Abstract
Purpose
At the global scale, soil contamination with persistent metals such as lead (Pb), zinc (Zn), and copper (Cu) induces a serious threat of entering the human food chain. In the recent past, different natural and synthetic compounds have been used to immobilize metals in soil environments. However, the mechanisms involved in amendment-induced immobilization of metals in soil remained unclear. The objective of the present work was therefore to determine the mechanisms involved in metal-phosphates formation in the rhizospheric soils of pea and tomato currently cultivated in kitchen gardens.
Materials and methods
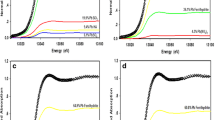
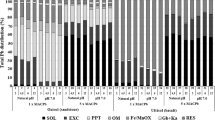
Pea and tomato were cultivated on a soil polluted by past industrial activities with Pb and Zn under two kinds of phosphate (P) amendments: (1) solid hydroxyapatite and (2) KH2PO4. The nature and quantities of metal-P formed in the rhizospheric soils were studied by using the selective chemical extractions and employing the combination of X-ray fluorescence micro-spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and electron microprobe methods. Moreover, the influence of soil pH and organic acids excreted by plant roots on metal-P complexes formation was studied.
Results and discussion
Our results demonstrated that P amendments have no effect on metal-P complex formation in the absence of plants. But, in the presence of plants, P amendments cause Pb and Zn immobilization by forming metal-P complexes. Higher amounts of metal-P were formed in the pea rhizosphere compared to the tomato rhizosphere and in the case of soluble P compared to the solid amendment. The increase in soil-metal contact time enhanced metal-P formation.
Conclusions
The different forms of metal-P formed for the different plants under two kinds of P amendments indicate that several mechanisms are involved in metal immobilization. Metal-P complex formation in the contaminated soil depends on the type of P amendment added, duration of soil-plant contact, type of plant species, and excretion of organic acids by the plant roots in the rhizosphere.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arshad M, Silvestre J, Pinelli E, Kallerhoff J, Kaemmerer M, Tarigo A, Shahid M, Guiresse M, Pradere P, Dumat C (2008) A field study of lead phytoextraction by various scented Pelargonium cultivars. Chemosphere 71:2187–2192
Austruy A (2012) Aspects physiologiques et biochimiques de la tolérance à l'arsenic chez les plantes supérieures dans un contexte de phytostabilisation d'une friche industrielle. Thèse de l'Université Blaise Pascal, Clermont Ferrand, 328 p
Austruy A, Wanat N, Moussard C, Vernay P, Joussein E, Ledoigt G, Hitmi A (2013) Physiological impacts of soil pollution and arsenic uptake in three plant species: Agrostis capillaris, Solanum nigrum and Vicia faba. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 90:28–34
Bolan DNS, Naidu R, Mahimairaja S, Baskaran S (1994) Influence of low-molecular-weight organic acids on the solubilization of phosphates. Biol Fert Soils 18:311–319
Cao T, Wang M, An L, Yu Y, Lou Y, Guo S, Zuo B, Liu Y, Wu J, Cao Y et al (2009) Air quality for metals and sulfur in Shanghai, China, determined with moss bags. Environ Pollut 157:1270–1278
Chaignon V, Hinsinger P (2003) A biotest for evaluating copper bioavailability to plants in a contaminated soil. J Environ Qual 32:824–833
Chrysochoou M, Dermatas D, Grubb DG (2007) Phosphate application to firing range soils for Pb immobilization: The unclear role of phosphate. J Hazard Mater 144:1–14
Crannell BS, Eighmy TT, Krzanowski JE, Eusden JD Jr, Shaw EL, Francis CA (2000) Heavy metal stabilization in municipal solid waste combustion bottom ash using soluble phosphate. Waste Manag 20:135–148
Debela F, Arocena JM, Thring RW, Whitcombe T (2010) Organic acid-induced release of lead from pyromorphite and its relevance to reclamation of Pb-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 80:450–456
Debela F, Arocena JM, Thring RW, Whitcombe T (2013) Organic acids inhibit the formation of pyromorphite and Zn-phosphate in phosphorous amended Pb- and Zn-contaminated soil. J Environ Manag 116:156–162
Douay F, Pruvot C, Waterlot C, Fritsch C, Fourrier H, Loriette A, Bidar G, Grand C, de Vaufleury A, Scheifler R (2009) Contamination of woody habitat soils around a former lead smelter in the North of France. Sci Total Environ 407:5564–5577
Dumat C, Chiquet A, Gooddy D, Aubry E, Morin G, Juillot F, Benedetti MF (2001) Metal ion geochemistry in smelter impacted soils and soil solutions. Bull Soc Geol Fr 172:539–548
Eighmy TT, Crannell BS, Butler LG, Cartledge FK, Emery EF, Oblas D, Krzanowski JE, EL Eusden S, Francis CA (1997) Heavy Metal Stabilization in Municipal Solid Waste Combustion Dry Scrubber Residue Using Soluble Phosphate. Environ Sci Technol 31:3330–3338
