Abstract
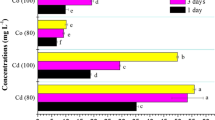
Phytoremediation is considered one of the well-established and sustainable techniques for the removal of heavy metals and metalloids from contaminated sites. The metal extraction ability of the plants can be enhanced by using suitable organic materials in combination with metal-tolerant plants. This experiment was carried out to investigate the phytoextraction potential of Mentha piperita L. for nickel (Ni) with and without citric acid (CA) amendment in hydroponic experiment. The experiment was performed in controlled glass containers with continuous aeration in complete randomized design (CRD). Juvenile M. piperita plants were treated with different concentrations of Ni (100, 250, and 500 μM) alone and/or combined with CA (5 mM). After harvesting the plants, the morpho-physiological and biochemical attributes as well as Ni concentrations in different tissues of M. piperita plants were measured. Results revealed that Ni stress significantly decreased the plant agronomic traits, photosynthesis in comparison to control. Nickel stress enhanced the antioxidant enzymes activities and caused the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in M. piperita. The CA treatment under Ni stress significantly improved the plant morpho-physiological and biochemical characteristics when compared with Ni treatments alone. The results demonstrated that CA enhanced the Ni concentrations in roots, stems, and leaves up to 138.2%, 54.2%, and 38%, respectively, compared to Ni-only-treated plants. The improvement in plant growth with CA under Ni stress indicated that CA is beneficial for Ni phytoextraction by using tolerant plant species.

Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd_Allah EF, Hashem A, Alam P, Ahmad P (2019) Silicon alleviates nickel-induced oxidative stress by regulating antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems in mustard plants. J Plant Growth Regul 38:1260–1273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-09931-y
Aebi H (1984) [13] Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Afshan S, Ali S, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Farid M, Abbas F, Ibrahim M, Mehmood MA, Abbasi GH (2015) Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of chromium, plant growth, and photosynthesis by alleviating the oxidative damages in Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:11679–11689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4396-8
Ahmad R, Ali S, Rizwan M, Dawood M, Farid M, Hussain A, Wijaya L, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2020) Hydrogen sulfide alleviates chromium stress on cauliflower by restricting its uptake and enhancing antioxidative system. Physiol Plant 168:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13001
Al Mahmud J, Bhuyan MHMB, Anee TI et al (2019) Reactive oxygen species metabolism and antioxidant defense in plants under metal/metalloid stress. In: Plant Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Springer International Publishing, pp 221–257
Al-Qurainy F (2009) Toxicity of heavy metals and their molecular detection on Phaseolus vulgaris (L.). Aust J Basic Appl Sci 3(3):3025–3035
Amjad M, Raza H, Murtaza B et al (2020) Nickel toxicity induced changes in nutrient dynamics and antioxidant profiling in two maize (Zea mays l.) hybrids. Plants. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9010005
Antić-Mladenović S, Frohne T, Kresović M, Stärk HJ, Tomić Z, Ličina V, Rinklebe J (2017) Biogeochemistry of Ni and Pb in a periodically flooded arable soil: fractionation and redox-induced (im)mobilization. J Environ Manag 186:141–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.06.005
Asati A, Pichhode M, Nikhil K (2016) Effect of heavy metals on plants: an overview. Int J Appl or Innov Eng Manag 5:2319–4847
Ashraf U, Tang X (2017) Yield and quality responses, plant metabolism and metal distribution pattern in aromatic rice under lead (Pb) toxicity. Chemosphere 176:141–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.103
Ashraf U, Kanu AS, Mo Z, Hussain S, Anjum SA, Khan I, Abbas RN, Tang X (2015) Lead toxicity in rice: effects, mechanisms, and mitigation strategies—a mini review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:18318–18332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5463-x
Ashraf U, Hussain S, Anjum SA, Abbas F, Tanveer M, Noor MA, Tang X (2017a) Alterations in growth, oxidative damage, and metal uptake of five aromatic rice cultivars under lead toxicity. Plant Physiol Biochem 115:461–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.04.019
Ashraf U, Kanu AS, Deng Q et al (2017b) Lead (Pb) toxicity; physio-biochemical mechanisms, grain yield, quality, and Pb distribution proportions in scented rice. Front Plant Sci 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00259
