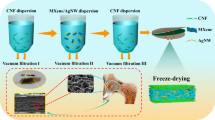
Abstract
With the development of modern electronics, especially the next generation of wearable electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials requires flexibility, ultrathin, lightweight and robustness to protect electronic devices from radiation pollution. In this work, the flexible and ultrathin dopamine modified MXene@cellulose nanofiber (DM@CNF) composite films with alternate multilayer structure have been developed by a facile vacuum filtration induced self-assembly approach. The multilayered DM@CNF composite films exhibit improved mechanical properties compared with the homogeneous DM/CNF film. By adjusting the layer number, the multilayered DM3@CNF2 composite film exhibits a tensile strength of 48.14 MPa and a toughness of 5.28 MJ·m−3 with a thickness about 19 µm. Interestingly that, the DM@CNF film with annealing treatment achieves significant improvement in conductivity (up to 17264 S·m−1) and EMI properties (SE of 41.90 dB and SSE/t of 10169 dB·cm2·g−1), which still maintains relatively high mechanical properties. It is highlighted that the ultrathin multilayered DM@CNF film exhibits superior EMI shielding performance compared with most of the metal-based, carbon-based and MXene-based shielding materials reported in the literature. These results will offer an appealing strategy to develop the ultrathin and flexible MXene-based materials with excellent EMI shielding performance for the next generation intelligent protection devices.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Shahzad, A. Iqbal, H. Kim, and C. M. Koo, 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes): Applications as an electrically conducting material, Adv. Mater. 32(51), 2002159 (2020)
D. W. Jiang, V. Murugadoss, Y. Wang, J. Lin, T. Ding, Z. C. Wang, Q. Shao, C. Wang, H. Liu, N. Lu, R. B. Wei, A. Subramania, and Z. H. Guo, Electromagnetic interference shielding polymers and nanocomposites — A review, Polym. Rev. (Phila. Pa.) 59(2), 280 (2019)
C. Xiang, R. H. Guo, S. J. Lin, S. X. Jiang, J. W. Lan, C. Wang, C. Cui, H. Y. Xiao, and Y. Zhang, Lightweight and ultrathin TiO2−Ti3C2Tx/graphene film with electromagnetic interference shielding, Chem. Eng. J. 360, 1158 (2019)
R. T. Liu, M. Miao, Y. H. Li, J. F. Zhang, S. M. Cao, and X. Feng, Ultrathin biomimetic polymeric Ti3C2Tx MXene composite films for electromagnetic interference shielding, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10(51), 44787 (2018)
H. Abbasi, M. Antunes, and J. I. Velasco, Recent advances in carbon-based polymer nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference shielding, Prog. Mater. Sci. 103, 319 (2019)
M. Hu, N. Zhang, G. Shan, J. Gao, J. Liu, and R. K. Y. Li, Two-dimensional materials: Emerging toolkit for construction of ultrathin high-efficiency microwave shield and absorber, Front. Phys. 13(4), 138113 (2018)
X. Li, G. C. Shan, R. G. Ma, C. H. Shek, H. B. Zhao, and S. Ramakrishna, Bioinspired mineral MXene hydrogels for tensile strain sensing and radionuclide adsorption applications, Front. Phys. 17(6), 63501 (2022)
B. Liu, L. Y. Qian, Y. L. Zhao, Y. W. Zhang, F. Liu, Y. Zhang, Y. Q. Xie, and W. Z. Shi, A polarization-sensitive, self-powered, broadband and fast Ti3C2Tx MXene photodetector from visible to near-infrared driven by photogalvanic effects, Front. Phys. 17(5), 53501 (2022)
