Abstract
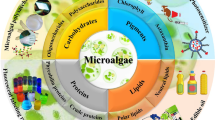
The ever-increasing concern for energy shortages and greenhouse effect has triggered the development of sustainable green technologies. Microalgae have received more attention due to the characteristics of biofuel production and CO2 fixation. From the perspective of autotrophic growth, the optimization of light quality has the potential to promote biomass production and bio-component accumulation in microalgae at low cost. In this study, bibliometric analysis was used to describe the basic features, identify the hotspots, and predict future trends of the research related to the light quality on microalgae cultivation. In addition, a mini-review referring to regulation methods of light quality was provided to optimize the framework of research. Results demonstrated that China has the greatest interest in this area. The destination of most research was to obtain biofuels and high-value-added products. Both blue and red lights were identified as the crucial spectrums for microalgae cultivation. However, sunlight is the most affordable light resource, which could not be fully utilized by microalgae through the photosynthetic process. Hence, some regulation approaches (e.g., dyes, plasmonic scattering, and carbon-based quantum dots) are proposed to increase the proportion of beneficial spectrum for enhancement of photosynthetic efficiency. In summary, this review introduces state-of-the-art research and provides theoretical guidance for light quality optimization in microalgae cultivation to obtain more benefits.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abomohra A, Shang H, El-Sheekh M, Eladel H, Ebaid R, Wang S, Wang Q (2019) Night illumination using monochromatic light-emitting diodes for enhanced microalgal growth and biodiesel production. Bioresour Technol 288:121514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121514
Abu-Ghosh S, Kumar VB, Fixler D, Dubinsky Z, Gedanken A, Iluz D (2017) Nitrogen-doped carbon dots prepared from bovine serum albumin to enhance algal astaxanthin production. Algal Res 23:161–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2017.01.011
Agnol LD, Neves RM, Maraschin M, Moura S, Luiz HL, Dias FTG, Bianchi O (2021) Green synthesis of Spirulina-based carbon dots for stimulating agricultural plant growth. Sustain Mater Techno 30:e00347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2021.e00347
Ajayan KV, Harilal CC, Gani P (2019) Performance of reflector coated LED Bio-box on the augmentation of growth and lipid production in aerophytic trebouxiophyceaen algae Coccomyxa sp. Algal Res 38:101401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2018.101401
Atta M, Idris A, Bukhari A, Wahidin S (2013) Intensity of blue LED light: a potential stimulus for biomass and lipid content in fresh water microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. Bioresour Technol 148:373–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.08.162
Baer S, Heining M, Schwerna P, Buchholz R, Hubner H (2016) Optimization of spectral light quality for growth and product formation in different microalgae using a continuous photobioreactor. Algal Res 14:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.01.011
Baldev E, MubarakAli D, Ilavarasi A, Pandiaraj D, Ishack KASS, Thajuddin N (2013) Degradation of synthetic dye, Rhodamine B to environmentally non-toxic products using microalgae. Colloid Surf B 105:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.01.008
Bhola V, Swalaha F, Kumar RR, Singh M, Bux F (2014) Overview of the potential of microalgae for CO2 sequestration. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(7):2103–2118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0487-6
Biller P, Ross AB (2011) Potential yields and properties of oil from the hydrothermal liquefaction of microalgae with different biochemical content. Bioresour Technol 102(1):215–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.028
Blanken W, Cuaresma M, Wijffels RH, Janssen M (2013) Cultivation of microalgae on artificial light comes at a cost. Algal Res 2(4):333–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2013.09.004
Burak H, Dunbar A, Gilmour DJ (2019) Enhancement of Dunaliella salina growth by using wavelength shifting dyes. J Appl Phycol 31(5):2791–2796. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01819-4
Cai T, Park SY, Li YB (2013) Nutrient recovery from wastewater streams by microalgae: status and prospects. Renew Sust Energ Rev 19:360–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.11.030
