway in Aspergillus flavus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 64(39), 7404–7413 (2016)
W.R. Li, Q.S. Shi, Y.S. Ouyang, Y.B. Chen, S.S. Duan, Antifungal effects of citronella oil against Aspergillus niger ATCC 16404. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97(16), 7483–7492 (2013)
S. Manso, F. Cacho-Nerin, R. Becerril, C. Nerín, Combined analytical and microbiological tools to study the effect on Aspergillus flavus of cinnamon essential oil contained in food packaging. Food Control 30(2), 370–378 (2013)
A.S.Y. Ting, E. Jioe, In vitro assessment of antifungal activities of antagonistic fungi towards pathogenic Ganoderma boninense under metal stress. Biol. Control 96, 57–63 (2016)
J. Tian, X.B. Zeng, Z.Z. Feng, X.M. Miao, X. Peng, Y.W. Wang, Zanthoxylum molle Rehd. Essential oil as a potential natural preservative in management of Aspergillus flavus. Ind. Crop. Prod. 60, 151–159 (2014)
T. Wu, D. Cheng, M.Y. He, S.Y. Pan, X.L. Yao, X.Y. Xu, Antifungal action and inhibitory mechanism of polymethoxylated flavoned from Citrus reticulate Blanco peel against Aspergillus niger. Food Control 35(1), 354–359 (2014)
J. Yun, D.G. Lee, Cecropin A-induced apoptosis is regulated by ion balance and glutathione antioxidant system in Candida albicans. IUBMB Life 68(8), 652–662 (2016)
J. Tian, X.Q. Ban, H. Zeng, J.S. He, Y.X. Chen, Y.W. Wang, The mechanism of antifungal action of essential oil from dill (Anethum graveolens L.) on Aspergillus flavus. PLoS One 7(1), e30147 (2012)
L.R. Li, Y.H. Shi, M.J. Cheserek, G.F. Su, G.W. Le, Antibacterial activity and dual mechanisms of peptide analog derived from cell-penetrating peptide against Salmonella typhimurium and Streptococcus pyogenes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97(4), 1711–1723 (2013)
H.J. Lee, J.S. Hwang, D.G. Lee, Scolopendin, an antimicrobial peptide from centipede, attenuates mitochondrial functions and triggers apoptosis in Candida albicans. Biochem. J. 474(5), 635–645 (2017)
G.P. Zhao, Y.Q. Li, G.J. Sun, H.Z. Mo, Antibacterial actions of glycinin basic peptide against Escherichia coli. J. Agric. Food Chem. 65(25), 5173–5180 (2017)
J. Zhang, X. Wu, S.Q. Zhang, Antifungal mechanism of antibacterial peptide, ABP-CM4, from Bombyx mori against Aspergillus niger. Biotechnol. Lett. 30(12), 2157–2163 (2008)
S. Shabala, L. Shabala, Ion transport and osmotic adjustment in plants and bacteria. Biomol Concepts 2(5), 407–419 (2011)
D.G. Lee, H.N. Kim, Y. Park, H.K. Kim, B.H. Choi, C.H. Choi, K.S. Hahm, Design of novel analogue peptides with potent antibiotic activity based on the antimicrobial peptide, HP (2–20), derived from N-terminus of Helicobacter pylori ribosomal protein L1. Biochim Biophys Acta, Proteins Proteomics. 1598, 185–194 (2002)
L.R. Li, J. Sun, S.F. Xia, X. Tian, M. Cheserek, G.W. Le, Mechanism of antifungal activity of antimicrobial peptide APP, a cell-penetrating peptide derivative, against Candida albicans: Intracellular DNA binding and cell cycle arrest. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 100(7), 3245–3253 (2016)
K. Akash, K.D. Abhishek, K.J. Dhruva, K.D. Nawal, Efficacy of Mentha spicata essential oil in suppression of Aspergillus flavus and aflatoxin contamination in chickpea with particular emphasis to mode of antifungal action. Protoplasma 253(3), 647–653 (2016)
T. Wu, D. Cheng, M.Y. He, S.Y. Pan, X.L. Yao, X.Y. Xu, Antifungal action and inhibitory mechanism of polymethoxylated flavones from Citrus reticulata Blanco peel against Aspergillus niger. Food Control 35(1), 354–359 (2014)
N. Delattin, B.P. Cammue, K. Thevissen, Reactive oxygen species-inducing antifungal agents and their activity against fungal biofilms. Future Med. Chem. 6(1), 77–90 (2014)