Ashraf U, Hussain S, Akbar N, Anjum SA, Hassan W, Tang X (2018) Water management regimes alter Pb uptake and translocation in fragrant rice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 149:128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.033
Awasthi K, Sinha P (2013) Nickel stress induced antioxidant defence system in sponge gourd (Luffa cylindrical). J Plant Physiol Pathol 1(1):2
Azam I, Afsheen S, Zia A et al (2015) Evaluating insects as bioindicators of heavy metal contamination and accumulation near industrial area of Gujrat, Pakistan. Biomed Res Int 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/942751
Ben Massoud M, Sakouhi L, Chaoui A (2019) Effect of plant growth regulators, calcium and citric acid on copper toxicity in pea seedlings. J Plant Nutr 42:1230–1242. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2019.1609506
Bhalerao SA, Sharma AS, Poojari AC (2015) Toxicity of nickel in plants. Int J Pure Appl Biosci 3:345–355. https://doi.org/10.1086/349961
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Chiappero J, del Rosario Cappellari L, Sosa Alderete LG, Palermo TB, Banchio E (2019) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria improve the antioxidant status in Mentha piperita grown under drought stress leading to an enhancement of plant growth and total phenolic content. Ind Crop Prod 139:111553
Chen X, Kumari D, Cao CJ et al (2019) A review on remediation technologies for nickel-contaminated soil. Hum Ecol Risk Assess An Int J:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1539639
Choudhury S, Panda SK (2005) Toxic effects, oxidative stress and ultrastructural changes in moss Taxithelium nepalense (Schwaegr.) Broth. under chromium and lead phytotoxicity. Water Air Soil Pollut 167:73–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-8682-9
Chiappero J, del Rosario Cappellari L, Sosa Alderete LG, Palermo TB, Banchio E (2019) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria improve the antioxidant status in Mentha piperita grown under drought stress leading to an enhancement of plant growth and total phenolic content. Ind Crop Prod 139:111553
dos Reis AR, de Queiroz Barcelos JP, de Souza Osório CRW et al (2017) A glimpse into the physiological, biochemical and nutritional status of soybean plants under Ni-stress conditions. Environ Exp Bot 144:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2017.10.006
Darandeh N, Hadavi E (2012) Effect of pre-harvest foliar application of citric acid and malic acid on chlorophyll content and post-harvest vase life of Lilium cv. Brunello Front Plant Sci 2. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2011.00106
Dhindsa RS, Plumb-dhindsa P, Thorpe TA (1981) Leaf senescence: correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J Exp Bot 32:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/32.1.93
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(98)00025-9
Farid M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Saeed R, Tauqeer HM, Sallah-Ud-Din R, Azam A, Raza N (2017) Microwave irradiation and citric acid assisted seed germination and phytoextraction of nickel (Ni) by Brassica napus L.: morpho-physiological and biochemical alterations under Ni stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:21050–21064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9751-5
Farid M, Ali S, Saeed R, Rizwan M, Bukhari SAH, Abbasi GH, Hussain A, Ali B, Zamir MSI, Ahmad I (2019) Combined application of citric acid and 5-aminolevulinic acid improved biomass, photosynthesis and gas exchange attributes of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) grown on chromium contaminated soil. Int J Phytoremediation 21:760–767. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2018.1556595
Fatima A, Farid M, Alharby HF et al (2020) Efficacy of fenugreek plant for ascorbic acid assisted phytoextraction of copper (Cu); a detailed study of Cu induced morpho-physiological and biochemical alterations. Chemosphere 251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126424
Firdaus-e-Bareen (2012) Chelate assisted phytoextraction using oilseed brassicas. In: Journal of Water Resource and Protection. pp 289–311
Freitas EV, Nascimento CW, Souza A, Silva FB (2013) Citric acid-assisted phytoextraction of lead: a field experiment. Chemosphere 92:213–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.103
Genchi G, Carocci A, Lauria G, Sinicropi MS, Catalano A (2020) Nickel: Human Health and Environmental Toxicology. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(3):679
Gill RA, Ali B, Yang S, Tong C, Islam F, Gill MB, Mwamba TM, Ali S, Mao B, Liu S, Zhou W (2017) Reduced glutathione mediates pheno-ultrastructure, kinome and transportome in chromium-induced Brassica napus L. Front Plant Sci 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.02037