B. Wen, M. S. Cao, M. M. Lu, W. Q. Cao, H. L. Shi, J. Liu, X. X. Wang, H. B. Jin, X. Y. Fang, W. Z. Wang, and J. Yuan, Reduced graphene oxides: Light-weight and high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding at elevated temperatures, Adv. Mater. 26(21), 3484 (2014)
B. Shen, W. T. Zhai, and W. G. Zheng, Ultrathin flexible graphene film: An excellent thermal conducting material with efficient EMI shielding, Adv. Funct. Mater. 24(28), 4542 (2014)
Y. Han, H. Zhong, N. Liu, Y. X. Liu, J. Lin, and P. Jin, In situ surface oxidized copper mesh electrodes for high-performance transparent electrical heating and electromagnetic interference shielding, Adv. Electron. Mater. 4(11), 1800156 (2018)
Y. Z. Feng, B. Wang, X. W. Li, Y. S. Ye, J. M. Ma, C. T. Liu, X. P. Zhou, and X. L. Xie, Enhancing thermal oxidation and fire resistance of reduced graphene oxide by phosphorus and nitrogen co-doping: Mechanism and kinetic analysis, Carbon 146, 650 (2019)
Y. Z. Feng, G. J. Han, B. Wang, X. P. Zhou, J. M. Ma, Y. S. Ye, C. T. Liu, and X. L. Xie, Multiple synergistic effects of graphene-based hybrid and hexagonal born nitride in enhancing thermal conductivity and flame retardancy of epoxy, Chem. Eng. J. 379, 122402 (2020)
X. F. Meng, D. H. Li, X. Q. Shen, and W. Liu, Preparation and magnetic properties of nano-Ni coated cenosphere composites, Appl. Surf. Sci. 256(12), 3753 (2010)
W. L. Song, X. T. Guan, L. Z. Fan, W. Q. Cao, C. Y. Wang, Q. L. Zhao, and M. S. Cao, Magnetic and conductive graphene papers toward thin layers of effective electromagnetic shielding, J. Mater. Chem. A 3(5), 2097 (2015)
K. S. Novoselov, D. V. Andreeva, W. C. Ren, and G. C. Shan, Graphene and other two-dimensional materials, Front. Phys. 14(1), 13301 (2019)
Y. C. Wang, L. H. Yao, Q. Zheng, and M. S. Cao, Graphene-wrapped multiloculated nickel ferrite: A highly efficient electromagnetic attenuation material for microwave absorbing and green shielding, Nano Res. 15(7), 6751 (2022)
M. S. Cao, W. L. Song, Z. L. Hou, B. Wen, and J. Yuan, The effects of temperature and frequency on the dielectric properties, electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave-absorption of short carbon fiber/silica composites, Carbon 48(3), 788 (2010)
L. H. Yao, W. Q. Cao, J. G. Zhao, Q. Zheng, Y. C. Wang, S. Jiang, Q. L. Pan, J. Song, Y. Q. Zhu, and M. S. Cao, Regulating bifunctional flower-like NiFe2O4/graphene for green EMI shielding and lithium ion storage, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 127, 48 (2022)
L. C. Jia, G. Q. Zhang, L. Xu, W. J. Sun, G. J. Zhong, J. Lei, D. X. Yan, and Z. M. Li, Robustly superhydrophobic conductive textile for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11(1), 1680 (2019)
L. C. Jia, C. G. Zhou, W. J. Sun, L. Xu, D. X. Yan, and Z. M. Li, Water-based conductive ink for highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding coating, Chem. Eng. J. 384, 123368 (2020)
L. C. Jia, K. Q. Ding, R. J. Ma, H. L. Wang, W. J. Sun, D. X. Yan, B. Li, and Z. M. Li, Highly conductive and machine-washable textiles for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding, Adv. Mater. Technol. 4(2), 1800503 (2019)
G. M. Weng, J. Y. Li, M. Alhabeb, C. Karpovich, H. Wang, J. Lipton, K. Maleski, J. Kong, E. Shaulsky, M. Elimelech, Y. Gogotsi, and A. D. Taylor, Layer-by-layer assembly of cross-functional semi-transparent MXene-carbon nanotubes composite films for next-generation electromagnetic interference shielding, Adv. Funct. Mater. 28(44), 1803360 (2018)
