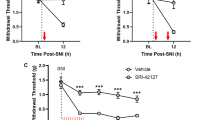
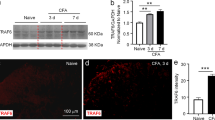
Abstract
Innate immune response acts as the first line of host defense against damage and is initiated following the recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). For double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) sensing, interferon gene stimulator (STING) was discovered to be an integral sensor and could mediate the immune and inflammatory response. Selective STING antagonist C-176 was administered and pain behaviors were assessed following spared nerve injury (SNI)-induced neuropathic pain. The level of serum dsDNA following neuropathic pain was assessed using Elisa analysis. STING signaling pathway, microglia activation, and proinflammatory cytokines were assessed by qPCR, western blots, Elisa, and immunofluorescence staining. STING agonist DMXAA was introduced into BV-2 cells to assess the inflammatory response in microglial cells. dsDNA was significantly increased following SNI and STING/TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1)/nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway was activated in vivo and vitro. Early but not the late intrathecal injection of C-176 attenuated SNI-induced pain hypersensitivity, microglia activation, proinflammatory factors, and phosphorylated JAK2/STAT3 in the spinal cord dorsal horn, and the analgesic effect of C-176 was greatly abolished by recombinant IL-6 following SNI. We provided evidence clarifying dsDNA mediated activation of microglia STING signaling pathway, after which promoting expression of proinflammatory cytokines that are required for hyperalgesia initiation in the spinal cord dorsal horn of SNI model. Further analysis showed that microglial STING/TBK1/NF-κB may contribute to pain initiation via IL-6 signaling. Pharmacological blockade of STING may be a promising target in the treatment of initiation of neuropathic pain.
Graphic Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAK:
-
BCL-2 homologous killer
- BAX:
-
BCL-2-like protein 4
- cGAS:
-
Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagles medium
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide dsDNA: double-stranded DNA
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- Iba1:
-
Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1
- IF:
-
Immunofluorescence
- IFNs:
-
Interferons
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin 1β
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin 6
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- IRF3:
-
Interferons regulatory factor 3
- JAK:
-
Janus-activated kinase
- L4:
-
Lumber 4
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemotactic protein 1
- mtDNA:
-
Mitochondrial DNA
- NeuN:
-
Neuronal nuclei
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-kappa B
- OFM:
-
Open Field Maze
- PAMPs:
-
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- PCR:
-
Polymerase Chain Reaction
- PFA:
-
Paraformaldehyde
- PWT:
-
Paw withdrawal threshold
- rIL-6:
-
Recombinant mice IL-6
- RT:
-
Room temperature
- SNI:
-
Spared nerve injury
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer activator of transcription 3
- STING:
-
Stimulator of interferon genes
- TBK1:
-
TANK-binding kinase 1
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- TFAM:
-
Transcription factor A, mitochondrial
- TWL:
-
Thermal withdrawal latency
- WB:
-
Western blot
References
Abdullah A, Zhang M, Frugier T, Bedoui S, Taylor JM, Crack PJ (2018) STING-mediated type-I interferons contribute to the neuroinflammatory process and detrimental effects following traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflammation 15:323