Cai MF, An CJ, Guy C (2021) A scientometric analysis and review of biogenic volatile organic compound emissions: research hotspots, new frontiers, and environmental implications. Renew Sust Energ Rev 149:111317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111317
Carvalho AP, Silva SO, Baptista JM, Malcata FX (2011) Light requirements in microalgal photobioreactors: an overview of biophotonic aspects. Appl Microbiol Biot 89(5):1275–1288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-3047-8
Chavan KJ, Chouhan S, Jain S, Singh P, Yadav M, Tiwari A (2014) Environmental factors influencing algal biodiesel production. Environ Eng Sci 31(11):602–611. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2014.0219
Chaves I, Pokorny R, Byrdin M, Hoang N, Ritz T, Brettel K, Essen LO, Van Der Horst GTJ, Batschauer A, Ahmad M (2011) The cryptochromes: blue light photoreceptors in plants and animals. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62:335–364. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103759
Chen CM, Hu ZG, Liu SB, Tseng H (2012) Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin Biol Ther 12(5):593–608. https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2012.674507
Chen FF, Leng YY, Lu Q, Zhou WU (2021) The application of microalgae biomass and bio-products as aquafeed for aquaculture. Algal Res 60:102541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2021.102541
Chia SR, Ong HC, Chew KW, Show PL, Phang SM, Ling TC, Nagarajan D, Lee DJ, Chang JS (2018) Sustainable approaches for algae utilisation in bioenergy production. Renew Energ 129:838–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.04.001
Croce R, Van Amerongen H (2014) Natural strategies for photosynthetic light harvesting. Nat Chem Biol 10(7):492–501. https://doi.org/10.1038/Nchembio.1555
Cui ZY, Kerekes JP (2018) Potential of red edge spectral bands in future Landsat satellites on agroecosystem canopy green leaf area index retrieval. Remote Sens 10(9):1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091458
Cui ZY, Kerekes JP (2018b) Impact of wavelength shift in relative spectral response at high angles of incidence in Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager and future Landsat design concepts. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sensing 56(10):5873–5883. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2827394
Cui ZY, Montanaro M, Gerace A, Schott JR, Markham B (2015) Requirement sensitivity studies for a future Landsat sensor. Conf Earth Obs Syst XX 9607:96070S. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2188482
Cui ZY, Kerekes J (2019) Potential of red edge spectral bands in future Landsat satellites on agroecosystem canopy chlorophyll content retrieval. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium 7168–7171. https://doi.org/10.1109/igarss.2019.8898783
Da Rosa ALD, Carissimi E, Dotto GL, Sander H, Feris LA (2018) Biosorption of rhodamine B dye from dyeing stones effluents using the green microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa. J Clean Prod 198:1302–1310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.128
De Mooij T, De Vries G, Latsos C, Wijffels RH, Janssen M (2016) Impact of light color on photobioreactor productivity. Algal Res 15:32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.01.015
Draaisma RB, Wijffels RH, Slegers PM, Brentner LB, Roy A, Barbosa MJ (2013) Food commodities from microalgae. Curr Opin Biotechnol 24(2):169–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2012.09.012
Estime B, Ren DC, Sureshkumar R (2015) Effects of plasmonic film filters on microalgal growth and biomass composition. Algal Res 11:85–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2015.06.004
Ezequiel J, Laviale M, Frankenbach S, Cartaxana P, Serodio J (2015) Photoacclimation state determines the photobehaviour of motile microalgae: the case of a benthic diatom. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 468:11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2015.03.004
Fernando KAS, Sahu S, Liu YM, Lewis WK, Guliants EA, Jafariyan A, Wang P, Bunker CE, Sun YP (2015) Carbon quantum dots and applications in photocatalytic energy conversion. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces 7(16):8363–8376. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b00448
Glemser M, Heining M, Schmidt J, Becker A, Garbe D, Buchholz R, Bruck T (2016) Application of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) in cultivation of phototrophic microalgae: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(3):1077–1088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7144-6
Hashimoto H, Sugai Y, Uragami C, Gardiner AT, Cogdell RJ (2015) Natural and artificial light-harvesting systems utilizing the functions of carotenoids. J Photochem Photobiol C-Photochem Rev 25:46–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2015.07.004
