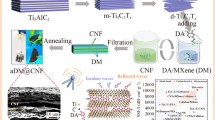
Abstract
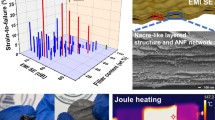
With the rapid development and popularization of intelligent, portable, and wearable flexible electronic devices, urgently required a new generation electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials to manage the increasing serious radiation pollution. In this work, ultrathin, lightweight, and flexible porous films with reasonable strength were fabricated via vacuum filtered the cellulose nanofiber (CNF) dispersion on both sides of the MXene–AgNWs film and followed by a freeze-drying process. The prepared porous composite film presents to be a typical sandwich-structured with dense in surface and porous inside. This novel and unique structure endows the sandwich-structured porous film with greatly improved EMI performance to 67.5 from 40 dB, enhanced absorption coefficient from 0.1 to 0.4, and satisfactory mechanical properties with a tensile strength of 20.3 MPa, a strain at break of 2.1%. Furthermore, the prepared films present the remarkable low-voltage-driven Joule heating performance. Therefore, ultrathin, lightweight, flexible, and versatile properties CNF–MXene–AgNWs composite porous film with an excellent EMI-shielding performance is hold great potential in the fields of aerospace, portable and wearable electronics.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of the ongoing study.
References
Abbasi H, Antunes M, Ignacio Velasco J (2019) Recent advances in carbon-based polymer nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Prog Mater Sci 103:319–373
Bai Y, Bi S, Wang W, Ding N, Lu Y, Jiang M, Ding C, Zhao W, Liu N, Bian J, Liu S, Zhao Q (2022) Biocompatible, stretchable, and compressible cellulose/MXene hydrogel for strain sensor and electromagnetic interference shielding. Soft Mater 20(4):444–454
Cao W-T, Chen F-F, Zhu Y-J, Zhang Y-G, Jiang Y-Y, Ma M-G, Chen F (2018) Binary strengthening and toughening of MXene/cellulose nanofiber composite paper with nacre-inspired structure and superior electromagnetic interference shielding properties. ACS Nano 12(5):4583–4593
Cao M-S, Cai Y-Z, He P, Shu J-C, Cao W-Q, Yuan J (2019) 2D MXenes: electromagnetic property for microwave absorption and electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem Eng J 359:1265–1302
Chen Z, Xu C, Ma C, Ren W, Cheng H-M (2013) Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Mater 25(9):1296–1300
Chen Q, Zhang K, Huang L, Li Y, Yuan Y (2022) Reduced graphene oxide/MXene composite foam with multilayer structure for electromagnetic interference shielding and heat insulation applications. Adv Eng Mater 24(9):2200098
Cheng Y, Lu Y, Xia M, Piao L, Liu Q, Li M, Zhou Y, Jia K, Yang L, Wang D (2021) Flexible and lightweight MXene/silver nanowire/polyurethane composite foam films for highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding and photothermal conversion. Compos Sci Technol 215:109023
Deng Z, Tang P, Wu X, Zhang H-B, Yu Z-Z (2021) Superelastic, ultralight, and conductive Ti3C2Tx MXene/acidified carbon nanotube anisotropic aerogels for electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(17):20539–20547
Fan Z, Wang D, Yuan Y, Wang Y, Cheng Z, Liu Y, Xie Z (2020) A lightweight and conductive MXene/graphene hybrid foam for superior electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem Eng J 381:122696
Guo Z, Ren P, Lu Z, Hui K, Yang J, Zhang Z, Chen Z, Jin Y, Ren F (2022a) Multifunctional CoFe2O4@MXene-AgNWs/cellulose nanofiber composite films with asymmetric layered architecture for high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding and remarkable thermal management capability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 14(36):41468–41480
Guo Z, Ren P, Wang J, Tang J, Zhang F, Zong Z, Chen Z, Jin Y, Ren F (2022b) Multifunctional sandwich-structured magnetic–electric composite films with Joule heating capacities toward absorption-dominant electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos Part B Eng 236:109836
Guo Z, Ren P, Wang J, Hou X, Tang J, Liu Z, Chen Z, Jin Y, Ren F (2023) Methylene blue adsorption derived thermal insulating N, S-co-doped TiC/carbon hybrid aerogel for high-efficient absorption-dominant electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem Eng J 451:138667
Han M, Yin X, Hantanasirisakul K, Li X, Iqbal A, Hatter CB, Anasori B, Koo CM, Torita T, Soda Y, Zhang L (2019) Anisotropic MXene aerogels with a mechanically tunable ratio of electromagnetic wave reflection to absorption. Adv Opt Mater 7(10):1900267
Hu X, Zhu C, Quan B, Sheng M, Wu H, Lu X, Qu J (2022) Engineering robust multifunctional composites with enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding and all-weather thermal management capability via simple layer-by-layer assembly. Chem Eng J 446:137423