Ahn J, Gutman D, Saijo S, Barber GN (2012) STING manifests self DNA-dependent inflammatory disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Baral P, Udit S, Chiu IM (2019) Pain and immunity: implications for host defence. Nat Rev Immunol
Barker RN, Erwig LP, Pearce WP, Devine A, Rees AJ (1999) Differential Effects of Necrotic or Apoptotic Cell Uptake on Antigen Presentation by Macrophages. Pathobiology 67:302–305
Barragan-Iglesias P, Franco-Enzastiga U, Jeevakumar V, Shiers S, Wangzhou A, Granados-Soto V, Campbell ZT, Dussor G, Price TJ (2020) Type I Interferons Act Directly on Nociceptors to Produce Pain Sensitization: Implications for Viral Infection-Induced Pain. J Neurosci 40:3517–3532
Bauer S (2006) Toll-erating self DNA. Nat Immunol 7:13–15
Beutler B (2009) Microbe sensing, positive feedback loops, and the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. Immunol Rev 227
Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS (2007) Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:57–69
Burdette DL, Vance RE (2013) STING and the innate immune response to nucleic acids in the cytosol. Nat Immunol 14:19–26
Cao F, Gao F, Xu AJ, Chen ZJ, Chen SS, Yang H, Yu HH, Mei W, Liu XJ, Xiao XP et al (2010) Regulation of spinal neuroimmune responses by prolonged morphine treatment in a rat model of cancer induced bone pain. Brain Res 1326:162–173
Chamilos G, Gregorio J, Meller S, Lande R, Kontoyiannis DP, Modlin RL, Gilliet M (2012) Cytosolic sensing of extracellular self-DNA transported into monocytes by the antimicrobial peptide LL37. Blood 120:3699
Chang HH, Miaw SC, Tseng W, Sun YW, Liu CC, Tsao HW, Ho IC (2013) PTPN22 Modulates Macrophage Polarization and Susceptibility to Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis. J Immunol
Chen G, Zhang YQ, Qadri YJ, Serhan CN, Ji RR (2018a) Microglia in Pain: Detrimental and Protective Roles in Pathogenesis and Resolution of Pain. Neuron 100:1292–1311
Chen Q, Sun L, Chen ZJ (2016) Regulation and function of the cGAS-STING pathway of cytosolic DNA sensing. Nat Immunol 17:1142–1149
Chen SP, Sun J, Zhou YQ, Cao F, Braun C, Luo F, Ye DW, Tian YK (2018b) Sinomenine attenuates cancer-induced bone pain via suppressing microglial JAK2/STAT3 and neuronal CAMKII/CREB cascades in rat models. Mol Pain 14:1744806918793232
Decosterd I, Woolf CJ (2000) Spared nerve injury: an animal model of persistent peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain 87:149–158
Deleo JA, Colburn RW, Nichols M, Malhotra A (1996) Interleukin-6-mediated hyperalgesia/allodynia and increased spinal IL-6 expression in a rat mononeuropathy model. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research the Official Journal of the International Society for Interferon & Cytokine Research 16:695–700
Deng L, Liang H, Xu M, Yang X, Burnette B, Arina A, Li XD, Mauceri H, Beckett M, Darga T et al (2014) STING-Dependent Cytosolic DNA Sensing Promotes Radiation-Induced Type I Interferon-Dependent Antitumor Immunity in Immunogenic Tumors. Immunity 41:843–852
Dominguez E, Mauborgne A, Mallet J, Desclaux M, Pohl M (2010) SOCS3-mediated blockade of JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway reveals its major contribution to spinal cord neuroinflammation and mechanical allodynia after peripheral nerve injury. J Neurosci
Dominguez E, Rivat C, Pommier B, Mauborgne A, Pohl M (2008) JAK/STAT3 pathway is activated in spinal cord microglia after peripheral nerve injury and contributes to neuropathic pain development in rat. J Neurochem 107:50–60
Donnelly CR, Jiang C, Andriessen AS, Wang K, Wang Z, Ding H, Zhao J, Luo X, Lee MS, Lei YL et al (2021) STING controls nociception via type I interferon signalling in sensory neurons. Nature