M. Crespo, M. González, A. L. Elías, L. Pulickal Rajukumar, J. Baselga, M. Terrones, and J. Pozuelo, Ultra-light carbon nanotube sponge as an efficient electromagnetic shielding material in the GHz range, Phys. Status Solidi Rapid Res. Lett. 8(8), 698 (2014)
Z. Li, L. Yu, C. Milligan, T. Ma, L. Zhou, Y. R. Cui, Z. Y. Qi, N. Libretto, B. Xu, J. W. Luo, E. Z. Shi, Z. W. Wu, H. L. Xin, W. N. Delgass, J. T. Miller, and Y. Wu, Two-dimensional transition metal carbides as supports for tuning the chemistry of catalytic nanoparticles, Nat. Commun. 9(1), 5258 (2018)
M. R. Lukatskaya, S. Kota, Z. F. Lin, M. Q. Zhao, N. Shpigel, M. D. Levi, J. Halim, P. L. Taberna, M. Barsoum, P. Simon, and Y. Gogotsi, Ultra-high-rate pseudocapacitive energy storage in two-dimensional transition metal carbides, Nat. Energy 2(8), 17105 (2017)
B. Anasori, M. R. Lukatskaya, and Y. Gogotsi, 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for energy storage, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2(2), 16098 (2017)
H. Lin, Y. Chen, and J. L. Shi, Insights into 2D MXenes for versatile biomedical applications: Current advances and challenges ahead, Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 5(10), 1800518 (2018)
M. Carey and M. W. Barsoum, MXene polymer nanocomposites: A review, Mater. Today Adv. 9, 100120 (2021)
J. Z. Zhang, N. Kong, S. Uzun, A. Levitt, S. Seyedin, P. A. Lynch, S. Qin, M. K. Han, W. R. Yang, J. Q. Liu, X. G. Wang, Y. Gogotsi, and J. M. Razal, Scalable manufacturing of free-standing, strong Ti3C2Tx MXene films with outstanding conductivity, Adv. Mater. 32(23), 2001093 (2020)
M. Naguib, O. Mashtalir, J. Carle, V. Presser, J. Lu, L. Hultman, Y. Gogotsi, and M. W. Barsoum, Two-dimensional transition metal carbides, ACS Nano 6(2), 1322 (2012)
C. Zhan, M. Naguib, M. Lukatskaya, P. R. C. Kent, Y. Gogotsi, and D. E. Jiang, Understanding the MXene pseudocapacitance, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 9(6), 1223 (2018)
J. C. Lei, X. Zhang, and Z. Zhou, Recent advances in MXene: Preparation, properties, and applications, Front. Phys. 10(3), 276 (2015)
J. Liu, H. B. Zhang, R. H. Sun, Y. F. Liu, Z. S. Liu, A. G. Zhou, and Z. Z. Yu, Hydrophobic, flexible, and lightweight MXene Foams for high-performance electromagnetic-interference shielding, Adv. Mater. 29(38), 1702367 (2017)
Z. L. Ma, S. L. Kang, J. Z. Ma, L. Shao, Y. L. Zhang, C. Liu, A. J. Wei, X. L. Xiang, L. F. Wei, and J. W. Gu, Ultraflexible and mechanically strong double-layered aramid nanofiber-Ti3C2Tx MXene/silver nanowire nanocomposite papers for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding, ACS Nano 14(7), 8368 (2020)
F. Shahzad, M. Alhabeb, C. B. Hatter, B. Anasori, S. Man Hong, C. M. Koo, and Y. Gogotsi, Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes), Science 353(6304), 1137 (2016)
O. Mashtalir, M. Naguib, V. N. Mochalin, Y. Dall’ Agnese, M. Heon, M. W. Barsoum, and Y. Gogotsi, Intercalation and delamination of layered carbides and carbonitrides, Nat. Commun. 4(1), 1716 (2013)
B. Akuzum, K. Maleski, B. Anasori, P. Lelyukh, N. J. Alvarez, E. C. Kumbur, and Y. Gogotsi, Rheological characteristics of 2D titanium carbide (MXene) dispersions: A guide for processing MXenes, ACS Nano 12(3), 2685 (2018)