He QN, Yang HJ, Wu L, Hu CX (2015) Effect of light intensity on physiological changes, carbon allocation and neutral lipid accumulation in oleaginous microalgae. Bioresour Technol 191:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.05.021
He K, Zhang JB, Zeng YM (2019) Knowledge domain and emerging trends of agricultural waste management in the field of social science: a scientometric review. Sci Total Environ 670:236–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.184
Hena S, Gutierrez L, Croue JP (2021) Removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) from wastewater using microalgae: a review. J Hazard Mater 403:124041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124041
Huang L, Kelly S, Lv KJ, Giurco D (2019) A systematic review of empirical methods for modelling sectoral carbon emissions in China. J Clean Prod 215:1382–1401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.058
Huang Y, Sun WJ, Qin ZC, Zhang W, Yu YQ, Li TT, Zhang Q, Wang GC, Yu LF, Wang YJ, Ding F, Zhang P (2022) The role of China’s terrestrial carbon sequestration 2010–2060 in offsetting energy-related CO2 emissions. Natl Sci Rev 9(8). https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwac057
Hwang TG, Kim GY, Han JI, Kim S, Kim JP (2020) Enhancement of lipid productivity of Chlorella sp. using light converting red fluorescent films based on aggregation-induced emission. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(42):15888–15897. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c04456
Hwang TG, Kim GY, Han JI, Park JM, Kim JP (2021) Highly efficient light-converting films based on diketopyrrolopyrrole with deep-red aggregation-induced emission for enhancing the lipid productivity of Chlorella sp. Sustain Energ Fuels 5(20):5205–5215. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1se00638j
Jaubert M, Bouly JP, Alcala MR, Falciatorel A (2017) Light sensing and responses in marine microalgae. Curr Opin Plant Biol 37:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2017.03.005
Jin CL, Yu BQ, Qian SY, Liu Q, Zhou XJ (2021) Impact of combined monochromatic light on the biocomponent productivity of Dunaliella salina. J Renew Sustain Energy 13(2):023101. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0041330
Kim CW, Sung MG, Nam K, Moon M, Kwon JH, Yang JW (2014a) Effect of monochromatic illumination on lipid accumulation of Nannochloropsis gaditana under continuous cultivation. Bioresour Technol 159:30–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.02.024
Kim DG, Lee C, Park SM, Choi YE (2014b) Manipulation of light wavelength at appropriate growth stage to enhance biomass productivity and fatty acid methyl ester yield using Chlorella vulgaris. Bioresour Technol 159:240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.02.078
Kim SH, Sunwoo IY, Hong HJ, Awah CC, Jeong GT, Kim SK (2019) Lipid and unsaturated fatty acid productions from three microalgae using nitrate and light-emitting diodes with complementary LED wavelength in a two-phase culture system. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42(9):1517–1526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02149-y
Kim SH, Lee UH, Lee SB, Jeong GT, Kim SK (2021) Improvement of unsaturated fatty acid production from porphyridium cruentum using a two-phase culture system in a photobioreactor with light-emitting diodes (LEDs). J Microbiol Biotechnol 31(3):456–463. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.2011.11004
Kong WN, Shen BX, Lyu HH, Kong J, Ma J, Wang ZZ, Feng S (2021) Review on carbon dioxide fixation coupled with nutrients removal from wastewater by microalgae. J Clean Prod 292:125975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.125975
Kwan PP, Banerjee S, Shariff M, Yusoff FM (2021) Influence of light on biomass and lipid production in microalgae cultivation. Aquac Res 52(4):1337–1347. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.15023
Latsos C, Van Houcke J, Blommaert L, Verbeeke GP, Kromkamp J, Timmermans KR (2021) Effect of light quality and quantity on productivity and phycoerythrin concentration in the cryptophyte Rhodomonas sp. J Appl Phycol 33(2):729–741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02338-3
Lau CC, Teh KY, Afifudeen CLW, Yee W, Aziz A, Cha TS (2022) Bright as day and dark as night: light-dependant energy for lipid biosynthesis and production in microalgae. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38(4):70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03245-0
