Abstract
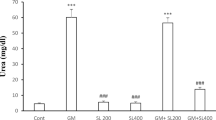
The current study was performed to investigate the nephroprotective efficacy of Spirulina platensis (SP) and the possible benefits of combining SP and ascorbic acid (AA) in protecting against amikacin (AMK)-induced nephrotoxicity in rabbits. Forty-two male New Zealand rabbits were allocated to seven equal groups, receiving (I) normal saline as negative controls, (II) oral SP (500 mg/kg body weight), (III) oral AA (20 mg/kg bw), (IV) intramuscular AMK injection (100 mg/kg bw), (V) AMK plus SP, (VI) AMK plus AA, or (VII) AMK plus SP and AA at the aforementioned doses. The treatments were given once/day for 7 days. Data analysis showed that in comparison to the control group, AMK-intoxicated rabbits showed significant increases (p ≤ 0.05) in serum concentrations of creatinine, uric acid, and urea, as well as renal tissue concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α], malondialdehyde [MDA], and nitric oxide [NO]. Moreover, significant (p ≤ 0.05) reductions in renal glutathione concentration, antioxidant enzymatic activities (catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase), and total antioxidant capacity were noted following AMK intoxication. Treatment by SP ameliorated most of the aforementioned AMK-induced alterations. Although treatment with AA significantly reduced the renal tissue MDA, NO, and TNF-α concentrations, it was not associated with significant ameliorations of AMK-induced changes in the serum concentrations of renal function markers or renal tissue antioxidant parameters. The nephroprotective effects of SP-AA combination were more potent than SP alone in several parameters. In conclusion, SP alone or in combination with AA minimized the nephrotoxic effects of AMK through their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
ascorbic acid
- AMK:
-
amikacin
- CAT:
-
catalase
- GPx:
-
glutathione peroxidase
- GSH:
-
reduced glutathione
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- NO:
-
nitric oxide
- SP :
-
Spirulina platensis
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- TAC:
-
total antioxidant capacity
References
Abdel-Daim MM, El-Ghoneimy A (2015) Synergistic protective effects of ceftriaxone and ascorbic acid against subacute deltamethrin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Ren Fail 37:297–304
Abdel-Daim MM, Ghazy EW (2015) Effects of Nigella sativa oil and ascorbic acid against oxytetracycline-induced hepato-renal toxicity in rabbits. Iran J Basic Med Sci 18:221–227
Abdel-Daim MM, Farouk SM, Madkour FF, Azab SS (2015) Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of Spirulina platensis in comparison to Dunaliella salina in acetic acid-induced rat experimental colitis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 37:126–139
Abdel-Daim M, El-Bialy BE, Rahman HG, Radi AM, Hefny HA, Hassan AM (2016) Antagonistic effects of Spirulina platensis against sub-acute deltamethrin toxicity in mice: biochemical and histopathological studies. Biomed Pharmacother 77:79–85
Abdel-Daim MM, Abushouk AI, Alkhalf MI, Toraih EA, Fawzy MS, Ijaz H, Aleya L, Bungau SG (2018) Antagonistic effects of Spirulina platensis on diazinon-induced hemato-biochemical alterations and oxidative stress in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:27463–27470
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Atasayar S, Gurer-Orhan H, Orhan H, Gurel B, Girgin G, Ozgunes H (2009) Preventive effect of aminoguanidine compared to vitamin E and C on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 61:23–32
Beutler E (1963) Improved method for determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Boscheri A, Weinbrenner C, Botzek B, Reynen K, Kuhlisch E, Strasser RH (2007) Failure of ascorbic acid to prevent contrast-media induced nephropathy in patients with renal dysfunction. Clin Nephrol 68:279–286
Bulut G, Basbugan Y, Ari E, Erten R, Bektas H, Alp HH, Bayram I (2016) Paricalcitol may improve oxidative DNA damage on experimental amikacin-induced nephrotoxicity model. Ren Fail 38:751–758