Foucault Y, Lévêque T, Xiong T, Schreck E, Austruy A, Shahid M, Dumat C (2013) Green manure plants for remediation of soils polluted by metals and metalloids: Ecotoxicity and human bioavailability assessment. Chemosphere 93:1430–1435
Fritsch C, Giraudoux P, Cœurdassier M, Douay F, Raoul F, Pruvot C, Waterlot C, de Vaufleury A, Scheifler R (2010) Spatial distribution of metals in smelter-impacted soils of woody habitats: influence of landscape and soil properties, and risk for wildlife. Chemosphere 81:141–155
Hashimoto Y, Takaoka M, Oshita K, Tanida H (2009) Incomplete transformations of Pb to pyromorphite by phosphate-induced immobilization investigated by X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectroscopy. Chemosphere 76:616–622
Huang H, Li T, Gupta DK, He Z, Yang X-E, Ni B, Li M (2012) Heavy metal phytoextraction by Sedum alfredii is affected by continual clipping and phosphorus fertilization amendment. J Environ Sci 24:376–386
Jiang G, Liu Y, Huang L, Fu Q, Deng Y, Hu H (2012) Mechanism of lead immobilization by oxalic acid-activated phosphate rocks. J Environ Sci (China) 24:919–925
Kotula PG, Keenan MR, Michael JR (2003) Automated analysis of SEM X-ray spectral images: a powerful new microanalysis tool. Microsc Microanal 9:1–17
Lapied E, Nahmani JY, Moudilou E, Chaurand P, Labille J, Rose J, Exbrayat J-M, Oughton DH, Joner EJ (2011) Ecotoxicological effects of an aged TiO2 nanocomposite measured as apoptosis in the anecic earthworm Lumbricus terrestris after exposure through water, food and soil. Environ Int 37:1105–1110
Leveque T, Capowiez Y, Schreck E, Mazzia C, Auffan M, Foucault Y, Austruy A, Dumat C (2013) Assessing ecotoxicity and uptake of metals and metalloids in relation to two different earthworm species (Eiseina hortensis and Lumbricus terrestris). Environ Pollut 179:232–241
Lopareva-Pohu A, Pourrut B, Waterlot C, Garçon G, Bidar G, Pruvot C, Shirali P, Douay F (2011) Assessment of fly ash-aided phytostabilisation of highly contaminated soils after an 8-year field trial: part 1. Influence on soil parameters and metal extractability. Sci Total Environ 409:647–654
Mavropoulos E, Rossi AM, Costa AM, Perez CAC, Moreira JC, Saldanha M (2002) Studies on the mechanisms of lead immobilization by hydroxyapatite. Environ Sci Technol 36:1625–1629
Mignardi S, Corami A, Ferrini V (2012) Evaluation of the effectiveness of phosphate treatment for the remediation of mine waste soils contaminated with Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn. Chemosphere 86:354–360
Mignardi S, Corami A, Ferrini V (2013) Immobilization of Co and Ni in Mining-Impacted Soils Using Phosphate Amendments. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1–10
Ministry of Environment Government of Japan (2007) Current status of the Brownfields Issue in Japan Interim Report, pp. 1–26. http://www.env.go.jp/en/water/soil/brownfields/interin-rep0703.pdf
Niazi NK, Bishop TFA, Singh B (2011a) Evaluation of spatial variability of soil arsenic adjacent to a disused cattle-dip site, using model-based geostatistics. Environ Sci Technol 45:10463–10470
Niazi NK, Singh B, Shah P (2011b) Arsenic speciation and phytoavailability in contaminated soils using a sequential extraction procedure and XANES spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 45:7135–7142
Niebes J-F, Dufey JE, Jaillard B, Hinsinger P (1993) Release of nonexchangeable potassium from different size fractions of two highly K-fertilized soils in the rhizosphere of rape (Brassica napus cv Drakkar). Plant Soil 155–156:403–406
Panfili F, Manceau A, Sarret G, Spadini L, Kirpichtchikova T, Bert V, Laboudigue A, Marcus MA, Ahamdach N, Libert M-F (2005) The effect of phytostabilization on Zn speciation in a dredged contaminated sediment using scanning electron microscopy, X-ray fluorescence, EXAFS spectroscopy, and principal components analysis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:2265–2284
Park JH, Bolan N, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2011) Isolation of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their potential for lead immobilization in soil. J Hazard Mater 185:829–836
Pourrut B, Shahid M, Dumat C, Winterton P, Pinelli E (2011) Lead uptake, toxicity, and detoxification in plants. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 213:113–136
Pourrut B, Shahid M, Douay F, Dumat C, Pinelli E (2013) Molecular mechanisms involved in lead uptake, toxicity and detoxification in higher plants. In: Gupta DK, Corpas FJ, Palma JM (eds) Heavy Metal Stress in Plants. Springer, Berlin, pp 121–147
Radwan MA, Salama AK (2006) Market basket survey for some heavy metals in Egyptian fruits and vegetables. Food Chem Toxicol 44:1273–1278
Raicevic S, Perovic V, Zouboulis AI (2009) Theoretical assessment of phosphate amendments for stabilization of (Pb + Zn) in polluted soil. Waste Manag 29:1779–1784
Schreck E, Foucault Y, Geret F, Pradere P, Dumat C (2011) Influence of soil ageing on bioavailability and ecotoxicity of lead carried by process waste metallic ultrafine particles. Chemosphere 85:1555–1562