Lee JY, Seo SH, Ahn CY, Lee CS, An KG, Srivastava A, Oh HM (2019) Green light as supplementary light for enhancing biomass production of Ettlia sp. and preventing population invasion from other microalgae. J Appl Phycol 31(4):2207–2215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-1737-x
Leng SQ, Jiao HT, Liu TG, Pan W, Chen JF, Chen J, Huang HJ, Peng HY, Wu ZB, Leng LJ, Zhou WG (2022) Co-liquefaction of Chlorella and soybean straw for production of bio-crude: effects of reusing aqueous phase as the reaction medium. Sci Total Environ 820:153348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153348
Li XP, Huff J, Crunkleton DW, Johannes TW (2021a) LED alternating between blue and red-orange light improved the biomass and lipid productivity of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Biotechnol 341:96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2021.09.008
Li XP, Manuel J, Slavens S, Crunkleton DW, Johannes TW (2021b) Interactive effects of light quality and culturing temperature on algal cell size, biomass doubling time, protein content, and carbohydrate content. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105(2):587–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-11068-y
Li JJ, Qian J, Tang JH, Jin ZY, Lu Q, Cheng JL, Zhou XQ, Zhang XR, Fu SY, Wan T, Li HG, Chen Q, Zhou WG (2022a) Enhancement of ammonium removal from landfill leachate using microalgae by an integrated strategy of nutrient balance and trophic mode conversion. Algal Res 61:102572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2021.102572
Li SN, Li X, Ho SH (2022b) How to enhance carbon capture by evolution of microalgal photosynthesis? Sep Purif Technol 291:120951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120951
Li X, Huff J, Crunkleton DW, Johannes TW (2023) Light intensity and spectral quality modulation for improved growth kinetics and biochemical composition of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Biotechnol 375:28–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2023.08.007
Liu Y, Wei D (2023) High-efficient CO2-to-protein bioconversion by oleaginous Coccomyxa subellipsoidea using light quality shift and nitrogen supplementation strategy. Chem Eng J 473:145166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.145166
Marchetti J, Bougaran G, Jauffrais T, Lefebvre S, Rouxel C, Saint-Jean B, Lukomska E, Robert R, Cadoret JP (2013) Effects of blue light on the biochemical composition and photosynthetic activity of Isochrysis sp (T-iso). J Appl Phycol 25(1):109–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9844-y
Marella TK, Tiwari AJBT (2020) Marine diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii based biorefinery for co-production of eicosapentaenoic acid and fucoxanthin. Bioresour Technol 307:123245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123245
Mulders KJM, Lamers PP, Martens DE, Wijffels RH (2014) Phototrophic pigment production with microalgae: biological constraints and opportunities. J Phycol 50(2):229–242. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpy.12173
Nwoba EG, Parleyhet DA, Laird DW, Alameh K, Moheimani NR (2019) Light management technologies for increasing algal photobioreactor efficiency. Algal Res 39:101433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2019.101433
Nwoba EG, Rohani T, Raeisossadati M, Vadiveloo A, Bahri PA, Moheimani NR (2021) Monochromatic light filters to enhance biomass and carotenoid productivities of Dunaliella salina in raceway ponds. Bioresour Technol 340:125689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125689
Ooms MD, Dinh CT, Sargent EH, Sinton D (2016) Photon management for augmented photosynthesis. Nat Commun 7:12699. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12699
Ouyang W, Wang YD, Lin CY, He MC, Hao FH, Liu HB, Zhu WH (2018) Heavy metal loss from agricultural watershed to aquatic system: a scientometrics review. Sci Total Environ 637:208–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.434
Patelou M, Infante C, Dardelle F, Randewig D, Kouri ED, Udvardi MK, Tsiplakou E, Mantecón L, Flemetakis E (2020) Transcriptomic and metabolomic adaptation of Nannochloropsis gaditana grown under different light regimes. Algal Res 45:101735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2019.101735
Phukan T, Syiem MB (2019) Modulation of oxidant and antioxidant homeostasis in the cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum Meg1 under UV-C radiation stress. Aquat Toxicol 213:105228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.105228
Pienkos PT, Darzins A (2009) The promise and challenges of microalgal-derived biofuels. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefining 3(4):431–440. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.159