Guan Q, Wang F, Xu C, Pan N, Lin J, Zhao R, Yang Y, Luo H (2018) Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil based on PMF: a case study in Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Chemosphere 193:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.151
Gupta M, Sharma P, Sarin NB, Sinha AK (2009) Differential response of arsenic stress in two varieties of Brassica juncea L. Chemosphere 74:1201–1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.023
Hasanuzzaman M, Fujita M (2013) Heavy metals in the environment current status, toxic effects on plants and phytoremediation. In: Phytotechnologies Remediation of Environmental Contamination. pp 7–73
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Hossain MS, Mahmud J, Rahman A, Inafuku M, Oku H, Fujita M (2017) Coordinated actions of glyoxalase and antioxidant defense systems in conferring abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Int J Mol Sci 18
Hasanuzzaman M, Alam MM, Nahar K, Mohsin SM, Bhuyan MHMB, Parvin K, Hawrylak-Nowak B, Fujita M (2019a) Silicon-induced antioxidant defense and methylglyoxal detoxification works coordinately in alleviating nickel toxicity in Oryza sativa L. Ecotoxicology 28:261–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-019-02019-z
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Fujita M, et al (2019b) Approaches for enhancing abiotic stress tolerance in plants
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
Helaoui S, Boughattas I, Hattab S, Mkhinini M, Alphonse V, Livet A, Bousserrhine N, Banni M (2020) Physiological, biochemical and transcriptomic responses of Medicago sativa to nickel exposure. Chemosphere. 249:126121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126121
Hossain MS, Abdelrahman M, Tran CD, Nguyen KH, Chu HD, Watanabe Y, Hasanuzzaman M, Mohsin SM, Fujita M, Tran LSP (2020) Insights into acetate-mediated copper homeostasis and antioxidant defense in lentil under excessive copper stress. Environ Pollut 258:113544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113544
Hu L, Zhang Z, Xiang Z, Yang Z (2016) Exogenous application of citric acid ameliorates the adverse effect of heat stress in tall fescue (Lolium arundinaceum). Front Plant Sci 7:179. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00179
Hussain MB, Ali S, Azam A, et al (2013) African journal of agricultural research morphological, physiological and biochemical responses of plants to nickel stress: a review. pdfs.semanticscholar.org 8:1596–1602. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR12.407
Hussain S, Rengel Z, Qaswar M, Amir M, Zafar-ul-Hye M (2019) Arsenic and heavy metal (cadmium, lead, mercury and nickel) contamination in plant-based foods. In: Plant and Human Health, vol 2. Springer, Cham, pp 447–490
J Al Mahmud, Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, et al (2018) Insights into citric acid-induced cadmium tolerance and phytoremediation in Brassica juncea L.: coordinated functions of metal chelation, antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:990–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.045
Jabeen A, Huang X, Aamir M (2015) The challenges of water pollution, threat to public health, flaws of water laws and policies in Pakistan. J Water Resour Prot 07:1516–1526. https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2015.717125
Kabra K, Chaudhary R, Sawhney RL (2008) Solar photocatalytic removal of cu(II), Ni(II), Zn(II) and Pb(II): speciation modeling of metal-citric acid complexes. J Hazard Mater 155:424–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.083
Kanwal U, Ali S, Shakoor MB, Farid M, Hussain S, Yasmeen T, Adrees M, Bharwana SA, Abbas F (2014) EDTA ameliorates phytoextraction of lead and plant growth by reducing morphological and biochemical injuries in Brassica napus L. under lead stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9899–9910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3001-x
Khalid S, Shahid M, Niazi NK, Murtaza B, Bibi I, Dumat C (2017) A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. J Geochem Explor 182:247–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.11.021
Khalid A, Farid M, Zubair M, Rizwan M, Iftikhar U, Ishaq HK, Farid S, Latif U, Hina K, Ali S (2020) Efficacy of Alternanthera bettzickiana to Remediate Copper and Cobalt Contaminated Soil Physiological and Biochemical Alterations. Int J Environ Res 1–13
Khan MR, Khan MM (2010) Effect of varying concentration of nickel and cobalt on the plant growth and yield of chickpea. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 4(6):1036–1046