Y. J. Wan, X. M. Li, P. L. Zhu, R. Sun, C. P. Wong, and W. H. Liao, Lightweight, flexible MXene/polymer film with simultaneously excellent mechanical property and high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding, Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 130, 105764 (2020)
H. Z. Huang, X. F. Sha, Y. Cui, S. Y. Sun, H. Y. Huang, Z. Y. He, M. Y. Liu, N. G. Zhou, X. Y. Zhang, and Y. Wei, Highly efficient removal of iodine ions using MXene-PDA-Ag2Ox composites synthesized by mussel-inspired chemistry, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 567, 190 (2020)
L. Y. Yang, J. Cui, L. Zhang, X. R. Xu, X. Chen, and D. P. Sun, A moisture-driven actuator based on polydopamine-modified MXene/bacterial cellulose nanofiber composite film, Adv. Funct. Mater. 31(27), 2101378 (2021)
W. T. Cao, C. Ma, S. Tan, M. G. Ma, P. B. Wan, and F. Chen, Ultrathin and flexible CNTs/MXene/cellulose nanofibrils composite paper for electromagnetic interference shielding, Nano-Micro Lett. 11(1), 72 (2019)
J. H. Chen, J. K. Xu, K. Wang, X. R. Qian, and R. C. Sun, Highly thermostable, flexible, and conductive films prepared from cellulose, graphite, and polypyrrole nanoparticles, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(28), 15641 (2015)
L. Q. Zhang, S. G. Yang, L. Li, B. Yang, H. D. Huang, D. X. Yan, G. J. Zhong, L. Xu, and Z. M. Li, Ultralight cellulose porous composites with manipulated porous structure and carbon nanotube distribution for promising electromagnetic interference shielding, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11(2), 2559 (2019)
W. T. Cao, F. F. Chen, Y. J. Zhu, Y. G. Zhang, Y. Y. Jiang, M. G. Ma, and F. Chen, Binary strengthening and toughening of MXene/cellulose nanofiber composite paper with nacre-inspired structure and superior electromagnetic interference shielding properties, ACS Nano 12(5), 4583 (2018)
J. L. Hart, K. Hantanasirisakul, A. C. Lang, B. Anasori, D. Pinto, Y. Pivak, J. T. van Omme, S. J. May, Y. Gogotsi, and M. L. Taheri, Control of MXenes’ electronic properties through termination and intercalation, Nat. Commun. 10(1), 522 (2019)
G. S. Lee, T. Yun, H. Kim, I. H. Kim, J. Choi, S. H. Lee, H. J. Lee, H. S. Hwang, J. G. Kim, D. W. Kim, H. M. Lee, C. M. Koo, and S. O. Kim, Mussel inspired highly aligned Ti3C2Tx MXene film with synergistic enhancement of mechanical strength and ambient stability, ACS Nano 14(9), 11722 (2020)
M. Alhabeb, K. Maleski, B. Anasori, P. Lelyukh, L. Clark, S. Sin, and Y. Gogotsi, Guidelines for synthesis and processing of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene), Chem. Mater. 29(18), 7633 (2017)
B. Zhou, Z. Zhang, Y. L. Li, G. J. Han, Y. Z. Feng, B. Wang, D. B. Zhang, J. M. Ma, and C. T. Liu, Flexible, robust, and multifunctional electromagnetic interference shielding film with alternating cellulose nanofiber and MXene layers, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(4), 4895 (2020)
W. Z. Bao, X. Tang, X. Guo, S. Choi, C. Y. Wang, Y. Gogotsi, and G. X. Wang, Porous cryo-dried MXene for efficient capacitive deionization, Joule 2(4), 778 (2018)
J. W. Fu, Z. H. Chen, M. H. Wang, S. J. Liu, J. H. Zhang, J. N. Zhang, R. P. Han, and Q. Xu, Adsorption of methylene blue by a high-efficiency adsorbent (polydopamine microspheres): Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis, Chem. Eng. J. 259, 53 (2015)