Iqbal A, Sambyal P, Koo CM (2020a) 2D MXenes for electromagnetic shielding: a review. Adv Funct Mater 30(47):2000883
Iqbal A, Shahzad F, Hantanasirisakul K, Kim MK, Kwon J, Hong J, Kim H, Kim D, Gogotsi Y, Koo CM (2020b) Anomalous absorption of electromagnetic waves by 2D transition metal carbonitride Ti3CNTx (MXene). Science 369(6502):446
Jia X, Shen B, Zhang L, Zheng W (2021) Construction of shape-memory carbon foam composites for adjustable EMI shielding under self-fixable mechanical deformation. Chem Eng J 405:126927
Kim BR, Lee HK, Kim E, Lee S-H (2010) Intrinsic electromagnetic radiation shielding/absorbing characteristics of polyaniline-coated transparent thin films. Synth Met 160(17–18):1838–1842
Lapka T, Vilcakova J, Kopecky D, Prokes J, Dendisova M, Moucka R, Sedlačík K, Hassouna F (2023) Flexible, ultrathin and light films from one-dimensional nanostructures of polypyrrole and cellulose nanofibers for high performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbohydr Polym 309:120662
Li Y, Shen B, Pei X, Zhang Y, Yi D, Zhai W, Zhang L, Wei X, Zheng W (2016) Ultrathin carbon foams for effective electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 100:375–385
Li Y, Chen Y, Liu Y, Zhang C, Qi H (2021) Holocellulose nanofibrils assisted exfoliation to prepare MXene-based composite film with excellent electromagnetic interference shielding performance. Carbohydr Polym 274:118652
Liu J, Zhang H-B, Sun R, Liu Y, Liu Z, Zhou A, Yu Z-Z (2017) Hydrophobic, flexible, and lightweight MXene foams for high-performance electromagnetic-interference shielding. Adv Mater 29(38):1702367
Liu H, Wang Z, Wang J, Yang Y, Wu S, You C, Tian N, Li Y (2022a) Structural evolution of MXenes and their composites for electromagnetic interference shielding applications. Nanoscale 14(26):9218–9247
Liu J, Mckeon L, Garcia J, Pinilla S, Barwich S, Möbius M, Stamenov P, Coleman JN, Nicolosi V (2022b) Additive manufacturing of Ti3C2-MXene-functionalized conductive polymer hydrogels for electromagnetic-interference shielding. Adv Mater 34(5):2106253
Oliveira FM, Gusmao R (2020) Recent advances in the electromagnetic interference shielding of 2D materials beyond graphene. ACS Appl Electron Mater 2(10):3048–3071
Quero F, Rosenkranz A (2021) Mechanical performance of binary and ternary hybrid MXene/nanocellulose hydro- and aerogels—a critical review. Adv Mater Interfaces 8(18):2100952
Shahzad F, Alhabeb M, Hatter CB, Anasori B, Hong SM, Koo CM, Gogotsi Y (2016) Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes). Science 353(6304):1137–1140
Tan H, Gou J, Zhang X, Ding L, Wang H (2023) Sandwich-structured Ti3C2Tx-MXene/reduced-graphene-oxide composite membranes for high-performance electromagnetic interference and infrared shielding. J Membr Sci 675:121560
Tang X, Luo J, Hu Z, Lu S, Liu X, Li S, Zhao X, Zhang Z, Lan Q, Ma P, Wang Z, Liu T (2022) Ultrathin, flexible, and oxidation-resistant MXene/graphene porous films for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano Res 16:1755–1763
Wan Y, Xiong P, Liu J, Feng F, Xun X, Gama FM, Zhang Q, Yao F, Yang Z, Luo H, Xu Y (2021) Ultrathin, strong, and highly flexible Ti3C2Tx MXene/bacterial cellulose composite films for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Nano 15(5):8439–8449
Wang L, Shi X, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Gu J (2020a) Lightweight and robust rGO/sugarcane derived hybrid carbon foams with outstanding EMI shielding performance. J Mater Sci Technol 52:119–126
Wang YY, Zhou ZH, Zhou CG, Sun WJ, Gao JF, Dai K, Yan DX, Li ZM (2020b) Lightweight and robust carbon nanotube/polyimide foam for efficient and heat-resistant electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave absorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(7):8704–8712
Wang Z, Cheng Z, Fang C, Hou X, Xie L (2020c) Recent advances in MXenes composites for electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave absorption. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 136:105956
Wang J, Ma X, Zhou J, Du F, Teng C (2022) Bioinspired, high-strength, and flexible MXene/aramid fiber for electromagnetic interference shielding papers with joule heating performance. ACS Nano 16(4):6700–6711
Wei Q, Pei S, Qian X, Liu H, Liu Z, Zhang W, Zhou T, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Cheng HM, Ren W (2020) Superhigh electromagnetic interference shielding of ultrathin aligned pristine graphene nanosheets film. Adv Mater 32(14):1907411
Wu X, Han B, Zhang HB, Xie X, Tu T, Zhang Y, Dai Y, Yang R, Yu ZZ (2020) Compressible, durable and conductive polydimethylsiloxane-coated MXene foams for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem Eng J 381:122622
