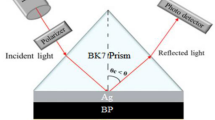
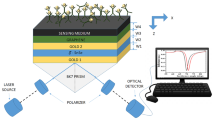
Abstract
This work offers a quite sensitive SPR-based sensor with a new heterostructure based on platinum and ITO using silver as the plasmonic metal to examine the detection of sulfolane, ethylene glycol, diethylene glycol, and polyethylene glycol (PEG-200 and PEG-600) in water. The widely utilized transfer matrix technique (TMM) was employed to evaluate the performance of the suggested sensor. The noble plasmonic material silver (Ag) with a thickness of 40 nm is utilized to induce surface plasmons. As an adhesive layer, Cytop is used between the ITO and sensing layer; the thickness of 0.5 nm has been taken. The sensor’s performance was evaluated in terms of reflectance, full width at half maximum (FWHM), detection accuracy, sensitivity, and figure of merit. These parameters are also evaluated by varying the platinum (P) and ITO (I) layers. The suggested sensor has a maximum sensitivity of 144.1988 degree/RIU (for \(P=1, I=9\)), DA of 1.8867 degree−1, and FoM of 98.66 RIU−1 (for \(P=3, I=1\)). The operating wavelength of 633 nm is used here for this numerical analysis.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
No data available.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Hatch LF, Matar S (1978) “No title,” Hydrocarb. Process 57(8):153–165
Reichardt C (2007) Solvents and solvent effects: an introduction. Org Process Res Dev 11(1):105–113. https://doi.org/10.1021/op0680082
Headley JV, Fedorak PM, Dickson LC (2002) A review of analytical methods for the determination of sulfolane and alkanolamines in environmental studies. J AOAC Int 85(1):154–162
Nguyen HH, Park J, Kang S, Kim M (2015) Surface plasmon resonance: a versatile technique for biosensor applications. Sensors (Switzerland) 15(5):10481–10510. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150510481
Bellassai N, Agata RD, Jungbluth V, Spoto G (2019) Surface plasmon resonance for biomarker detection. Ddv Non-invasive Cancer Diagn 7:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00570
Asif M et al (2020) The role of biosensors in coronavirus disease-2019 outbreak. Curr Opin Electrochem 23:174–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2020.08.011
Mauriz E (2020) Recent progress in plasmonic biosensing schemes for virus detection. Sensors 20(17). https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174745
Taha BA, Al Mashhadany Y, Hafiz Mokhtar MH, M. S. Dzulkefly Bin Zan, and N. Arsad, “An analysis review of detection coronavirus disease, (2019) (COVID-19) based on biosensor application”. Sensors 20(23):2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236764
Akowuah EK, Gorman T, Haxha S (2009) Design and optimization of a novel surface plasmon resonance biosensor based on Otto configuration. Opt Express 17(26):23511–23521. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.17.023511
Verma A, Prakash A, Tripathi R (2015) Sensitivity enhancement of surface plasmon resonance biosensor using graphene and air gap. Opt Commun 357:106–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2015.08.076
Li L et al (2017) Dual Kretschmann and Otto configuration fiber surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Opt Express 25(22):26950–26957. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.25.026950
Uniyal A, Srivastava G Pal A, Taya S, Muduli A (2023) Recent advances in optical biosensors for sensing applications : a review. Plasmonics no. 0123456789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01803-2
Taya SA et al (2023) Highly sensitive sensor based on SPR nanostructure employing graphene and perovskite layers for the determination of blood hemoglobin concentration. Optik (Stuttg) 281:170857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2023.170857
Karki B, Vasudevan B, Uniyal A, Pal A, Srivastava V (2022) Hemoglobin detection in blood samples using a graphene-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Optik (Stuttg) 270:169947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.169947
Singh S et al (2022) Sensitivity enhancement of SPR biosensor employing heterostructure blue phosphorus/MoS2and silicon layer. Emerg Mater Res 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1680/jemmr.22.00009
Singh S, Sharma AK, Lohia P, Dwivedi DK, Singh PK (2022) Design and modelling of high-performance surface plasmon resonance refractive index sensor using BaTiO3, MXene and nickel hybrid nanostructure. Plasmonics 17(5):2049–2062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-022-01692-x
Rikta KA, Anower MS, Rahman MS, Rahman MM (2021) SPR biosensor using SnSe-phosphorene heterostructure. Sens. Bio-Sensing Res 33:100442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2021.100442
Uniyal A, Chauhan B, Pal A, Tomar S, Uniyal PD (2023) Surface plasmon resonance sensor for enhancement of sensitivity. J Graph Era Univ 11:177–190. https://doi.org/10.13052/jgeu0975-1416.1124
