Abstract
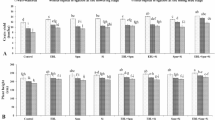
High temperature poses a severe extortion to productivity of many crops like wheat. Therefore, well documented roles of brassinosteroid (BR) and silicon (Si) in terms of abiotic stress tolerance, the current study was designed to evaluate the response of wheat (Triticum aestivum L. Var. PBW-343) to 24-epibrassinolide (EBL) mediated by silicon grown under high temperature stress. At 10- and 12-day stage after sowing, the seedlings were administered Si (0.8 mM) through the sand, and the plants at 20, 22, or 24 days after sowing (DAS) were given EBL (0.01μM) through foliage. Plants were treated to high-temperature stress (35/28 or 40/35 °C), for 24 h with 12-h photoperiod in plant growth chamber at 25- and 26-day stage of growth. High temperatures cause significant reduction in growth performance and photosynthesis-related attributes at 35 days after sowing. However, antioxidant enzymes and proline content also augmented substantially with increasing temperature. BR and Si enhanced antioxidant activity and proline content, which was earlier increased by the high temperature. It is established that interaction of EBL and Si considerably improved the growth features, photosynthetic efficacy, and several biochemical traits under high-temperature stress through elevated antioxidant system and osmoprotectant.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
AbdAllah EF, Hashem A, Alqarawi AA, Wirth S, Egamberdieva D (2017) Calcium application enhances growth and alleviates the damaging effects induced by cd stress in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). J Plant Interact 12:237–243
Agarie S, Uchida H, Agata W, Kubota F, Kaufman PT (1998) Effects of silicon on transpiration and leaf conductance in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Prod Sci 1:89–95
Ahmad P, Latef AAA, Hashem A, AbdAllah EF, Gucel S, Tran LSP (2016) Nitric oxide mitigates salt stress by regulating levels of osmolytes and antioxidant enzymes in chickpea. Front Plant Sci 7:347
Ali B, Hayat S, Hasan SA, Ahmad A (2006) Effect of root applied 28-homobrassinolide on the performance of Lycopersicon esculentum. Sci Hortic 110(3):267–273
Ali B, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2007) 28-Homobrassinolide ameliorates the salt stress in chickpea (Cicer arietinum). Environ Exp Bot 59:33–41
Anon S, Fernandez JA, Franco JA, Torrecillas A, Alarcon JJ, Sanchez-Blanco MJ (2004) Effect of water stress and night temperature preconditioning on water relations and morphological and anatomical changes of Lotus creticus plants. Sci Hortic 101:333–342
Ashraf M, Hafeez M (2004) Thermotolerance of pearl millet and maize at early growth stages: growth and nutrient relations. Biol Plan 48(1):81–86
Bajguz A, Hayat S (2009) Effects of brassinosteroids on the plant responses to environmental stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 47(1):1–8
Barlow K, Christy B, O’Leary G, Riffkin P, Nuttall J (2015) Simulating the impact of extreme heat and frost events on wheat crop production, a review. Field Crop Res 171:109–119
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare IW (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Beauchamp CO, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and assays applicable to acrylamide gels. Ann Biochem 44:276–287
Brunings AM, Datnoff LE, Ma JF, Mitani N, Nagamura Y, Rathinasabapathi B, Kirst M (2009) Differential gene expression of rice in response to silicon and rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Ann Appl Biol 155:161–170
Cao S, Xu Q, Cao Y, Qian K, An K, Zhu Y, Binzeng H, Zhao H, Kuai B (2005) Loss of function mutation in DET2 gene lead to an enhanced resistance to oxidative stress in Arabidopsis. Physiol Plant 123:57–66
Chance B, Maehly AC (1955) Assay of catalase and peroxidases. Methods Enzymol 2:764–775
Chen C-T, Chen T-H, Lo K-F, Chiu C-Y (2004) Effects of proline on copper transport in rice seedlings under excess copper stress. Plant Sci 166(1):103–111
Clouse SD, Sasse JM (1998) Brassinosteroids: essential regulators of plant growth and development. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:427–451
Cosgrove DJ, Bedinger P, Durachko DM (1997) Group I allergens of grass pollen as cell wall-loosening agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:6559–6564
Divi UK, Krishna P (2009) Brassinosteroid: a biotechnological target for enhancing crop yield and stress tolerance. New Biotech 26(3):131–136