Chen MF, Yang CM, Su CM, Hu ML (2014) Vitamin C protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and damage without reducing its effectiveness in C57BL/6 mice xenografted with Lewis lung carcinoma. Nutr Cancer 66:1085–1091
Cherng SC, Cheng SN, Tarn A, Chou TC (2007) Anti-inflammatory activity of c-phycocyanin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Life Sci 81:1431–1435
Coulombe JJ, Favreau L (1963) A new simple semimicro method for colorimetric determination of urea. Clin Chem 9:102–108
Cunnane G, FitzGerald O, Beeton C, Cawston TE, Bresnihan B (2001) Early joint erosions and serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase 1, matrix metalloproteinase 3, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 44:2263–2274
Dogan EE, Erkoc R, Ekinci I, Hamdard J, Doner B, Cikrikcioglu MA, Karatoprak C, Coban G, Ozer OF, Kazancioglu R (2017) Protective effect of dexpanthenol against nephrotoxic effect of amikacin: an experimental study. Biomed Pharmacother 89:1409–1414
Frei B, England L, Ames BN (1989) Ascorbate is an outstanding antioxidant in human blood plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci 86:6377–6381
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
Hadjipour N (2011) Histopathological comparison of gentamycin and amikacin nephrotoxicity in rabbits. J Anim Vet Adv 10:1003–1006
Hosseini SM, Khosravi-Darani K, Mozafari MR (2013) Nutritional and medical applications of spirulina microalgae. Mini Rev Med Chem 13:1231–1237
Hwang JH, Chen JC, Yang SY, Wang MF, Liu TC, Chan YC (2011) Expression of COX-2 and NMDA receptor genes at the cochlea and midbrain in salicylate-induced tinnitus. Laryngoscope 121:361–364
Ibrahim AE, Abdel-Daim MM (2015) Modulating effects of Spirulina platensis against tilmicosin-induced cardiotoxicity in mice. Cell J (Yakhteh) 17:137
Jenkins A, Thomson AH, Brown NM, Semple Y, Sluman C, MacGowan A, Lovering AM, Wiffen PJ (2016) Amikacin use and therapeutic drug monitoring in adults: do dose regimens and drug exposures affect either outcome or adverse events? A systematic review. J Antimicrob Chemother 71:2754–2759
Kadi I-E, Dahdouh F (2016) Vitamin C pretreatment protects from nickel-induced acute nephrotoxicity in mice. Arch Ind Hyg Toxicol 67:210–215
Kara A, Cetin H, Oktem F, Metin Ciris I, Altuntas I, Kaya S (2016) Amikacin induced renal damage and the role of the antioxidants on neonatal rats. Ren Fail 38:671–677
Kaynar K, Gul S, Ersoz S, Ozdemir F, Ulusoy H, Ulusoy S (2007) Amikacin-induced nephropathy: is there any protective way? Ren Fail 29:23–27
Koracevic D, Koracevic G, Djordjevic V, Andrejevic S, Cosic V (2001) Method for the measurement of antioxidant activity in human fluids. J Clin Pathol 54:356–361
Krause KM, Serio AW, Kane TR, Connolly LE (2016) Aminoglycosides: an overview. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 6:a027029
Larsen K (1972) Creatinine assay by a reaction-kinetic principle. Clin Chim Acta 41:209–217
Lopez-Novoa JM, Quiros Y, Vicente L, Morales AI, Lopez-Hernandez FJ (2011) New insights into the mechanism of aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity: an integrative point of view. Kidney Int 79:33–45
Moreira MA, Nascimento MA, Bozzo TA, Cintra A, da Silva SM, Dalboni MA, Mouro MG, Higa EM (2014) Ascorbic acid reduces gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats through the control of reactive oxygen species. Clin Nutr (Edinburgh, Scotland) 33:296–301
Nishikimi M, Appaji N, Yagi K (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46:849–854
Padayatty SJ, Katz A, Wang Y, Eck P, Kwon O, Lee J-H, Chen S, Corpe C, Dutta A, Dutta SK (2003) Vitamin C as an antioxidant: evaluation of its role in disease prevention. J Am Coll Nutr 22:18–35
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Palli E, Makris D, Papanikolaou J, Garoufalis G, Tsilioni I, Zygoulis P, Zakynthinos E (2017) The impact of N-acetylcysteine and ascorbic acid in contrast-induced nephropathy in critical care patients: an open-label randomized controlled study. Crit Care (London, England) 21:269