Schreck E, Laplanche C, Le Guédard M, Bessoule J-J, Austruy A, Xiong T, Foucault Y, Dumat C (2013) Influence of fine process particles enriched with metals and metalloids on Lactuca sativa L. leaf fatty acid composition following air and/or soil-plant field exposure. Environ Pollut 179:242–249
Shahid M, Pinelli E, Pourrut B, Silvestre J, Dumat C (2011) Lead-induced genotoxicity to Vicia faba L. roots in relation with metal cell uptake and initial speciation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:78–84
Shahid M, Arshad M, Kaemmerer M, Pinelli E, Probst A, Baque D, Pradere P, Dumat C (2012a) Long-term field metal extraction by Pelargonium: phytoextraction efficiency in relation to plant maturity. Int J Phytorem 14:493–505
Shahid M, Dumat C, Aslam M, Pinelli E (2012b) Assessment of lead speciation by organic ligands using speciation models. Chem Spec Bioavailab 24:248–252
Shahid M, Dumat C, Silvestre J, Pinelli E (2012c) Effect of fulvic acids on lead-induced oxidative stress to metal sensitive Vicia faba L. plant. Biol Fertil Soils 48:689–697
Shahid M, Pinelli E, Dumat C (2012d) Review of Pb availability and toxicity to plants in relation with metal speciation; role of synthetic and natural organic ligands. J Hazard Mater 219–220:1–12
Shahid M, Ferrand E, Schreck E, Dumat C (2013a) Behavior and impact of zirconium in the soil-plant system: plant uptake and phytotoxicity. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 221:107–127
Shahid M, Dumat C, Pourrut B, Silvestre J, Laplanche C, Pinelli E (2013b) Influence of EDTA and citric acid on lead-induced oxidative stress to Vicia faba roots. J Soils Sediments. doi:10.1007/s11368-013-0724-0
Shahid M, Xiong T, Castrec-Rouelle M, Leveque T, Dumat C (2013c) Water extraction kinetics of metals, arsenic and dissolved organic carbon from industrial contaminated poplar leaves. J Environ Sci 25:2451–2459
Shahid M, Xiong T, Masood N, Leveque T, Quenea K, Austruy A, Foucault Y, Dumat C (2013d) Influence of plant species and phosphorus amendments on metal speciation and bioavailability in a smelter impacted soil: a case study of food-chain contamination. J Soils Sediments. doi:10.1007/s11368-013-0745-8
Shahid M, Dumat C, Pourrut B, Sabir M, Pinelli E (2014a) Assessing the effect of metal speciation on lead toxicity to Vicia faba pigment contents. J Geochem Explor. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.01.003
Shahid M, Austruy A, Echevarria G, Arshad M, Sanaullah M, Aslam M, Nadeem M, Nasim W, Dumat C (2014b) EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of heavy metals: a review. Soil Sediment Contam 23:389–416
Shahid M, Pinelli E, Pourrut B, Dumat C (2014c) Effect of organic ligands on lead-induced oxidative damage and antioxidant defence in the leaves of Vicia faba plants. J Geochem Explor. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.01.008
Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Marshall FM (2008) Heavy metal (Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb) contamination of vegetables in urban India: A case study in Varanasi. Environ Pollut 154:254–263
Suzuki T, Niinae M, Koga T, Akita T, Ohta M, Choso T (2014) EDDS-enhanced electrokinetic remediation of heavy metal-contaminated clay soils under neutral pH conditions. Coll Surf A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 440:145–150
Tang X, Yang J (2012) Long-term stability and risk assessment of lead in mill waste treated by soluble phosphate. Sci Total Environ 438:299–303
Uzu G, Sobanska S, Aliouane Y, Pradere P, Dumat C (2009) Study of lead phytoavailability for atmospheric industrial micronic and sub-micronic particles in relation with lead speciation. Environ Pollut 157:1178–1185
Valsami-Jones E, Ragnarsdottir KV, Putnis A, Bosbach D, Kemp AJ, Cressey G (1998) The dissolution of apatite in the presence of aqueous metal cations at pH 2–7. Chem Geol 151:215–233
Waterlot C, Pruvot C, Ciesielski H, Douay F (2011) Effects of a phosphorus amendment and the pH of water used for watering on the mobility and phytoavailability of Cd, Pb and Zn in highly contaminated kitchen garden soils. Ecol Eng 37:1081–1093
Weng W, Han G, Du P, Shen G (2002) The effect of citric acid addition on the formation of sol–gel derived hydroxyapatite. Mater Chem Phys 74:92–97
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the National Research Agency under reference ANR-12-0011-VBDU and from ADEME, France.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jaume Bech
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Austruy, A., Shahid, M., Xiong, T. et al. Mechanisms of metal-phosphates formation in the rhizosphere soils of pea and tomato: environmental and sanitary consequences. J Soils Sediments 14, 666–678 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-014-0862-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-014-0862-z