Qian J, Zhang JQ, Jin ZY, Cheng JL, Li JJ, Song HW, Lu Q, Li HG, Wan T, Fu SY, Li J, Zhou WG (2022) Enhancing algal yield and nutrient removal from anaerobic digestion piggery effluent by an integrated process-optimization strategy of fungal decolorization and microalgae cultivation. Appl Sci-Basel 12(9):4741. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094741
Ramanna L, Rawat I, Bux F (2017) Light enhancement strategies improve microalgal biomass productivity. Renew Sust Energ Rev 80:765–773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.202
Ramanna L, Rawat I, Zerrouki D, Bux F (2018) A novel organic dye-based approach to increase photon flux density for enhanced microalgal pigment production. J Clean Prod 198:187–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.016
Rawat KS, Sood SK (2021) Knowledge mapping of computer applications in education using CiteSpace. Comput Appl Eng Educ 29(5):1324–1339. https://doi.org/10.1002/cae.22388
Ren HY, Zhu GQ, Ni J, Shen MW, Show PL, Sun FF (2022) Enhanced photoautotrophic growth of Chlorella vulgaris in starch wastewater through photo-regulation strategy. Chemosphere 307:135533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135533
Rosenberg JN, Mathias A, Korth K, Betenbaugh MJ, Oyler GA (2011) Microalgal biomass production and carbon dioxide sequestration from an integrated ethanol biorefinery in Iowa: a technical appraisal and economic feasibility evaluation. Biomass Bioenerg 35(9):3865–3876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2011.05.014
Saratale RG, Ponnusamy VK, Jeyakumar RB, Sirohi R, Piechota G, Shobana S, Dharmaraja J, Lay CH, Saratale GD, Shin HS, Ashokkumar V (2022) Microalgae cultivation strategies using cost-effective nutrient sources: recent updates and progress towards biofuel production. Bioresour Technol 361:127691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127691
Saravanan A, Deivayanai VC, Kumar PS, Rangasamy G, Varjani S (2022) CO2 bio-mitigation using genetically modified algae and biofuel production towards a carbon net-zero society. Bioresour Technol 363:127982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127982
Schulze PSC, Barreira LA, Pereira HGC, Perales JA, Varela JCS (2014) Light emitting diodes (LEDs) applied to microalgal production. Trends Biotechnol 32(8):423–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2014.06.001
Schulze PSC, Pereira HC, Santos TFC, Schueler L, Guerra R, Barreira LA, Perales JA, Varela JCS (2016) Effect of light quality supplied by light emitting diodes (LEDs) on growth and biochemical profiles of Nannochloropsis oculata and Tetraselmis chuii. Algal Res 16:387–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.03.034
Senge MO, Ryan AA, Letchford KA, MacGowan SA, Mielke T (2014) Chlorophylls, symmetry, chirality, and photosynthesis. Symmetry-Basel 6(3):781–843. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym6030781
Seo YH, Cho C, Lee JY, Han JI (2014) Enhancement of growth and lipid production from microalgae using fluorescent paint under the solar radiation. Bioresour Technol 173:193–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.012
Seo SH, Ha JS, Yoo C, Srivastava A, Ahn CY, Cho DH, La HJ, Han MS, Oh HM (2017) Light intensity as major factor to maximize biomass and lipid productivity of Ettlia sp in CO2-controlled photoautotrophic chemostat. Bioresour Technol 244:621–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.020
Sharma AK, Ghodke PK, Manna S, Chen WH (2021) Emerging technologies for sustainable production of biohydrogen production from microalgae: a state-of-the-art review of upstream and downstream processes. Bioresour Technol 342:126057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126057
Shu CH, Tsai CC, Liao WH, Chen KY, Huang HC (2012) Effects of light quality on the accumulation of oil in a mixed culture of Chlorella sp and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 87(5):601–607. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2750
Shuba ES, Kifle D (2018) Microalgae to biofuels: “promising” alternative and renewable energy, review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 81:743–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.08.042
Silvello MAD, Goncalves IS, Azambuja SPH, Costa SS, Silva PGP, Santos LO, Goldbeck R (2022) Microalgae-based carbohydrates: a green innovative source of bioenergy. Bioresour Technol 344:126304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126304
