Abstract
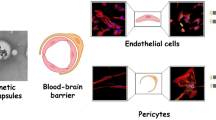
Blood-brain barrier is a tightly packed layer of endothelial cells surrounding the brain that acts as the main obstacle for drugs enter the central nervous system (CNS), due to its unique features, as tight junctions and drug efflux systems. Therefore, since the incidence of CNS disorders is increasing worldwide, medical therapeutics need to be improved. Consequently, aiming to surpass blood-brain barrier and overcome CNS disabilities, silencing P-glycoprotein as a drug efflux transporter at brain endothelial cells through siRNA is considered a promising approach. For siRNA enzymatic protection and efficient delivery to its target, two different nanoparticles platforms, solid lipid (SLN) and poly-lactic-co-glycolic (PLGA) nanoparticles were used in this study. Polymeric PLGA nanoparticles were around 115 nm in size and had 50 % of siRNA association efficiency, while SLN presented 150 nm and association efficiency close to 52 %. Their surface was functionalized with a peptide-binding transferrin receptor, in a site-oriented manner confirmed by NMR, and their targeting ability against human brain endothelial cells was successfully demonstrated by fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. The interaction of modified nanoparticles with brain endothelial cells increased 3-fold compared to non-modified lipid nanoparticles, and 4-fold compared to non-modified PLGA nanoparticles, respectively. These nanosystems, which were also demonstrated to be safe for human brain endothelial cells, without significant cytotoxicity, bring a new hopeful breath to the future of brain diseases therapies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE, Yusof SR, Begley DJ (2010) Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis 37:13–25
Amin ML, Joo JY, Yi DK, An SS (2015) Surface modification and local orientations of surface molecules in nanotherapeutics. J Control Release 207:131–142
Araújo F, Shrestha N, Shahbazi MA, Liu D, Herranz-Blanco B, Mäkilä EM, Salonen JJ, Hirvonen JT, Granja PL, Sarmento B, Santos HA (2015) Microfluidic assembly of a multifunctional tailorable composite system designed for site specific combined oral delivery of peptide drugs. ACS Nano 9:8291–8302
Bataineh H, Pestovsky O, Bakac A (2012) pH-induced mechanistic changeover from hydroxyl radicals to iron(iv) in the Fenton reaction. Chem Sci 3:1594–1599
Bauer B, Hartz AMS, Fricker G, Miller DS (2005) Modulation of p-glycoprotein transport function at the blood-brain barrier. Exp Biol Med 230:118–127
Bhaskar S, Tian F, Stoeger T, Kreyling W, de la Fuente JM, Grazu V, Borm P, Estrada G, Ntziachristos V, Razansky D (2010) Multifunctional Nanocarriers for diagnostics, drug delivery and targeted treatment across blood-brain barrier: perspectives on tracking and neuroimaging. Part Fibre Toxicol 7:3
Caldeira LR, Fernandes FR, Costa DF, Frezard F, Afonso LC, Ferreira LA (2015) Nanoemulsions loaded with amphotericin B: a new approach for the treatment of leishmaniasis. Eur J Pharm Sci 70:125–131
Campbell ML, Guerra FD, Dhulekar J, Alexis F, Whitehead DC (2015) Target-specific capture of environmentally relevant gaseous aldehydes and carboxylic acids with functional nanoparticles. Chemistry 21:14834–14842
Cui ZK, Fan J, Kim S, Bezouglaia O, Fartash A, Wu BM, Aghaloo T, Lee M (2015) Delivery of siRNA via cationic Sterosomes to enhance osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Control Release 217:42–52
das Neves J, Michiels J, Arien KK, Vanham G, Amiji M, Bahia MF, Sarmento B (2012) Polymeric nanoparticles affect the intracellular delivery, antiretroviral activity and cytotoxicity of the microbicide drug candidate dapivirine. Pharm Res 29:1468–1484
Esfandyari-Manesh M, Mostafavi SH, Majidi RF, Koopaei MN, Ravari NS, Amini M, Darvishi B, Ostad SN, Atyabi F, Dinarvand R (2015) Improved anticancer delivery of paclitaxel by albumin surface modification of PLGA nanoparticles. J Pharm Sci 23:28
Fisher M, Abramov M, Van Aerschot A, Xu D, Juliano RL, Herdewijn P (2007) Inhibition of MDR1 expression with altritol-modified siRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 35:1064–1074
Fonte P, Soares S, Sousa F, Costa A, Seabra V, Reis S, Sarmento B (2014) Stability study perspective of the effect of freeze-drying using cryoprotectants on the structure of insulin loaded into PLGA nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 15:3753–3765
Gabathuler R (2010) Approaches to transport therapeutic drugs across the blood-brain barrier to treat brain diseases. Neurobiol Dis 37:48–57
Gilmore JL, Yi X, Quan L, Kabanov AV (2008) Novel nanomaterials for clinical neuroscience. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 3:83–94
Gomes MJ, Martins S, Sarmento B (2015) siRNA as a tool to improve the treatment of brain diseases: mechanism, targets and delivery. Ageing Res Rev 21:43–54
Guo L, Chen B, Liu R, Liu P, Xia G, Wang Y, Li X, Chen W, Wang X, Jiang H (2015) Biocompatibility assessment of polyethylene glycol-poly L-lysine-poly lactic-Co-glycolic acid nanoparticles in vitro and in vivo. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 15:3710–3719
Hong W, Chen D, Jia L, Gu J, Hu H, Zhao X, Qiao M (2014) Thermo- and pH-responsive copolymers based on PLGA-PEG-PLGA and poly(l-histidine): synthesis and in vitro characterization of copolymer micelles. Acta Biomater 10:1259–1271
