Abstract
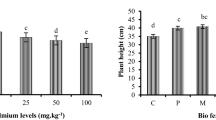
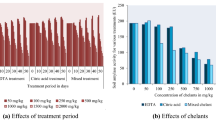
The effect of EDTA and citric acid on accumulation, toxicity of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb), and growth of Moso bamboo was investigated in current experiment. The availability of heavy metals in soil and its uptake by plants has indicated toxicity. The results revealed that EDTA and citric acid has reduced biomass of Moso bamboo but non-significant difference in biomass was observed compared with control. Application of EDTA (10 mmol kg−1) has significantly improved copper (Cu) by 56.5 and 84.9% in roots and above ground parts of plants. Application of EDTA (10 mmol kg−1) has significantly enhanced lead (Pb) by 51.8 and 210.8% in roots and above ground parts of Moso bamboo. Furthermore, treatment of EDTA has significantly improved activities of water-soluble Cd, Cu, and Pb in soil by 98.9, 70.1, and 73.1 times compared with control. In case of contents of diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA)-extractable metals, the treatment of EDTA (10 mmol kg−1) has produced maximum increase of 244.5 mg kg−1 Zn and 157.9 mg kg−1 Pb, respectively. It is concluded that effect of EDTA was superior compared with citric acid for improvement of phytoremediation potential of Moso bamboo.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agricultural Chemistry Committee of China (1983) Conventional methods of soil and agricultural chemistry analysis. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals-concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881
Chen JR, Peng DL, Shafi M, Li S, Wu JS, Ye ZQ, Wang Y, Yan WB, Liu D (2015a) Phytoremediation potential of Moso bamboo ( Phyllostachys pubescens) for zinc and ultrastructure changes under zinc toxicity. Russ J Ecol 46:444–449
Chen JR, Shafi M, Li S, Wang Y, Wu JS, Ye ZQ, Peng DL, Yan WB, Liu D (2015b) Copper induced oxidative stresses, antioxidant responses and phytoremediation potential of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens). Sci Rep 5:100–103
del Dacera DM, Babel S (2006) Use of citric acid for heavy metals extraction from contaminated sewage sludge for land application. Water Sci Technol A J Int Assoc Water Pollut Res 54:129–135
Duarte B, Delgado M, Caçador I (2007) The role of citric acid in cadmium and nickel uptake and translocation, in Halimione portulacoides. Chemosphere 69:836–840
Grčman H, Velikonja-Bolta Š, Vodnik D, Kos B, Leštan D (2001) EDTA enhanced heavy metal phytoextraction: metal accumulation, leaching and toxicity. Plant Soil 235:105–114
Han YL, Zhang LL, Gu JG, Zhao JZ, Fu JJ (2018) Citric acid and EDTA on the growth, photosynthetic properties and heavy metal accumulation of Iris halophila Pall. cultivated in Pb mine tailings. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 128:15–21
Hosseini SS, Lakzian A, Halajnia A (2017) The effect of EDTA and citric acid on soil enzymes activity, substrate induced respiration and Pb availability in a contaminated soil. Majallah-iābvaKhāk 30:2032–2045
Kabra K, Chaudhary R, Sawhney RL (2008) Solar photocatalytic removal of Cu(II), Ni(II), Zn(II) and Pb(II): speciation modeling of metal–citric acid complexes. J Hazard Mater 155:424–432
Kim SH, Lee IS (2010) Comparison of the ability of organic acids and EDTA to enhance the phytoextraction of metals from a multi-metal contaminated soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84:255–259
Lai HY, Chen ZS (2006) The influence of EDTA application on the interactions of cadmium, zinc, and lead and their uptake of rainbow pink (Dianthus chinensis). J Hazard Mater 137:1710–1718
Lee J, Sung K (2014) Effects of chelates on soil microbial properties, plant growth and heavy metal accumulation in plants. Ecol Eng 73:386–394
Li YF, Zhang JJ, Chang SX, Jiang PK, Zhou GM, Fu SL, Yan ER, Wu JS, Lin L (2013) Long-term management effects on soil organic carbon pools and chemical composition in Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) forests in subtropical China. For Ecol Manag 303:121–130
Li TQ, Hu YY, Du XH, Shen CH, Wu JS (2014) Salicylic acid alleviates the adverse effects of salt stress in Torreya grandis cv. Merrillii seedlings by activating photosynthesis and enhancing antioxidant systems. PLoS One 9(10):e109492
Li S, Islam E, Peng DL, Chen JR, Wang Y, Wu JS, Ye ZQ, Yan WB, Lu KP, Liu D (2015) Accumulation and localization of cadmium in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) grown hydroponically. Acta Physiol Plant 37:1–7
Li S, Wang Y, Mahmood Q, Chen JR, Wu JS, Ye ZQ, Peng DL, Yan WB, Kouping Lu KP, Liu D (2017) Cu induced changes of ultrastructure and bioaccumulation in the leaf of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys Pubescens). J Plant Nutr 41:288–296