M. Sharma, R. Manoharlal, N. Puri, R. Prasad, Antifungal curcumin induces reactive oxygen species and triggers an early apoptosis but prevents hyphae development by targeting the global repressor TUP1 in Candida albicans. Biosci. Rep. 30(6), 391–404 (2010)
A. Lupetti, A.P. Annema, S. Senesi, M. Campa, J.T.V. Dissel, P.H. Nibbering, Internal thiols and reactive oxygen species in candidacidal activity exerted by an N-terminal peptide of human lactoferrin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 46(6), 1634–1639 (2002)
J.J. Cheng, T.S. Park, L.C. Chio, A.S. Fischl, X.S. Ye, Induction of apoptosis by sphingoid long-chain bases in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23(1), 163–177 (2003)
A. Lachelle, R.R. Jason, L. Sebastian, W. Regine, N.T. Gregory, Membrane activity of biomimetic facially amphiphilic antibiotics. J. Phys. Chem. B 110(8), 3527–3532 (2006)
M. Giudici, J.A. Poveda, M.L. Molina, L.D.L. Canal, R.J.M. González, K. Pfüller, U. Pfüller, J. Villalaín, Antifungal effects and mechanism of action of viscotoxin A3. FEBS J. 273(1), 72–83 (2006)
L. Kaiserer, C. Oberparleiter, G.R. Weiler, W. Burgstaller, E. Leiter, F. Marx, Characterization of the Penicillium chrysogenum antifungal protein PAF. Arch. Microbiol. 180(3), 204–210 (2003)
R. Petruzzelli, M.E. Clementi, S. Marini, M. Coletta, E.D. Stasio, B. Giardina, F. Misiti, Respiratory inhibition of isolated mammalian mitochondria by salivary antifungal peptide histatin-5. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 311(4), 1034–1040 (2003)
U. Schönfelder, A. Radestock, P. Elsner, U.C. Hipler, Cyclodextrin-induced apoptosis in human keratinocytes is caspase-8 dependent and accompanied by mitochondrial cytochrome c release. Exp. Dermatol. 15(11), 883–890 (2006)
M.T. Andrés, M.V. Díaz, J.F. Fierro, Human lactoferrin induces apoptosis-like cell death in Candida albicans: Critical role of K+-channel-mediated K+ efflux. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52(11), 4081–4088 (2008)
E.M. Barbu, F. Shirazi, D.M. Mcgrath, N. Albert, R.L. Sidman, R. Pasqualini, W. Arap, D.P. Kontoyiannis, An antimicrobial peptidomimetic induces Mucorales cell death through mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. PLoS One 8(10), e76981 (2013)
J. Reiter, E. Herker, F. Madeo, M.J. Schmitt, Viral killer toxins induce caspase-mediated apoptosis in yeast. J. Cell Biol. 168(3), 353–358 (2005)
J. Lee, J.S. Hwang, I.S. Hwang, J. Cho, E. Lee, Y. Kim, D.G. Lee, Coprisin-induced antifungal effects in Candida albicans correlate with apoptotic mechanisms. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 52(11-12), 2302–2311 (2012)
J.H. Hwang, I.S. Hwang, Q.H. Liu, E.R. Woo, D.G. Lee, (+)-Medioresinol leads to intracellular ROS accumulation and mitochondria-mediated apoptotic cell death in Candida albicans. Biochimie 94(8), 1784–1793 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31371839), Major Plan of Studying and Developing (2018YYSP001), 2017-year Support Program for Introduction of Urgently-needed talents in Western Economic Upwarping Zone and Poverty-alleviation-exploitation Key Area in Shandong Province, as well as the Program for Science and Technology Innovation Team in Universities of Henan Province (16IRTSTHN007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, L., Li, Y., Wang, Z. et al. Antifungal Actions of Glycinin Basic Peptide against Aspergillus niger through the Collaborative Damage to Cell Membrane and Mitochondria. Food Biophysics 14, 97–107 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-018-9561-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-018-9561-4