Y. Zhang, W. H. Cheng, W. X. Tian, J. Y. Lu, L. Song, K. M. Liew, B. B. Wang, and Y. Hu, Nacre-inspired tunable electromagnetic interference shielding sandwich films with superior mechanical and fire-resistant protective performance, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(5), 6371 (2020)
Z. H. Zhou, Q. C. Song, B. X. Huang, S. Y. Feng, and C. H. Lu, Facile fabrication of densely packed Ti3C2 MXene/nanocellulose composite films for enhancing electromagnetic interference shielding and electro-/photothermal performance, ACS Nano 15(7), 12405 (2021)
X. F. Zhao, D. E. Holta, Z. Y. Tan, J. H. Oh, I. J. Echols, M. Anas, H. X. Cao, J. L. Lutkenhaus, M. Radovic, and M. J. Green, Annealed Ti3C2Tz MXene films for oxidation-resistant functional coatings, ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 3(11), 10578 (2020)
Y. J. Wan, P. L. Zhu, S. H. Yu, R. Sun, C. P. Wong, and W. H. Liao, Anticorrosive, ultralight, and flexible carbon-wrapped metallic nanowire hybrid sponges for highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding, Small 14(27), 1800534 (2018)
S. H. Ryu, Y. K. Han, S. J. Kwon, T. Kim, B. M. Jung, S. B. Lee, and B. Park, Absorption-dominant, low reflection EMI shielding materials with integrated metal mesh/TPU/CIP composite, Chem. Eng. J. 428, 131167 (2022)
L. Feng, Y. Zuo, X. He, X. J. Hou, Q. G. Fu, H. J. Li, and Q. Song, Development of light cellular carbon nanotube@graphene/carbon nanocomposites with effective mechanical and EMI shielding performance, Carbon 168, 719 (2020)
R. T. Liu, M. Miao, Y. H. Li, J. F. Zhang, S. M. Cao, and X. Feng, Ultrathin biomimetic polymeric Ti3C2Tx MXene composite films for electromagnetic interference shielding, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10(51), 44787 (2018)
R. S. Li, L. Ding, Q. Gao, H. M. Zhang, D. Zeng, B. A. Zhao, B. B. Fan, and R. Zhang, Tuning of anisotropic electrical conductivity and enhancement of EMI shielding of polymer composite foam via CO2-assisted delamination and orientation of MXene, Chem. Eng. J. 415, 128930 (2021)
Z. S. Liu, Y. Zhang, H. B. Zhang, Y. Dai, J. Liu, X. F. Li, and Z. Z. Yu, Electrically conductive aluminum ion-reinforced MXene films for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding, J. Mater. Chem. C 8(5), 1673 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2022YFB3807200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52201022 and 21973012), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (Nos. 2020J01474, 2021J06011, and 2020J01351), and the “Qishan Scholar” Scientific Research Startup Project of Fuzhou University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Supporting Information
11467_2022_1234_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Flexible and ultrathin dopamine modified MXene and cellulose nanofiber composite films with alternating multilayer structure for superior electromagnetic interference shielding performance
Supplementary material, approximately 5.63 MB.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, Q., Liu, H., Chen, Z. et al. Flexible and ultrathin dopamine modified MXene and cellulose nanofiber composite films with alternating multilayer structure for superior electromagnetic interference shielding performance. Front. Phys. 18, 33300 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-022-1234-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-022-1234-6