Pham TX, Park YK, Lee JY (2016) Anti-inflammatory effects of Spirulina platensis extract via the modulation of histone deacetylases. Nutrients 8:381
Qasim B, Mohammed NM, Abd AH (2014) The nephroprotective effects of vardenafil against amikacin induced nephrotoxicity in rabbits. Int J Adv Res 2:747–755
Sairio E, Kasanen A, Kangas L, Nieminen AL, Nieminen L (1978) The nephrotoxicity and renal accumulation of amikacin, tobramycin and gentamycin in rats, rabbits and Guinea pigs. Exp Pathol 15:370–375
Sandhu C, Newman DJ, Morgan R, Belli AM, Oliveira D (2002) The role of oxygen free radicals in contrast induced nephrotoxicity. Acad Radiol 9(Suppl 2):S436–S437
Sinanoglu O, Yener AN, Ekici S, Midi A, Aksungar FB (2012) The protective effects of spirulina in cyclophosphamide induced nephrotoxicity and urotoxicity in rats. Urology 80(1392):e1–e6
Soheili M, Khosravi-Darani K (2011) The potential health benefits of algae and micro algae in medicine: a review on Spirulina platensis. Curr Nutr Food Sci 7:279–285
Somchit MN, Mohamed NA, Ahmad Z, Zakaria ZA, Shamsuddin L, Omar-Fauzee M, Kadir AA (2014) Anti-inflammatory and anti-pyretic properties of Spirulina platensis and Spirulina lonar: a comparative study. Pak J Pharm Sci 27:1277–1280
Szczepanik W, Kaczmarek P, Jezowska-Bojczuk M (2004) Oxidative activity of copper(II) complexes with aminoglycoside antibiotics as implication to the toxicity of these drugs. Bioinorg Chem Appl 2:55–68
Talaulikar VS, Manyonda IT (2011) Vitamin C as an antioxidant supplement in women’s health: a myth in need of urgent burial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 157:10–13
Uchiyama M, Mihara M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 86:271–278
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J (2007) Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:44–84
Wang L, Wang X, Wu H, Liu R (2014) Overview on biological activities and molecular characteristics of sulfated polysaccharides from marine green algae in recent years. Mar Drugs 12:4984–5020
Wargo KA, Edwards JD (2014) Aminoglycoside-induced nephrotoxicity. J Pharm Pract 27:573–577
Whitehead TP, Bevan EA, Miano L, Leonardi A (1991) Defects in diagnostic kits for determination of urate in serum. Clin Chem 37:879–881
Yamagishi S-i, Edelstein D, Du X-l, Brownlee M (2001) Hyperglycemia potentiates collagen-induced platelet activation through mitochondrial superoxide overproduction. Diabetes 50:1491–1494
Yazar E, Elmas M, Altunok V, Sivrikaya A, Oztekin E, Birdane YO (2003) Effects of aminoglycoside antibiotics on renal antioxidants, malondialdehyde levels, and some serum biochemical parameters. Can J Vet Res 67:239–240
Yousef M, Salem M, Kamel K, Hassan G, El-Nouty F (2003) Influence of ascorbic acid supplementation on the haematological and clinical biochemistry parameters of male rabbits exposed to aflatoxin B1. J Environ Sci Health B 38:193–209
Yousef JM, Chen G, Hill PA, Nation RL, Li J (2012) Ascorbic acid protects against the nephrotoxicity and apoptosis caused by colistin and affects its pharmacokinetics. J Antimicrob Chemother 67:452–459
Yuan XM, Li W (2003) The iron hypothesis of atherosclerosis and its clinical impact. Ann Med 35:578–591
Yusuf MS, Hassan MA, Abdel-Daim MM, El Nabtiti AS, Ahmed AM, Moawed SA, El-Sayed AK, Cui H (2016) Value added by Spirulina platensis in two different diets on growth performance, gut microbiota, and meat quality of Japanese quails. Vet World 9:1287–1293
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All animal care procedures were performed following the guidelines of the European Communities Council Directive (86/609/EEC) and were approved by the local ethical research committee at Suez Canal University (Ismailia, Egypt).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Daim, M.M., Ahmed, A., Ijaz, H. et al. Influence of Spirulina platensis and ascorbic acid on amikacin-induced nephrotoxicity in rabbits. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 8080–8086 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04249-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04249-4