Sirisuk P, Sunwoo I, Kim SH, Awah CC, Ra CH, Kim JM, Jeong GT, Kim SK (2018) Enhancement of biomass, lipids, and polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) production in Nannochloropsis oceanica with a combination of single wavelength light emitting diodes (LEDs) and low temperature in a three-phase culture system. Bioresour Technol 270:504–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.025
Song CF, Liu ZZ, Wang CL, Li SH, Kitamura Y (2020) Different interaction performance between microplastics and microalgae: the bio-elimination potential of Chlorella sp. L38 and Phaeodactylum tricornutum MASCC-0025. Sci Total Environ 723:138146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138146
Song QQ, Kong FY, Liu BF, Song XT, Ren NQ, Ren HY (2023a) Insights into the effect of rhamnolipids on the anaerobic fermentation and microalgae lipid production of waste activated sludge: performance and mechanisms. ACS ES&T Eng. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestengg.2c00372
Song XT, Kong FY, Liu BF, Song QQ, Ren NQ, Ren HY (2023b) Thallium-mediated NO signaling induced lipid accumulation in microalgae and its role in heavy metal bioremediation. Water Res 239:120027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.120027
Stadnichuk IN, Krasilnikov PM, Zlenko DV (2015) Cyanobacterial phycobilisomes and phycobiliproteins. Microbiology 84(2):101–111. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261715020150
Sun YB, Zhang JX, Xu JL, Cao JY, Li YR (2023) The effects of different LED lights on the main nutritional compositions of Isochrysis. Fishes 8(3):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8030124
Suparmaniam U, Lam MK, Uemura Y, Lim JW, Lee KT, Shuit SH (2019) Insights into the microalgae cultivation technology and harvesting process for biofuel production: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 115:109361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109361
Suparmaniam U, Lam MK, Lim JW, Yusup S, Tan IS, Lau SY, Kodgire P, Kachhwaha SS (2022) Influence of environmental stress on microalgae growth and lipid profile: a systematic review. Phytochem Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-022-09810-7
Takaichi S (2011) Carotenoids in Algae: distributions, biosyntheses and functions. Mar Drugs 9(6):1101–1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9061101
Teo CL, Atta M, Bukhari A, Taisir M, Yusuf AM, Idris A (2014) Enhancing growth and lipid production of marine microalgae for biodiesel production via the use of different LED wavelengths. Bioresour Technol 162:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.113
Torkamani S, Wani SN, Tang YJ, Sureshkumar R (2010) Plasmon-enhanced microalgal growth in miniphotobioreactors. Appl Phys Lett 97(4):043703. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3467263
Ubando AT, Africa ADM, Maniquiz-Redillas MC, Culaba AB, Chen WH, Chang JS (2021) Microalgal biosorption of heavy metals: a comprehensive bibliometric review. J Hazard Mater 402:123431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123431
Udayan A, Pandey AK, Sirohi R, Sreekumar N, Sang BI, Sim SJ, Kim SH, Pandey A (2022) Production of microalgae with high lipid content and their potential as sources of nutraceuticals. Phytochem Rev 22(4):833–860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-021-09784-y
Vadiveloo A, Moheimani NR, Cosgrove JJ, Bahri PA, Parlevliet D (2015) Effect of different light spectra on the growth and productivity of acclimated Nannochloropsis sp (Eustigmatophyceae). Algal Res 8:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2015.02.001
Wagner I, Steinweg C, Posten C (2016) Mono- and dichromatic LED illumination leads to enhanced growth and energy conversion for high-efficiency cultivation of microalgae for application in space. Biotechnol J 11(8):1060–1071. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201500357
Wang BL, Wang X, Hu YW, Chang MX, Bi YH, Hu ZY (2015) The combined effects of UV-C radiation and H2O2 on Microcystis aeruginosa, a bloom-forming cyanobacterium. Chemosphere 141:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.06.020
Wijffels RH, Barbosa MJ, Eppink MHM (2010) Microalgae for the production of bulk chemicals and biofuels. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefining 4(3):287–295. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.215
Wobbe L, Bassi R, Kruse O (2016) Multi-level light capture control in plants and green algae. Trends Plant Sci 21(1):55–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2015.10.004
Wu WB, Tan L, Chang HX, Zhang CF, Tan XF, Liao Q, Zhong NB, Zhang XM, Zhang YB, Ho SH (2023) Advancements on process regulation for microalgae-based carbon neutrality and biodiesel production. Renew Sust Energ Rev 171:112969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2022.112969