Dunphy G, Flannery SM, Almine JF, Connolly DJ, Paulus C, Jonsson KL, Jakobsen MR, Nevels MM, Bowie AG, Unterholzner L (2018) Non-canonical Activation of the DNA Sensing Adaptor STING by ATM and IFI16 Mediates NF-kappaB Signaling after Nuclear DNA Damage. Mol Cell 71:745–760 e745
Fairbanks CA (2003) Spinal delivery of analgesics in experimental models of pain and analgesia. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55:1007–1041
Grace PM, Rolan PE, Hutchinson MR (2011) Peripheral immune contributions to the maintenance of central glial activation underlying neuropathic pain. Brain Behav Immun 25:1322–1332
Haag SM, Gulen MF, Reymond L, Gibelin A, Abrami L, Decout A, Heymann M, van der Goot FG, Turcatti G, Behrendt R, Ablasser A (2018) Targeting STING with covalent small-molecule inhibitors. Nature 559:269–273
Hilkens CM, Schlaak JF, Kerr IM (2003) Differential responses to IFN-alpha subtypes in human T cells and dendritic cells. J Immunol 171:5255–5263
Hou Y, Liang H, Rao E, Zheng W, Huang X, Deng L, Zhang Y, Yu X, Xu M, Mauceri H et al (2018) Non-canonical NF-kappaB Antagonizes STING Sensor-Mediated DNA Sensing in Radiotherapy. Immunity 49:490–503 e494
Hornung V, Latz E (2010) Intracellular DNA recognition. Nat Rev Immunol 10:123–130
Hunter MM, Wang A, Parhar KS, Johnston MJG, Rooijen NV, Beck PL, Mckay DM (2010) In Vitro-Derived Alternatively Activated Macrophages Reduce Colonic Inflammation in Mice. Gastroenterology 138:1395–1405
Inoue K, Tsuda M (2018) Microglia in neuropathic pain: cellular and molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Neurosci 19:138–152
Jensen TS, Baron R, Haanpää M, Kalso E, Loeser JD, Rice AS, Treede RD (2011) A new definition of neuropathic pain. Pain 152:2204–2205
Jiang X, Liu G, Hu Z, Chen G, Chen J, Lv Z (2019) cGAMP inhibits tumor growth in colorectal cancer metastasis through the STING/STAT3 axis in a zebrafish xenograft model. Fish Shellfish Immunol 95:220–226
Kawai T, Akira S (2009) The roles of TLRs, RLRs and NLRs in pathogen recognition. Int Immunol
Kawasaki Y, Zhang L, Cheng JK, Ji RR (2008) Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord. J Neurosci 28:5189–5194
Kim D, You B, Jo EK, Han SK, Simon MI, Lee SJ (2010) NADPH oxidase 2-derived reactive oxygen species in spinal cord microglia contribute to peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:14851–14856
Kobayashi K, Imagama S, Ohgomori T, Hirano K, Uchimura K, Sakamoto K, Hirakawa A, Takeuchi H, Suzumura A, Ishiguro N, Kadomatsu K (2013) Minocycline selectively inhibits M1 polarization of microglia. Cell Death Dis 4:e525
Larner AC, Chaudhuri A, Darnell JE Jr (1986) Transcriptional induction by interferon. New protein (s) determine the extent and length of the induction. J Biol Chem 261:453–459
Le WD, Rowe D, Xie WJ, Ortiz I, Appel SH (2001) Microglial Activation and Dopaminergic Cell Injury: An In Vitro Model Relevant to Parkinson’s Disease. The Journal of Neuroence: the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroence 21:8447–8455
Li N, Zhou H, Wu H, Wu Q, Duan M, Deng W, Tang Q (2019) STING-IRF3 contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction, inflammation, apoptosis and pyroptosis by activating NLRP3. Redox Biol 24:101215
Li T, Chen ZJ (2018) The cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway connects DNA damage to inflammation, senescence, and cancer. J Exp Med 215:1287–1299
Li T, Liu T, Chen X, Li L, Feng M, Zhang Y, Wan L, Zhang C, Yao W (2020) Microglia induce the transformation of A1/A2 reactive astrocytes via the CXCR7/PI3K/Akt pathway in chronic post-surgical pain. J Neuroinflammation 17:211