Li YF, Hu SD, Chen JH, Müller K, Li YC, Fu WJ, Lin ZW, Wang HL (2018) Effects of biochar application in forest ecosystems on soil properties and greenhouse gas emissions: a review. J Soils Sediments 18:546–563
Lim TT, Chui PC, Goh KH (2005) Process evaluation for optimization of EDTA use and recovery for heavy metal removal from a contaminated soil. Chemosphere 58:1031–1040
Liu D, Li S, Islam E, Chen JR, Wu JS, Ye ZQ, Peng DL, Yan WB, Lu KP (2015a) Lead accumulation and tolerance of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) seedlings: applications of phytoremediation. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 16:123–130
Liu H, Liu YG, Zeng GM, Xie J, Zheng BH, Tan XF, Wang DF, Sun ZC, Nie J, Jiang ZJ, Can C, Liu W, Wang SH (2015b) Mitigation mechanism of Cd-contaminated soils by different levels of exogenous low-molecular-weight organic acids with Phytolacca americana. RSC Adv 5:47–49
Ma JF, Shen R, Nagao S, Tanimoto E (2004) Aluminum targets elongating cells by reducing cell wall extensibility in wheat roots. Plant Cell Physiol 45:583–589
Muhammad D, Chen F, Zhao J, Zhang G, Wu F (2009) Comparison of EDTA- and citric acid-enhanced phytoextraction of heavy metals in artificially metal contaminated soil by Typha angustifolia. Int J Phytoremediat 11:558–574
Mühlbachová G (2011) Soil microbial activities and heavy metal mobility in long-term contaminated soils after addition of EDTA and EDDS. Ecol Eng 37:1064–1071
Mühlbachová G, Száková J, Tlustoš P (2012) The heavy metal availability in long-term polluted soils as affected by EDTA and alfalfa meal treatments. Plant Soil Environ 58:551–556
Sciences ER (2015) Lead accumulation and tolerance of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) seedlings: applications of phytoremediation. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 16:123–130
Shen B (2015) Effect of EDTA and citric acid on Houttuynia cordata Thunb in mining soils contaminated heavy metals. Sichuan Agricultural University, Sichuan
Suthar V, Memon KS, Mahmood-Ul-Hassan M (2014) EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of contaminated calcareous soils: heavy metal bioavailability, extractability, and uptake by maize and sesbania. Environ Monit Assess 186:3957–3968
Usman ARA, Almaroai YA, Ahmad M, Vithanage M, Yong SO (2013) Toxicity of synthetic chelators and metal availability in poultry manure amended Cd, Pb and As contaminated agricultural soil. J Hazard Mater 262:1022–1030
Wan XM, Mei L, Chen TB (2016) Cost–benefit calculation of phytoremediation technology for heavy-metal-contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ s563–564:796–802
Wang X, Lin H, Feng Y, Pi Y, Cui Q (2006) Effects of EDTA and citric acid on phytoremediation of cd and Ni contaminated soil. J Agro-Environ Sci 25:1487–1492
Wang N, Shan HU, Dan WU, Wang Y (2013) Effects of CA and EDTA on growth of Chlorophytum comosum in copper-contaminated soil. Acta Ecol Sin 33:631–639
Wu LH, Luo YM, Xing XR, Christie P (2004) EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil with Indian mustard and associated potential leaching risk. Agric Ecosyst Environ 102:307–318
Yan WB, Mahmood Q, Peng DL, Fu WJ, Chen T, Wang Y, Li S, Chen JR, Liu D (2015) The spatial distribution pattern of heavy metals and risk assessment of moso bamboo forest soil around lead-zinc mine in Southeastern China. Soil Tillage Res 153:120–130
Yan WB, Liu D, Peng DL, Mahmood Q, Chen T, Wang Y, Li S, Chen JR (2016) Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in the farmland along mineral product transportation routes in Zhejiang, China. Soil Use Manag 32:338–349
Yang M, Li YF, Li YC, Chang SX, Yue T, Fu WJ, Jiang PK, Zhou GM (2017) Effects of inorganic and organic fertilizers on soil CO2 efflux and labile organic carbon pools in an intensively managed Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) plantation in subtropical China. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 48:332–344
Funding
The study was financially supported through a grant from the Natural Science Foundation of China (31670617), key research and development project of Science Technology Department of Zhejiang province (2015C03020-2), and key research and development project of Science Technology Department of Zhejiang province (2018C03028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Zhong, B., Shafi, M. et al. Effect of EDTA and citric acid on absorption of heavy metals and growth of Moso bamboo. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 18846–18852 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2040-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2040-0