Dwivedi RS, Randhawa NS (1974) Evaluation of rapid test for hidden hunger of zinc in plants. Plant Soil 40:445–451
Epstein E (1994) The anomaly of silicon in plant biology. Proc Natl Acad Sci 91(1):11–17
Epstein E (1999) Silicon. Annu Rev Plant Biol 50(1):641–664
Fariduddin Q, Yusuf M, Chalkoo S, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2011) 28-homobrassinolide improves growth and photosynthesis in Cucumis sativus L. through an enhanced antioxidant system in the presence of chilling stress. Photosynthetica 49:55–64
Fariduddin Q, Mir BA, Yusuf M, Ahmad A (2014) 24-epibrassinolide and/or putrescine trigger physiological and biochemical responses for the salt stress mitigation in Cucumis sativus L. Photosynthetica 52(3):464–474
Farooq M, Wahid A, Basra SMA, Islam-ud-Din (2009) Improving water relations and gas exchange with brassinosteroids in rice under drought stress. J Agron Crop Sci 195:262–269
Felner M (2003) Recent progress in brassinosteriod research: hormone perception and signal transduction. In: Hayat S, Ahmad A (eds) Brassinosteriods: Bioactivity and crop productivity. Kluwer Academic Publisher, Dordrecht, pp 46–69
Gong HJ, Chen KM, Chen GC, Wang S, Zhang CL (2003) Effects of silicon on growth of wheat under drought. J Plant Nutr 26(5):1055–1063
Gong H, Zhu X, Wang K, Chen S, Wang C, Zhang C (2005) Silicon alleviates oxidative damage of wheat plants in pots under drought. Plant Sci 169(2):313–321
Gou W, Hou YL, Wang SG, Zhu YG (2005) Effect of silicate on the growth and arsenate uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings in solution culture. Plant Soil 272:173e181
Hasan SA, Hayat S, Ali B, Ahmad A (2008) 28-homobrassinolide protects chickpea (Cicer arietinum) from cadmium toxicity by stimulating antioxidant. Environ Pollut 151:60–66
Hayat S, Yadav S, Wani AS, Irfan M, Ahmad A (2011) Comparative effect of 28-homobrassinolide and 24-epibrassinolide on the growth, carbonic anhydrase activity and photosynthetic efficiency of Lycopersicon esculentum. Photosynthetica 49:397–404
Herde O, Peña-Cortés H, Fuss H, Willmitzer L, Fisahn J (1999) Effects of mechanical wounding, current application and heat treatment on chlorophyll fluorescence and pigment composition in tomato plants. Physiol Plant 105:179–184
Hodson MJ, Evans DE (1995) Aluminium/silicon interactions in higher plants. J Exp Bot 46:161e171
Horiguchi T, Morita S (1987) Mechanism of manganese toxicity and tolerance of plants. Effect of silicon on alleviation of manganese toxicity of barley. J Plant Nutr 10:2299e2310
Khan TA, Fariduddin Q, Yusuf M (2015) Lycopersicon esculentum under low temperature stress: an approach towards enhanced antioxidants and yield by brassinosteroids. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(18):14178–14188
Khan TA, Fariduddin Q, Yusuf M (2017) Low temperature stress: is phytohormones application a remedy? Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:21574–21590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9948-7
Krause GH, Somersalo S (1989) Fluorescence as a tool in photosynthesis research: application in studies of photoinhibition, cold acclimation and freezing stress. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 323:281–293
Liu YJ, Zhao ZG, Di J, Si CXJ, Han LZ (2009) Brassinosteroids alleviate chilling-induced oxidative damage by enhancing antioxidant defense system in suspension cultured cells of Chorispora bungeana. Plant Growth Regul 59:207–214
Liu T, Li Y, Ren J, Zhang C, Kong M, Song X, Zhou J, Hou X (2013) Over-expression of BcFLC1 from non-heading Chinese cabbage enhances cold tolerance in Arabidopsis. Biol Plant 57:262–266
Ma JF (2003) Functions of silicon in higher plants. In: Muller WEG (ed) Silicon biomineralization. Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp 127–147
Ma QQ, Zou Q, Li YH, LI DQ, Wang W (2004) Amelioration of water status and improvement of the antioxidant enzyme activities by exogenous Glycine betaine in water-stressed wheat seedlings. Acta Argon Sinica 4:321–328
Mir BA, Khan TA, Fariduddin Q (2015) 24-epibrassinolide and spermidine modulate photosynthesis and antioxidant systems in Vigna radiata under salt and zinc stress. Inter. J Adv Res 3:592–608
Moldes CA, de Lima Filho OF, Camina JM, Kinachek SG, Molas ML, Tsai SM (2013) Assessment of the effects of silicon on antioxidant enzymes in cotton plants by multivariate analysis. J Agric Food Chem 61:11243–11249