Huang RQ, Qu YH, Ke WL, Zhu JH, Pei YY, Jiang C (2007) Efficient gene delivery targeted to the brain using a transferrin-conjugated polyethyleneglycol-modified polyamidoamine dendrimer. FASEB J 21:1117–1125
Hung CF, Hwang TL, Chang CC, Fang JY (2005) Physicochemical characterization and gene transfection efficiency of lipid emulsions with various co-emulsifiers. Int J Pharm 289:197–208
Jain PP, Leber R, Nagaraj C, Leitinger G, Lehofer B, Olschewski H, Olschewski A, Prassl R, Marsh LM (2014) Liposomal nanoparticles encapsulating iloprost exhibit enhanced vasodilation in pulmonary arteries. Int J Nanomedicine 9:3249–3261
Kang T, Jiang M, Jiang D, Feng X, Yao J, Song Q, Chen H, Gao X, Chen J (2015) Enhancing glioblastoma-specific penetration by functionalization of nanoparticles with an iron-mimic peptide targeting transferrin/transferrin receptor complex. Mol Pharm 12:2947–2961
Kuo YC, Chen HH (2010) Effect of electromagnetic field on endocytosis of cationic solid lipid nanoparticles by human brain-microvascular endothelial cells. J Drug Target 18:447–456
Lamichhane SP, Arya N, Ojha N, Kohler E, Shastri VP (2015) Glycosaminoglycan-functionalized poly-lactide-co-glycolide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, cytocompatibility, and cellular uptake. Int J Nanomedicine 10:775–789
Mahringer A, Ott M, Reimold I, Reichel V, Fricker G (2011) The ABC of the blood-brain barrier - regulation of drug efflux pumps. Curr Pharm Des 17:2762–2770
Martin-Banderas L, Munoz-Rubio I, Prados J, Alvarez-Fuentes J, Calderon-Montano JM, Lopez-Lazaro M, Arias JL, Leiva MC, Holgado MA, Fernandez-Arevalo M (2015) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of Delta(9)-tetrahidrocannabinol/PLGA nanoparticles for cancer chemotherapy. Int J Pharm 487:205–212
Moos T, Morgan EH (2000) Transferrin and transferrin receptor function in brain barrier systems. Cell Mol Neurobiol 20:77–95
Murthy SK (2007) Nanoparticles in modern medicine: state of the art and future challenges. Int J Nanomedicine 2:129–141
Neves AR, Queiroz JF, Weksler B, Romero IA, Couraud PO, Reis S (2015) Solid lipid nanoparticles as a vehicle for brain-targeted drug delivery: two new strategies of functionalization with apolipoprotein E. Nanotechnology 26:495103
Platzer G, Okon M, McIntosh L (2014) pH-dependent random coil 1H, 13C, and 15N chemical shifts of the ionizable amino acids: a guide for protein pK a measurements. J Biomol NMR 60:109–129
ResearchAndMarkets (2007) Drug delivery technology - revolutionizing CNS therapies: pharmavision
Soares S, Fonte P, Costa A, Andrade J, Seabra V, Ferreira D, Reis S, Sarmento B (2013) Effect of freeze-drying, cryoprotectants and storage conditions on the stability of secondary structure of insulin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 456:370–381
Venkateswarlu V, Manjunath K (2004) Preparation, characterization and in vitro release kinetics of clozapine solid lipid nanoparticles. J Control Release 95:627–638
Wang CF, Sarparanta MP, Makila EM, Hyvonen ML, Laakkonen PM, Salonen JJ, Hirvonen JT, Airaksinen AJ, Santos HA (2015) Multifunctional porous silicon nanoparticles for cancer theranostics. Biomaterials 48:108–118
Weksler B, Romero IA, Couraud PO (2013) The hCMEC/D3 cell line as a model of the human blood brain barrier. Fluids Barriers CNS 10
Zhang Q, Wang A, Meng Y, Ning T, Yang H, Ding L, Xiao X, Li X (2015) NMR method for accurate quantification of polysorbate 80 copolymer composition. Anal Chem 87:9810–9816
Zimmermann JL, Nicolaus T, Neuert G, Blank K (2010) Thiol-based, site-specific and covalent immobilization of biomolecules for single-molecule experiments. Nat Protoc 5:975–985
Acknowledgments
This work was financed by European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) through the Programa Operacional Factores de Competitividade – COMPETE 2020 – Operacional Programme for Competitiveness and Internationalisation (POCI), Portugal 2020, and by Portuguese funds through FCT – Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia/ Ministério da Ciência e Tecnologia e Inovação in the framework of the project “Institute for Research and Innovation in Health Sciences” (POCI-01-0145-FEDER-007274) and the project UID/BIM/04293/2013, and co-financed by North Portugal Regional Operational Programme (ON.2 – O Novo Norte) in the framework of project SAESCTN-PIIC&DT/2011, under the National Strategic Reference Framework (NSRF). Maria João Gomes and Carlos Fernandes gratefully acknowledge Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), Portugal, for financial support (grant SFRH/BD/90404/2012 and SFRH/BD/98519/2013, respectively). The authors would like to acknowledge all the help of Victória Leiro with the NMR experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 192 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gomes, M.J., Fernandes, C., Martins, S. et al. Tailoring Lipid and Polymeric Nanoparticles as siRNA Carriers towards the Blood-Brain Barrier – from Targeting to Safe Administration. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 12, 107–119 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-016-9685-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-016-9685-6