Kim SH, Lee IS (2010) Comparison of the ability of organic acids and edta to enhance the phytoextraction of metals from a multi-metal contaminated soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84:255–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9888-0
Kumar KV, Patra DD (2012) Alteration in yield and chemical composition of essential oil of Mentha piperita L. plant: effect of fly ash amendments and organic wastes. Ecol Eng 47:237–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.06.019
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) [34] Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol 148:350–382 Academic Press
Limmer M, Burken J (2016) Phytovolatilization of organic contaminants. Environ Sci Technol 50:6632–6643
Liu D, Li S, Islam E, Chen JR, Wu JS, Ye ZQ, Peng DL, Yan WB, Lu KP (2015a) Lead accumulation and tolerance of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) seedlings: applications of phytoremediation. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 16:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1400107
Liu H, Liu YG, Zeng GM, Xie JL, Zheng BH, Tan XF, Wang DF, Sun ZC, Nie J, Jiang ZJ, Gan C, Liu W, Wang SF (2015b) Mitigation mechanism of cd-contaminated soils by different levels of exogenous low-molecular-weight organic acids and Phytolacca americana. RSC Adv 5:45502–45509. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra05700k
Maalik U, Farid M, Zubair M, Ali S, Riwan M, Shafqat M, Ishaq HK (2020) Rice Production, Augmentation, Escalation, and Yield Under Water Stress. In: Agronomic Crops. Springer, Singapore, pp 117–128
Mallhi ZI, Rizwan M, Mansha A, Ali Q, Asim S, Ali S, Hussain A, Alrokayan SH, Khan HA, Alam P, Ahmad P (2019) Citric acid enhances plant growth, photosynthesis, and phytoextraction of lead by alleviating the oxidative stress in castor beans. Plants 8:525. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8110525
Merlot S (2020) Understanding Nickel Responses in Plants: More than Just an Interaction with Iron Homeostasis. Plant Cell Physiol 61(3):443–444
Metzner H, Rau H, Senger H (1965) Untersuchungen zur Synchronisierbarkeit einzelner Pigmentmangel-Mutanten von Chlorella. Planta 65:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384998
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22(5):867–880
Nguyen TXT, Amyot M, Labrecque M (2017) Differential effects of plant root systems on nickel, copper and silver bioavailability in contaminated soil. Chemosphere 168:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.047
Pandey AK, Kumar P, Saxena MJ, Maurya P (2020) Distribution of aromatic plants in the world and their properties. In Feed Addit 89–114. Academic Press
Parlak KU (2016) Effect of nickel on growth and biochemical characteristics of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings. Elsevier 76:1–5
Parmar S, Singh V (2015) Phytoremediation approaches for heavy metal pollution : a review. J Plant Sci Res 2:1–8
Parvin K, Nahar K, Hasanuzzaman M et al (2019) Calcium-mediated growth regulation and abiotic stress tolerance in plants. In: Plant Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Springer International Publishing, pp 291–331
Pinto E, Catalani LH, Lopes NP, di Mascio P, Colepicolo P (2000) Peridinin as the major biological carotenoid quencher of singlet oxygen in marine algae gonyaulax polyedra. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 268:496–500. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2000.2142
Qiang T, Fan G, Yufeng G, Toru I, Takeshi K (2018) Desorption characteristics of Cr(III), Mn(II), and Ni(II) in contaminated soil using citric acid and citric acid-containing wastewater. Soils Found 58:50–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2017.12.001
Rathika R, Khalifa AYZ, Srinivasan P, Praburaman L, Kamala-Kannan S, Selvankumar T, Kim W, Govarthanan M (2020) Effect of citric acid and vermi-wash on growth and metal accumulation of Sorghum bicolor cultivated in lead and nickel contaminated soil. Chemosphere:243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125327
Rawat KS, Kumar R, Singh SK (2020) Distribution of nickel in different agro-climatic zones of Jharkhand, India. Geol Ecol Landscapes 4(1):52–58
Saleem MH, Ali S, Rehman M, et al (2020) Plants jute: a potential candidate for phytoremediation of metals-a review. mdpi.com 9:258. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020258
Sallah-Ud-Din R, Farid M, Saeed R, Ali S, Rizwan M, Tauqeer HM, Bukhari SAH (2017) Citric acid enhanced the antioxidant defense system and chromium uptake by Lemna minor L. grown in hydroponics under Cr stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(21):17669–17678
Sarwar N, Imran M, Shaheen MR, Ishaque W, Kamran MA, Matloob A, Rehim A, Hussain S (2017) Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere 171:710–721