Rhodes C et al (2006) Surface plasmon resonance in conducting metal oxides. J Appl Phys 100(5). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2222070
Rhodes C et al (2008) Dependence of plasmon polaritons on the thickness of indium tin oxide thin films. J Appl Phys 103(9):93108. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2908862
Khamh H, Sachet E, Kelly K, Maria J-P, Franzen S (2018) As good as gold and better: conducting metal oxide materials for mid-infrared plasmonic applications. J Mater Chem C 6(31):8326–8342. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TC05760A
Shah K, Sharma NK, Sajal V (2018) Analysis of fiber optic SPR sensor utilizing platinum based nanocomposites. Opt Quantum Electron 50(6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-018-1533-x
Shah K, Sharma NK (2022) Theoretical study on fiber optic SPR sensor using indium nitride. Indian J Phys 96(1):275–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-020-01960-8
Huang T (2017) Highly sensitive SPR sensor based on D-shaped photonic crystal fiber coated with indium tin oxide at near-infrared wavelength. Plasmonics 12(3):583–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0301-7
Verma RK (2018) Sensitivity enhancement of a lossy mode resonance based tapered fiber optic sensor with an optimum taper profile. J Phys D Appl Phys 51(41):415302. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aadb0f
Mishra AK, Mishra SK (2015) Infrared SPR sensitivity enhancement using ITO/TiO2/silicon overlays. Europhys Lett 112(1):10001. https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/112/10001
Lin Y-C, Chen L-Y, Chiu F-C (2019) Lossy mode resonance-based glucose sensor with high-κ dielectric film. Crystals 9(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9090450
Zeng S et al (2013) Size dependence of Au NP-enhanced surface plasmon resonance based on differential phase measurement. Sensors Actuators B Chem 176:1128–1133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.09.073
Otto A (1968) Excitation of nonradiative surface plasma waves in silver by the method of frustrated total reflection. Zeitschrift für Phys A Hadron Nucl 216(4):398–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01391532
Sharma AK, Jha R, Pattanaik HS (2010) Design considerations for surface plasmon resonance based detection of human blood group in near infrared. J Appl Phys 107(3):34701. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3298503
Bruna M, Borini S (2009) Optical constants of graphene layers in the visible range. Appl Phys Lett 94(3):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3073717
Gupta BD, Sharma AK (2005) Sensitivity evaluation of a multi-layered surface plasmon resonance-based fiber optic sensor: a theoretical study. Sensors Actuators B Chem 107(1)40–46 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2004.08.030
Kumar S, Kumar A (2021) Results in Optics ITO / Polymer matrix assisted surface plasmon resonance based fiber optic sensor,” Results Opt 5:100173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rio.2021.100173
Mishra AK (2017) Giant infrared sensitivity of surface plasmon resonance-based refractive index sensor. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0619-9
Gaur DS, Purohit A, Mishra SK, Mishra AK (2022) An interplay between lossy mode resonance and surface plasmon resonance and their sensing applications
Mishra SK, Mishra AK, Misra KP, Verma RK (2022) Detection of alcohol content in food products by lossy mode resonance technique. J Electrochem Soc 169(7):77504
Sharma S, Mishra SK (2023) Exploiting the advantages of Ag/ITO/enzyme trapped gel layers to develop a highly sensitive and selective fiber optic plasmonic urea sensor
Mishra AK, Mishra SK, Gupta BD (2015) Gas-clad two-way fiber optic SPR sensor: a novel approach for refractive index sensing. Plasmonics 10:1071–1076
Singh S, Mishra SK, Gupta BD (2013) Sensitivity enhancement of a surface plasmon resonance based fibre optic refractive index sensor utilizing an additional layer of oxides. Sensors Actuators A Phys 193:136–140
Verma k et al (2021) Robust visual tracking with occlusion handling using Gaussian mixture modeling. 258
Almawgani AHM, Sarkar P, Pal A, Srivastava H, Uniyal A (2023) Titanium disilicide, black phosphorus–based surface plasmon resonance sensor for dengue detection. Plasmonics no. 0123456789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01856-3
Sharma NK, Shukla S, Sajal V (2017) Surface plasmon resonance based fiber optic sensor using an additional layer of platinum: a theoretical study. Optik (Stuttg) 133:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.01.004
Han L, Ding H, Landry NNA, Hua M, Huang T (2020) Highly sensitive SPR sensor based on Ag-ITO-BlueP/TMDCs-graphene heterostructure. Plasmonics 15(5):1489–1498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01165-z