Xue R, Fu L, Dong SS, Yang HW, Zhou DD (2020) Promoting Chlorella photosynthesis and bioresource production using directionally prepared carbon dots with tunable emission. J Colloid Interface Sci 569:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.02.080
Yang LB, Su QS, Si BC, Zhang YL, Zhang YH, Yang H, Zhou XF (2022) Enhancing bioenergy production with carbon capture of microalgae by ultraviolet spectrum conversion via graphene oxide quantum dots. Chem Eng J 429:132230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132230
Ye M, Li Q, Li YY (2023) Evaluation of anaerobic membrane bioreactor treating dairy processing wastewater: elemental flow, bioenergy production and reduction of CO2 emission. Bioresour Technol 385:129342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129342
You XG, Yang LB, Zhou XF, Zhang YL (2022) Sustainability and carbon neutrality trends for microalgae-based wastewater treatment: a review. Environ Res 209:112860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112860
Yuan H, Zhang XR, Jiang ZY, Wang XY, Wang Y, Cao LM, Zhang XX (2020) Effect of light spectra on microalgal biofilm: cell growth, photosynthetic property, and main organic composition. Renew Energy 157:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.04.109
Zhang QT, Ma J, Qiu GY, Li L, Geng S, Hasi E, Li C, Wang GY, Li XY (2012) Potential energy production from algae on marginal land in China. Bioresour Technol 109:252–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.08.084
Zhang ML, Wang HB, Song YX, Huang H, Shao MW, Liu Y, Li H, Kang ZH (2018) Pristine carbon dots boost the growth of Chlorella vulgaris by enhancing photosynthesis. ACS Appl Bio Mater 1(3):894–902. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.8b00319
Zhang H, Chen AL, Huang LD, Zhang CW, Gao BY (2021) Transcriptomic analysis unravels the modulating mechanisms of the biomass and value-added bioproducts accumulation by light spectrum in Eustigmatos cf. Polyphem (Eustigmatophyceae). Bioresour Technol 338:125523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125523
Zhang WG, Zhao CZ, Liu J, Sun SQ, Zhao YJ, Wei J (2021b) Effects of exogenous GR24 on biogas upgrading and nutrient removal by co-culturing microalgae with fungi under mixed LED light wavelengths. Chemosphere 281:130791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130791
Zhang H, Gong PY, Cai QH, Zhang CW, Gao BY (2022) Maximizing fucoxanthin production in Odontella aurita by optimizing the ratio of red and blue light-emitting diodes in an auto-controlled internally illuminated photobioreactor. Bioresour Technol 344:126260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126260
Zhang L, Yang L, Chen J, Zhang Y, Zhou X (2023) Enhancing efficient reclaim of phosphorus from simulated urine by magnesium-functionalized biochar: adsorption behaviors, molecular-level mechanistic explanations and its potential application. Sci Total Environ 906:167293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167293
Zhao YJ, Sun SQ, Hu CW, Zhang H, Xu J, Ping LF (2015) Performance of three microalgal strains in biogas slurry purification and biogas upgrade in response to various mixed light-emitting diode light wavelengths. Bioresour Technol 187:338–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.03.130
Zhou W, Chen QJ, Meng S (2019) Knowledge mapping of credit risk research: scientometrics analysis using CiteSpace. Ekon Istraz 32(1):3457–3484. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677x.2019.1660202
Zuanazzi NR, Ghisi ND, Oliveira EC (2020) Analysis of global trends and gaps for studies about 2,4-D herbicide toxicity: a scientometric review. Chemosphere 241:125016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125016
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [U21A20322, 42006139], China Baowu Low Carbon Metallurgy Innovation Foundation-BWLCF202105, and the Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse (Tongji University) [No. 2022–4-ZD-05].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Yongyuan Hong and Libin Yang: conceived the manuscript. Yongyuan Hong and Yalei Zhang: scientometric analysis part. Yongyuan Hong, Xiaogang You and Haigeng Zhang: light quality review and regulation approach part. Yongyuan Hong, Libin Yang, Xiaying Xin, and Xuefei Zhou: original draft, review, and editing. Libin Yang, Xuefei Zhou, and Yalei Zhang: funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, Y., Yang, L., You, X. et al. Effects of light quality on microalgae cultivation: bibliometric analysis, mini-review, and regulation approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31192-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31192-2