Abstract
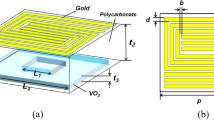
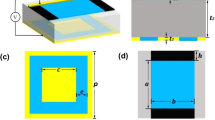
In this article, we demonstrate a tunable ultra-broadband metamaterial absorber (TUMA) in terahertz (THz) band which is based on the multilayered structure composed of an Au reflective layer, polyimide dielectric layers, and vanadium dioxide (VO2) periodic structures, respectively. We gain the tunable absorption spectra because of the room temperature phased-changed character of VO2. The relative bandwidth reaches to 81.2% and the absorption rate is over 90% at the frequency range of 1.63–3.86 THz when the temperature (t1) is 350 K, but when t1 = 300 K, the presented absorber is acted as a reflector whose absorption is small besides the frequency points of 9.75 THz and 9.81 THz. For the sake of comprehending the physical mechanism in-depth, the electric field (E-field) diagrams, the surface current distributions and the power loss density (PLD) of the TUMA are investigated. The influences of structural arguments and incident angle (θ) on the absorption are also analyzed. The emulated consequences show that the absorption spectrum can be regulated by changing structural parameters and incident angle and the tunable absorption regions can be obtained by altering the external temperature.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayhurst C, Byrne P, Eldridge PR, Mallucci CL (2009) Application of electromagnetic technology to neuronavigation: a revolution in image-guided neurosurgery. J Neurosurg 111(6):1179–1184
Yatsui K, Jiang W (2000) Development and applications of pulsed electromagnetic technology. Trans Inst Electr Eng Jpn 120(1):7–11
Uman MA, Mclain DK, Krider EP (1975) The electromagnetic radiation from a finite antenna. Am J Phys 43(1):33–38
Wang C, Han X, P X, Zhang X, Y D, S H, Wang J, Wang X (2011) The electromagnetic property of chemically reduced graphene oxide and its application as microwave absorbing material. Appl Phys Lett 98(7):217
Feng YB, Qiu T, Shen CY, Li XY (2006) Electromagnetic and absorption properties of carbonyl iron/rubber radar absorbing materials. IEEE Trans Magn 42(3):363–368
Ding F, Cui Y, Ge X, Jin Y, He S (2012) Ultra-broadband microwave metamaterial absorber. Appl Phys Lett 100(10):103506–103506-4
Ma Y, Chen Q, Grant J, Saha SC, Khalid A, Cumming DRS (2011) A terahertz polarization insensitive dual band metamaterial absorber. Opt Lett 36(6):945–947
Shen X, Cui TJ, Zhao J, Ma HF, Jiang WX, Li H (2011) Polarization-independent wide-angle triple-band metamaterial absorber. Opt Express 19(10):9401–9407
T H, Emil AK, Andrew CS, Kebin F, Willie JP, Richard DA, Eric AS, Zhang X (2011) Microwave and terahertz wave sensing with metamaterials. Opt Express 19(22):21620–21626
Alnaib I, Jansen C, Koch M (2008) Thin-film sensing with planar asymmetric metamaterial resonators. Appl Phys Lett 93(8):083507
Grbic A, Eleftheriades GV (2003) Negative refraction, growing evanescent waves, and sub-diffraction imaging in loaded transmission-line metamaterials. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech 51(12):2297–2305
Casse BDF, Lu WT, Huang YJ, Gultepe E, Menon L, Sridhar S (2010) Super-resolution imaging using a three-dimensional metamaterials nanolens. Appl Phys Lett 96(2):023114
Li W, Coppens ZJ, Besteiro LV, Wang W, Valentine J (2015) Circularly polarized light detection with hot electrons in chiral plasmonic metamaterials. Nat Commun 6:8379
Park S, Hong JT, Choi S, Kim H, Park W, Han S, Park J, Lee S, Kim D, Ahn Y (2015) Detection of microorganisms using terahertz metamaterials. Sci Rep 4(1):4988–4988
Xiong H, Hong JS, Luo CM, Zhong LL (2013) An ultrathin and broadband metamaterial absorber using multi-layer structures. J Appl Phys 114(6):OP181
Liu S, Chen H, Cui TJ (2015) A broadband terahertz absorber using multi-layer stacked bars. Appl Phys Lett 106(15):151601
Gu S, Barrett JP, Hand TH, Popa BI, Cummer SA (2010) A broadband low-reflection metamaterial absorber. J Appl Phys 108(6):064913
Dao RN, Kong XR, Zhang HF, Su XR (2019) A tunable broadband terahertz metamaterial absorber based on the vanadium dioxide. Optik 180:619–625
Erentok A, Ziolkowski RW, Nielsen JA, Greegor RB, Parazzoli CG, Tanielian MH, Cummer SA, Popa BI, Hand TH, Vier DC, Schultz S (2007) Low frequency lumped element-based negative index metamaterial. Appl Phys Lett 91(18):84104
Chen X, Gong H, Dai S, Zhao D, Yang Y, Li Q, Qiu M (2013) Near-infrared broadband absorber with film-coupled multilayer nanorods. Opt Lett 38(13):2247–2249
Wang GD, Liu MH, Hu XW, Kong LH, Cheng LL, Chen ZQ (2013) Broadband and ultra-thin terahertz metamaterial absorber based on multi-circular patches. Eur Phys J B 86(7):304
Cheng YZ, Wang Y, Nie Y, Gong RZ, Xiong X, Wang X (2012) Design, fabrication and measurement of a broadband polarization-insensitive metamaterial absorber based on lumped elements. J Appl Phys 111(4):44902
H L, Gan X, Mao D, Fan Y, Zhao J (2017) Nearly perfect absorption of light in monolayer molybdenum disulfide supported by multilayer structures. Opt Express 25(18):21630
H L, Li YW, Yue ZJ, Mao D, Zhao JL (2019) Topological insulator based Tamm plasmon polaritons. APL Photo 4:040801
Lu H, Li YW, Yue ZJ, Mao D, Zhao JL (2019) Induced reflection in Tamm plasmon systems. Opt Express 27:5383–5392
Zhao Y, Huang QP, Cai HL, Lin XX, Lua YL (2018) A broadband and switchable VO2-based perfect absorber at the THz frequency. Opt Commun 426:443–449
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Open Research Program in China’s State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves (Grant No. K201927) and Jiangsu Overseas Visiting Scholar Program for the University prominent Young & Middle-aged Teachers and Presidents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dao, R., Kong, X., Zhang, HF. et al. A Tunable Ultra-Broadband Metamaterial Absorber with Multilayered Structure. Plasmonics 15, 169–175 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-01013-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-01013-9