Montoya T, Nomura T, Yokota T, Farrar K, Harrison K, Jones T, Kaneta JGD, Kamiya W, Szekeres M, Bishop GJ (2005) Patterns of dwarf expression and brassinosteroid accumulation in tomato reveal the importance of brassinosteroid synthesis during fruit development. Plant J 42:262–269
Morales D, Rodriguez P, Dell’amico J, Nicolas E, Torrecillas A, Sanchez-Blanco MJ (2003) High temperature preconditioning and thermal shock imposition affects water relations, gas exchange and root hydraulic conductivity in tomato. Biol Plant 47:203–208
Nakaya M, Tsukaya H, Murakami N, Kato M (2002) Brassinosteroids control the proliferation of leaf cells of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 43(2):239–244
Prasad PVV, Boote KJ, Allen LH, Sheehy JE, Thomas JMG (2006) Species, ecotype and cultivar differences in spikelet fertility and harvest index of rice in response to high temperature stress. Field Crop Res 95:398–411
Rehman B, Yusuf M, Khan TA, Fariduddin Q, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2016) Silicon elicited varied physiological and biochemical responses on Indian mustard: a concentration dependent study. Israel J Plant Sci 63:158–166
Romero-Aranda MR, Jurado O, Cuartero J (2006) Silicon alleviates the deleterious salt effect on tomato plant growth by improving plant water status. J Plant Physiol 163:847–855
Sairam RK, Tyagi A (2004) Physiology and molecular biology of salinity stress tolerance in plants. Curr Sci 86:407–421
Shah F, Huang J, Cui K, Nie L, Shah T, Chen C, Wang K (2011) Impact of high-temperature stress on rice plant and its traits related to tolerance. J Agric Sci 149:545–556
Shanmugam S, Kjaer KH, Ottosen CO, Rosenqvist E, Sharma DK, Wollenweber B (2013) The alleviating effect of elevated CO2 on heat stress susceptibility of two wheat (Triticum aestivumL.) cultivars. J Agron Crop Sci 199:340–350
Sharma DK, Andersen SB, Ottosen CO, Rosenqvist E (2014) Wheat cultivars selected for high Fv/Fm under heat stress maintain high photosynthesis, total chlorophyll, stomatal conductance, transpiration and dry matter. Physiol Plant 153:284–298
Silva ON, Lobato AKS, Avila FW, Costa RCL, Oliveira Neto CF, Santos Filho BG, Martins Filho AP, Lemos RP, Pinho JM, Medeiros MBCL, Cardos MS, Andrade IP (2012) Silicon-induced increase in chlorophyll is modulated by leaf water potential in two water-deficient tomato cultivars. Plant Soil Environ 58:481–486
Smith A, Nutrifert (2011) Silicon’s key role in plant growth. Australian Grain, pp 35
Soundararajan P, Sivanesan I, Jana S, Jeong BR (2014) Influence of silicon supplementation on the growth and tolerance to high temperature in Salvia splendens. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 55:271–279
Upadhyaya A, Davis TD, Larsen MH, Walsen RH, Sankhla M (1990) Uniconazole induced thermotolerance in soybean seedling root tissue. Physiol Plant 79:78–84
Upadhyaya A, Davis TD, Sankhla M (1991) Heat shock tolerance and anti-oxidant activity in moth bean seedlings treated with tetayclasis. Plant Growth Regul 10:215–222
Wahid A, Clouse TJ (2007) Expression of dehydrins under heat stress and their relationship with water relations of sugarcane leaves. Biol Plant 51(1):104–109
Wahid A, Gelani S, Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2007) Heat tolerance in plants: an overview. Environ Exp Bot 61(3):199–223
Xia XJ, Wang YJ, Zhou YH, Tao Y, Mao WH, Shi K, Asami T, Chen Z, Yu JQ (2009) Reactive oxygen species are involved in brassinosteroid-induced stress tolerance in cucumber. Plant Physiol 150(2):801–814
Yu JQ, Huang LF, Hu WH, Zhou YH, Mao WH, Ye SF, Nogués S (2004) A role for brassinosteroids in the regulation of photosynthesis in Cucumis sativus. J Exp Bot 55:1135–1143
Yusuf M, Fariduddin Q, Hayat S, Hasan SA, Ahmad A (2011) Protective response of 28-homobrassinolide in cultivars of Triticum aestivum with different levels of nickel. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:68–76
Zhong-hu H, Rajaram S (1994) Differential responses of bread wheat characters to high temperature. Euphytica. 72:197–203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, M., Khan, T.A., Yusuf, M. et al. Silicon-mediated role of 24-epibrassinolide in wheat under high-temperature stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 17163–17172 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04938-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04938-0