Shah T, Wahid S, Ilyas M, Hasanuzzaman M (2019) Nitric oxide and phytohormones cross-talk during abiotic stresses responses in plants. In: Reactive Oxygen, Nitrogen and Sulfur Species in Plants. Wiley, pp 533–554
Sheetal KR, Singh SD, Anand A, Prasad S (2016) Heavy metal accumulation and effects on growth, biomass and physiological processes in mustard. Indian J Plant Physiol 21:219–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-016-0221-8
Singh R, Gautam N, Mishra A, Gupta R (2011) Heavy metals and living systems: an overview. Indian J Pharm 43:246–253
Srivastava RK, Pandey P, Rajpoot R, Rani A, Dubey RS (2014) Cadmium and lead interactive effects on oxidative stress and antioxidative responses in rice seedlings. Protoplasma 251:1047–1065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0614-3
Syam N, Wardiyati T, Maghfoer MD, Handayanto E, Ibrahim B, Muchdar A (2016) Effect of accumulator plants on growth and nickel accumulation of soybean on metal-contaminated soil. Agric Agric Sci Procedia 9:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aaspro.2016.02.109
Tognacchini A, Rosenkranz T, van der Ent A, Machinet GE, Echevarria G, Puschenreiter M (2020) Nickel phytomining from industrial wastes: Growing nickel hyperaccumulator plants on galvanic sludges. J Environ Manag 254:109798
Van Assche F, Clijsters H (1990) Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant Cell Environ 13:195–206
Wang N, Hu S, Wu D, Wang Y (2013) Effects of CA and EDTA on growth of Chlorophytum comosum in copper- contaminated soil. Shengtai Xuebao/ Acta Ecol Sin 33:631–639. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201112021843
Wang G, Xia X, Yang J, Tariq M, Zhao J, Zhang M, Huang K, Lin K, Zhang W (2020) Exploring the bioavailability of nickel in a soil system: Physiological and histopathological toxicity study to the earthworms (Eisenia fetida). J Hazard Mater 383:121169
Yousaf B, Amina LG et al (2016) The importance of evaluating metal exposure and predicting human health risks in urban-periurban environments influenced by emerging industry. Chemosphere 150:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.007
Yu G, Ma J, Jiang P, et al (2019) The mechanism of plant resistance to heavy metal. In: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. Institute of Physics publishing
Zaheer IE, Ali S, Rizwan M, Farid M, Shakoor MB, Gill RA, Najeeb U, Iqbal N, Ahmad R (2015) Citric acid assisted phytoremediation of copper by Brassica napus L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 120:310–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.06.020
Zhang J, Kirkham MB (1994) Drought-stress-induced changes in activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase in wheat species. Plant Cell Physiol 35:785–791. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a078658
Zhang X, Zhong B, Shafi M, Guo J, Liu C, Guo H, Peng D, Wang Y, Liu D (2018) Effect of EDTA and citric acid on absorption of heavy metals and growth of Moso bamboo. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:18846–18852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2040-0
Zhang H, Zhang LL, Li J et al (2020) Comparative study on the bioaccumulation of lead, cadmium and nickel and their toxic effects on the growth and enzyme defence strategies of a heavy metal accumulator, Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06968-0
Zhu YL, Zayed AM, Qian JH, Souza M, Terry N (1999) Phytoaccumulation of trace elements by wetland plants: II. Water hyacinth. J Environ Qual 28:339–344. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1999.00472425002800010042x
Acknowledgments
The authors are highly thankful to the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan, University of Gujrat, Pakistan, and GC University Faisalabad, Pakistan, for providing laboratory and financial support granting award of project no. HEC/NRPU/8996/2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Significance of research work
Reported results provided hopeful outcomes and sustainable fate of Ni phytoextraction. The present study confirmed the ecotoxicity of Ni in M. piperita and the efficacy of CA amendment to enhance the Ni bioavailability in culture media and to alleviate Ni-induced ecotoxicity. M. piperita significantly accumulate Ni under CA amendment as confirmed from the results.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 29 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khair, K.U., Farid, M., Ashraf, U. et al. Citric acid enhanced phytoextraction of nickel (Ni) and alleviate Mentha piperita (L.) from Ni-induced physiological and biochemical damages. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 27010–27022 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08978-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08978-9