Liu S, Karaganis S, Mo RF, Li XX, Wen RX, Song XJ (2020) IFNbeta Treatment Inhibits Nerve Injury-induced Mechanical Allodynia and MAPK Signaling By Activating ISG15 in Mouse Spinal Cord. J Pain 21:836–847
Luo W, Wang Y, Zhang L, Ren P, Shen YH (2020) Critical Role of Cytosolic DNA and Its Sensing Adaptor STING in Aortic Degeneration, Dissection, and Rupture. Circulation 141:42–66
Mathur V, Burai R, Vest RT, Bonanno LN, Lehallier B, Zardeneta ME, Mistry KN, Do D, Marsh SE, Abud EM et al (2017) Activation of the STING-Dependent Type I Interferon Response Reduces Microglial Reactivity and Neuroinflammation. Neuron 96:1290–1302 e1296
Mc A, Jmd A, Ddlba B (2012) The role of the immune system in the generation of neuropathic pain - ScienceDirect. Lancet Neurol 11:629–642
Möser C, Kynast K, Baatz K, Russe OQ, Niederberger E (2011) The Protein Kinase IKKε Is a Potential Target for the Treatment of Inflammatory Hyperalgesia. J Immunol 187:2617
Moser CV, Stephan H, Altenrath K, Kynast KL, Russe OQ, Olbrich K, Geisslinger G, Niederberger E (2015) TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) modulates inflammatory hyperalgesia by regulating MAP kinases and NF-kappaB dependent genes. J Neuroinflammation 12:100
Nicholson SE, Hilton DJ (1998) The SOCS proteins: a new family of negative regulators of signal transduction. J Leukoc Biol 63:665–668
Palm NW, Medzhitov R (2009) Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev 227:221–233
Patrushev M, Kasymov V, Patrusheva V, Ushakova T, Gogvadze V, Gaziev A (2004) Mitochondrial permeability transition triggers the release of mtDNA fragments. Cellular & Molecular Life Sciences Cmls 61:3100–3103
Peng J, Gu N, Zhou L, Eyo UB, Murugan M, Gan WB, Wu LJ (2016) Microglia and monocytes synergistically promote the transition from acute to chronic pain after nerve injury. Nat Commun 7:12029
Peng Y, Zhuang J, Ying G, Zeng H, Zhou H, Cao Y, Chen H, Xu C, Fu X, Xu H et al (2020) Stimulator of IFN genes mediates neuroinflammatory injury by suppressing AMPK signal in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neuroinflammation 17:165
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Verri WA, Chiu IM (2016) Nociceptor Sensory Neuron–Immune Interactions in Pain and Inflammation. Trends Immunol 5
Robinson SM, Mann DA (2010) Role of nuclear factor κB in liver health and disease. Clin Sci 118:691–705
Saitoh T, Fujita N, Hayashi T, Takahara K, Satoh T, Lee H, Matsunaga K, Kageyama S, Omori H, Noda T et al (2009) Atg9a controls dsDNA-driven dynamic translocation of STING and the innate immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:20842–20846
Sauter B, Albert ML, Francisco L, Larsson M, Somersan S, Bhardwaj N (2000) Consequences of cell death: exposure to necrotic tumor cells, but not primary tissue cells or apoptotic cells, induces the maturation of immunostimulatory dendritic cells. J Exp Med 191:423–434
Sliter DA, Martinez J, Hao L, Chen X, Sun N, Fischer TD, Burman JL, Li Y, Zhang Z, Narendra DP et al (2018) Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING-induced inflammation. Nature 561:258–262
Sommer C, Leinders M, Uceyler N (2018) Inflammation in the pathophysiology of neuropathic pain. Pain 159:595–602
Sorge RE, Mapplebeck J, Rosen S, Beggs S, Taves S, Alexander JK, Martin LJ, Austin JS, Sotocinal SG, Chen D (2015) Different immune cells mediate mechanical pain hypersensitivity in male and female mice. Nat Neurosci 18:1081–1083
Van Steenwinckel J, Reaux-Le Goazigo A, Pommier B, Mauborgne A, Dansereau MA, Kitabgi P, Sarret P, Pohl M, Melik Parsadaniantz S (2011) CCL2 released from neuronal synaptic vesicles in the spinal cord is a major mediator of local inflammation and pain after peripheral nerve injury. J Neurosci 31:5865–5875