Wu N, Yang Y, Wang C, Wu Q, Pan F, Zhang R, Liu J, Zeng Z (2023) Ultrathin cellulose nanofiber assisted ambient-pressure-dried, ultralight, mechanically robust, mechanically robust, multifunctional MXene aerogels. Adv Mater 35(1):2207969
Xu H, Yin X, Li X, Li M, Liang S, Zhang L, Cheng L (2019) Lightweight Ti2CTx MXene/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite foams for electromagnetic wave shielding with absorption-dominated feature. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(10):10198–10207
Yu Z, Dai T, Yuan S, Zou H, Liu P (2020) Electromagnetic interference shielding performance of anisotropic polyimide/graphene composite aerogels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(27):30990–31001
Yun T, Kim H, Iqbal A, Cho YS, Lee GS, Kim MK, Kim SJ, Kim D, Gogotsi Y, Kim SO, Koo CM (2020) Electromagnetic shielding of monolayer MXene assemblies. Adv Mater 32(9):1906769
Zeng Z, Jin H, Chen M, Li W, Zhou L, Zhang Z (2016) Lightweight and anisotropic porous MWCNT/WPU composites for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Funct Mater 26(2):303–310
Zhai J, Cui C, Li A, Guo R, Cheng C, Ren E, Xiao H, Zhou M, Zhang J (2022) Waste cotton fabric/MXene composite aerogel with heat generation and insulation for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Ceram Int 48(10):13464–13474
Zhan Z, Song Q, Zhou Z, Lu C (2019) Ultrastrong and conductive MXene/cellulose nanofiber films enhanced by hierarchical nano-architecture and interfacial interaction for flexible electromagnetic interference shielding. J Mater Chem C 7(32):9820–9829
Zhang Y, Gu J (2022) A perspective for developing polymer-based electromagnetic interference shielding composites. Nano-Micro Lett 14(1):89
Zhang H-B, Yan Q, Zheng W-G, He Z, Yu Z-Z (2011) Tough graphene-polymer microcellular foams for electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3(3):918–924
Zhang Y, Ruan K, Gu J (2021a) Flexible sandwich-structured electromagnetic interference shielding nanocomposite films with excellent thermal conductivities. Small 17(42):2101951
Zhang Y, Ruan K, Shi X, Qiu H, Pan Y, Yan Y, Gu J (2021b) Ti3C2Tx/rGO porous composite films with superior electromagnetic interference shielding performances. Carbon 175:271–280
Zhang F, Ren P, Guo Z, Wang J, Chen Z, Zong Z, Hu J, Jin Y, Ren F (2022a) Asymmetric multilayered MXene-AgNWs/cellulose nanofiber composite films with antibacterial properties for high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding. J Mater Sci Technol 129:181–189
Zhang L, Luo J, Zhang S, Yan J, Huang X, Wang L, Gao J (2022b) Interface sintering engineered superhydrophobic and durable nanofiber composite for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. J Mater Sci Technol 98:62–71
Zhou M, Wang J, Tan S, Ji G (2023) Top-down construction strategy toward sustainable cellulose composite paper with tunable electromagnetic interference shielding. Mater Today Phys 31:100962
Zhu Y, Liu J, Guo T, Wang JJ, Tang X, Nicolosi V (2021) Multifunctional Ti3C2Tx MXene composite hydrogels with strain sensitivity toward absorption-dominated electromagnetic-interference shielding. ACS Nano 15(1):1465–1474
Zong Z, Ren P, Guo Z, Wang J, Hu J, Chen Z, Jin Y, Wang F, Ren F (2022) Synergistic effect of 2D TiC and 1D CNT towards absorption-dominant high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding in 3D macroporous carbon aerogel. Carbon 197:40–51
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52102303), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M650268), the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2022JM-257) and Foundation of Education Department of Shaanxi Province [20JK0805].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FR: Writing-original draft, data curation, software. JZ: Methodology, formal analysis, resources. TW: Validation, software. FZ: Data curation, formal analysis. ZG: Software. YJ: Supervision, resources. PR: Conceptualization, resources.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests as defined by Springer, or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion reported in this paper.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
According to the guide for authors, I would like to declare on behalf of my co-author that this work described was an original comment that has not been published previously. All the authors listed have approved the manuscript that is enclosed.
Consent for publication
The manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, F., Zhang, J., Wu, T. et al. Bioinspired, ultra-light and sandwich structured MXene–AgNWs/cellulose nanofiber porous film for excellent electromagnetic interference shielding with Joule heating performance. Cellulose 31, 2341–2353 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05736-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05736-9