Karki B, Uniyal A, Srivastava G, Pal A (2023) Black phosphorous and cytop nanofilm-based long-range SPR sensor with enhanced quality factor. J Sensors 2023. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/2102915
Pandey S, Singh S, Agarwal S, Sharma AK, Lohia P, Dwivedi DK (2022) Simulation study to improve the sensitivity of surface plasmon resonance sensor by using ferric oxide, nickel and antimonene nanomaterials. Optik (Stuttg) 267:169757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.169757
Srivastava S, Singh S, Mishra AC, Lohia P, Dwivedi DK (2023) Numerical study of titanium dioxide and MXene nanomaterial-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor for virus SARS-CoV-2 detection. Plasmonics no. 0123456789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01874-1
Yadav A, Kumar A, Sharan P (2022) Sensitivity enhancement of a plasmonic biosensor for urine glucose detection by employing black phosphorous. J Opt Soc Am B 39(1):200–206. https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.444838
Karki B, Uniyal A, Chauhan B, Pal A (2022) Sensitivity enhancement of a graphene, zinc sulfide-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor with an Ag metal configuration in the visible region. J Comput Electron. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-022-01854-4
Almawgani AHM, Uniyal A, Sarkar P, Srivastava G (2023) Sensitivity enhancement of optical plasmon-based sensor for detection of the hemoglobin and glucose : a numerical approach. Opt Quantum Electron. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05219-4
Almawgani AHM, Uniyal A, Sarkar P, Srivastava G, Alzahrani A (2023) Creatinine detection by surface plasmon resonance sensor using layers of cerium oxide and graphene over conventional Kretschmann configuration. Plasmonics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01891-0
Ansari G, Pal A, Srivastava AK, Verma G (2023) Detection of hemoglobin concentration in human blood samples using a zinc oxide nanowire and graphene layer heterostructure based refractive index biosensor. Opt Laser Technol 164(2):111. https://doi.org/10.1016/0030-3992(80)90045-6
Uniyal A, Pal A, Chauhan B (2022) Long-range Spr sensor employing platinum diselenide and cytop nanolayers giving improved performance. Phys B Condens Matter 649:414487. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4230023
Pandey PS, Raghuwanshi SK, Singh Y (2022) Enhancement of the sensitivity of a surface plasmon resonance sensor using a nobel structure based on barium titanate–graphene -silver. Opt Quantum Electron. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-03803-8
Mudgal N, Saharia A, Agarwal A, Singh G (2020) ZnO and bi-metallic (Ag–Au) layers based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor with BaTiO3 and graphene for biosensing applications. IETE J Res. https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2020.1844074
Kushwaha AS, Kumar A, Kumar R, Srivastava SK (2018) A study of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) based biosensor with improved sensitivity. Photonics Nanostructures - Fundam Appl 31:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.photonics.2018.06.003
Rahman MS, Anower MS, Hasan MR, Hossain MB, Haque MI (2017) Design and numerical analysis of highly sensitive Au-MoS2-graphene based hybrid surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Opt Commun 396:36–43
Moznuzzaman M, Rafiqul Islam M, Biplob Hossain M, Mustafa Mehedi I (2020) Modeling of highly improved SPR sensor for formalin detection. Results Phys 16:102874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102874
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Amrindra Pal: conceptualization (equal), writing—review and editing (equal). Arun Uniyal: methodology (equal), writing—review and editing (equal). Partha Sarkar: investigation (equal), methodology (equal). Gaurav Srivastava: investigation (equal), methodology (equal). Hira Lal Yadav: formal analysis (equal), methodology (equal). Gaurav Dhiman: supervision (lead), draft preparation. Sofyan A. Taya: supervision (lead), investigation. Arjuna Muduli: supervision (lead), investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable. The work presented in this manuscript is mathematical modelling only for the proposed biosensor. No experiment was performed on the human body and living organisms/animals. So, ethical approval from an ethical committee is not required.
Consent to Participate
I am willing to participate in the work presented in this manuscript.
Consent for Publication
The author has given their consent to publish this work.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pal, A., Uniyal, A., Sarkar, P. et al. Detecting Binary Mixtures of Sulfolane with Ethylene Glycol, Diethylene Glycol, and Polyethylene Glycol in Water Using Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor: A Numerical Investigation. Plasmonics 19, 1019–1029 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02054-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02054-x