Abstract
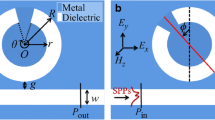
In this paper, two Fano resonances are achieved in the proposed plasmonic system. Theoretical analysis and simulation results show that two discrete states coupled with a continua lead to these Fano resonances. The discrete states are provided by the side-coupled square cavity, and a baffle plate placed in metal-dielectric-metal waveguide is used to produce a continuous transmission spectrum. The resonant wavelengths and the linewidth of these Fano resonances can be easily tuned by adjusting the parameters of system. This system exhibits high sensitivities as high as 850 and 1120 nm/RIU corresponding to two Fano resonances, and the figure of merit can reach to 1.7 × 105 by optimizing the system. By introducing another square cavity, four Fano resonances are obtained which originate from four discrete states coupled with continua, and they can be tuned independently. The flexible multi-Fano resonances system has significant application bio-nanosensor, nonlinear, and slow light devices.









Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Miroshnichenko AE, Flach S, Kivshar YS (2009) Fano resonances in nanoscale structures. Rev Mod Phys 82:2257–2298
Lukyanchuk B, Zheludev NI, Maier SA, Halas NJ, Nordlander P, Giessen H, Chong CT (2010) The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat Mater 9:707–715
Fang Y, Sun M (2015) Nanoplasmonic waveguides: towards applications in integrated nanophotonic circuits. Light Science & Applications 4(6):e249
Fano U (1961) Effects of configuration interaction on intensities and phase shifts. Phys Rev 124:1866–1878
Hao F, Sonnefraud Y, Van DP, Maier SA, Halas NJ, Nordlander P (2008) Symmetry breaking in plasmonic nanocavities: subradiant lspr sensing and a tunable Fano resonance. Nano Lett 8:3983–3988
Hao F, Nordlander P, Sonnefraud Y, Van DP, Maier SA (2009) Tunability of subradiant dipolar and Fano-type plasmon resonances in metallic ring/disk cavities: implications for nanoscale optical sensing. ACS Nano 3(3):643–652
Chen J, Li Z, Yue S, Xiao J, Gong Q (2012) Plasmon-induced transparency in asymmetric t-shape single slit. Nano Lett 12(5):2494–2498
Lassiter JB, Sobhani H, Fan JA, Kundu J, Capasso F, Nordlander P et al (2010) Fano resonances in plasmonic nanoclusters: geometrical and chemical tunability. Nano Lett 10(8):3184–3189
Yang ZJ, Wang QQ, Lin HQ (2013) Tunable two types of Fano resonances in metal–dielectric core–shell nanoparticle clusters. Appl Phys Lett 103(11):111115
Wang F, Wang X, Zhou H, Zhou Q, Hao Y, Jiang X, Yang J (2009) Fano-resonance-based Mach-Zehnder optical switch employing dual-bus coupled ring resonator as two-beam interferometer. Opt Express 17(9):7708–7716
Artar A, Yanik AA, Altug H (2011) Directional double Fano resonances in plasmonic hetero-oligomers. Nano Lett 11(9):3694–3700
Wu C, Khanikaev AB, Shvets G (2011) Broadband slow light metamaterial based on a double-continuum Fano resonance. Phys Rev Lett 106(10):152–161
Zhan S, Peng Y, He Z, Li B, Chen Z, Xu H et al (2016) Tunable nanoplasmonic sensor based on the asymmetric degree of Fano resonance in MDM waveguide. Sci Rep 6
Wang D, Yu X, Yu Q (2013) Tuning multiple Fano and plasmon resonances in rectangle grid quasi-3D plasmonic-photonic nanostructures. Appl Phys Lett 103(5):053117
Gramotnev DK, Bozhevolnyi SI (2010) Plasmonics beyond the diffraction limit. Nat Photon 4(2):83–91
Verhagen E, Dionne JA, Kuipers LK, Atwater HA, Polman A (2008) Near-field visualization of strongly confined surface plasmon polaritons in metal-insulator-metal waveguides. Nano Lett 8(9):2925–2929
Kocabaş ŞE, Veronis G, Miller DAB, Fan S (2008) Modal analysis and coupling in metal-insulator-metal waveguides. Phys Rev B 79(3):035120
Choo H, Kim MK, Staffaroni M, Seok TJ, Bokor J, Cabrini S et al (2012) Nanofocusing in a metal-insulator-metal gap plasmon waveguide with a three-dimensional linear taper. Nat Photon 6(12):838–844
Chen J, Li Z, Zhang R, Deng Z, Xiao J, Gong Q (2013) Response line-shapes in compact coupled plasmonic resonator systems. Plasmonics 8:1129–1134
Chen Z, Cao X, Song X, Wang L, Yu L (2015) Side-coupled cavity-induced Fano resonance and its application in nanosensor. Plasmonics 11:307–313
Wen K, Hu Y, Chen L, Zhou J, Lei L, Guo Z (2014) Fano resonance with ultra-high figure of merits based on plasmonic metal-insulator-metal waveguide. Plasmonics 10:27–32
Chen J, Sun C, Gong Q (2014) Fano resonances in a single defect nanocavity coupled with a plasmonic waveguide. Opt Lett 39(1):52–55
Qi J, Chen Z, Chen J, Li Y, Qiang W, Xu J et al (2014) Independently tunable double Fano resonances in asymmetric mim waveguide structure. Opt Express 22(12):14688–14695
Chen Z, Song X, Duan G, Wang L (2015) Multiple Fano resonances control in MIM side-coupled cavities systems. IEEE Photonics J 7(3):1–10
Zhang Y, Li S, Zhang X, Chen Y, Wang L, Zhang Y et al (2016) Evolution of Fano resonance based on symmetric/asymmetric plasmonic waveguide system and its application in nanosensor. Opt Commun 370:203–208
Yun B, Hu G, Cui Y (2013) Resonant mode analysis of the nanoscale surface plasmon polariton waveguide filter with rectangle cavity. Plasmonics 8:267–275
Manolatou C, Khan MJ, Fan S, Villeneuve PR (1999) Coupling of modes analysis of resonant channel add-drop filters. IEEE J Quantum Elect 35:1322–1331
Suh W, Wang Z, Fan S (2004) Temporal pled-mode theory and the presence of non-orthogonal modes in lossless multimode cavities. IEEE J Quantum Elect 40:1511–1518
Noual A, Pennec Y, Akjouj A, Djafari-Rouhani B, Dobrzynski L (2009) Nanoscale plasmon waveguide including cavity resonator. J Phys-Condens Mat 21(37):375301
Bertolotti M (1984) Waves and fields in optoelectronics. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379
Lai G, Liang R, Zhang Y, Bian Z, Yi L, Zhan G et al (2015) Double plasmonic nanodisks design for electromagnetically induced transparency and slow light. Opt Express 23(5):6554–6561
Lu H, Liu X, Gong Y, Mao D, Wang G (2011) Analysis of nanoplasmonic wavelength demultiplexing based on metal-insulator-metal waveguides. JOSA B 28(7):1616–1621
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and technology of China (Grant No. 2016YFA0301300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 11374041, Grant 11574035 and Grant 11404030), and the Fund of State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics, and the Optical Communications (Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications), People’s Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Song, X., Chen, Z. et al. Tunable Multi-Fano Resonances in MDM-Based Side-Coupled Resonator System and its Application in Nanosensor. Plasmonics 12, 1665–1672 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0432-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0432-x