Watkins LR, Milligan ED, Maier SF (2001) Glial activation: a driving force for pathological pain. Trends Neurosci 24:450–455
West AP, Khoury-Hanold W, Staron M, Tal MC, Pineda CM, Lang SM, Bestwick M, Duguay BA, Raimundo N, MacDuff DA et al (2015) Mitochondrial DNA stress primes the antiviral innate immune response. Nature 520:553–557
West AP, Shadel GS (2017) Mitochondrial DNA in innate immune responses and inflammatory pathology. Nat Rev Immunol
White MJ, McArthur K, Metcalf D, Lane RM, Cambier JC, Herold MJ, van Delft MF, Bedoui S, Lessene G, Ritchie ME et al (2014) Apoptotic caspases suppress mtDNA-induced STING-mediated type I IFN production. Cell 159:1549–1562
Woller SA, Ocheltree C, Wong SY, Bui A, Fujita Y, Dos Santos GG, Yaksh TL, Corr M (2019) Neuraxial TNF and IFN-beta co-modulate persistent allodynia in arthritic mice. Brain Behav Immun 76:151–158
Xu N, Tang XH, Pan W, Xie ZM, Zhang GF, Ji MH, Yang JJ, Zhou MT, Zhou ZQ (2017) Spared Nerve Injury Increases the Expression of Microglia M1 Markers in the Prefrontal Cortex of Rats and Provokes Depression-Like Behaviors. Front Neurosci 11:209
Zhang CX, Ye SB, Ni JJ, Cai TT, Liu YN, Huang DJ, Mai HQ, Chen QY, He J, Zhang XS et al (2019) STING signaling remodels the tumor microenvironment by antagonizing myeloid-derived suppressor cell expansion. Cell Death Differ 26:2314–2328
Zhao Q, Wei Y, Pandol SJ, Li L, Habtezion A (2018) STING Signaling Promotes Inflammation in Experimental AcutePancreatitis. Gastroenterology 1822–1835
Zhou YQ, Liu DQ, Chen SP, Chen N, Sun J, Wang XM, Cao F, Tian YK, Ye DW (2020) Nrf2 activation ameliorates mechanical allodynia in paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. Acta Pharmacol Sin
Zhou YQ, Liu DQ, Chen SP, Sun J, Zhou XR, Rittner H, Mei W, Tian YK, Zhang HX, Chen F, Ye DW (2018) Reactive oxygen species scavengers ameliorate mechanical allodynia in a rat model of cancer-induced bone pain. Redox Biol 14:391–397
Zhou YQ, Liu Z, Liu ZH, Chen SP, Li M, Shahveranov A, Ye DW, Tian YK (2016) Interleukin-6: an emerging regulator of pathological pain. J Neuroinflammation 13:141
Zhu Q, Man SM, Gurung P, Liu Z, Vogel P, Lamkanfi M, Kanneganti TD (2014) Cutting edge: STING mediates protection against colorectal tumorigenesis by governing the magnitude of intestinal inflammation. J Immunol 193:4779–4782
Zhu Y, An X, Zhang X, Qiao Y, Zheng T, Li X (2019) STING: a master regulator in the cancer-immunity cycle. Mol Cancer 18:152
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Pei-Xiang Lan for helpful guidance and discussions.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of P.R. China 82071556 and 81873793.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WM, DWY and YQZ conceived the project and supervised all experiments. JS and BYX analyzed data, prepared figures and wrote manuscripts. JYL, LQZ, JYW and SJG performed experiments on behavioral tests, western blot, ELISA, and immunofluorescence. DYL and SZ revised manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
All experiments were approved by the Experimental Animal Care and Use Committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and were in agreement with the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Zhou, Yq., Xu, By. et al. STING/NF-κB/IL-6-Mediated Inflammation in Microglia Contributes to Spared Nerve Injury (SNI)-Induced Pain Initiation. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 17, 453–469 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-021-10031-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-021-10031-6