Abstract
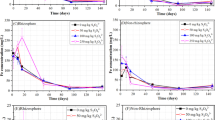
Arsenic (As) and lead (Pb) commonly co-exist with high concentrations in paddy soil mainly due to human activities in south of China. This study investigates the effect of ferrous sulfate (FeSO4) amendment and water management on rice growth and arsenic (As) and lead (Pb) accumulation in rice plants. A paddy soil co-contaminated with As and Pb was chosen for the pot experiment with three FeSO4 levels (0, 0.25, and 1%, on a dry weight basis) and two water managements (flooded, non-flooded). The concentrations of As and Pb in iron plaques and rice plants were determined. Application of FeSO4 and non-flooded conditions significantly accelerated the growth of rice plants. With the addition of FeSO4, iron plaques were significantly promoted and most of the As and Pb were sequestered in the iron plaques. The addition of 0.25% FeSO4 and non-flooded conditions did not significantly change the accumulation of As and Pb in rice grains. The practice also significantly decreased the translocation factor (TF) of As and Pb from roots to above-ground parts which might have been aided by the reduction of As and Pb availability in soil, the preventing effect of rice roots, and the formation of more reduced glutathione (GSH). Flooded conditions decreased the Pb concentration in rice plants, but increased As accumulation. Moreover, rice grew thin and weak and even died under flooded conditions. Overall, an appropriate FeSO4 dose and non-flooded conditions might be feasible for rice cultivation, especially addressing the As issue in the co-contaminated soil. However, further detailed studies to decrease the accumulation of Pb in edible parts and the field application in As and Pb co-contaminated soil are recommended.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arao T, Kawasaki A, Baba K, Mori S, Matsumoto S (2009) Effects of water management on cadmium and arsenic accumulation and dimethylarsinic acid concentrations in Japanese rice. Environ Sci Technol 43(24):9361–9367. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9022738
Ashraf U, Hussain S, Anjum SA, Abbas F, Tanveer M, Noor MA, Tang X (2017) Alterations in growth, oxidative damage, and metal uptake of five aromatic rice cultivars under lead toxicity. Plant Physiol Bioch 115:461–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.04.019
Bakirdere S, Bolucek C, Yaman M (2016) Determination of contamination levels of Pb, Cd, Cu, Ni, and Mn caused by former lead mining gallery. Environ Monit Assess 188(3):132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5134-5
Barla A, Shrivastava A, Majumdar A, Upadhyay MK, Bose S (2017) Heavy metal dispersion in water saturated and water unsaturated soil of Bengal delta region, India. Chemosphere 168:807–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.132
Batty LC, Baker AJM, Wheeler BD, Curtis CD (2000) The effect of pH and plaque on the uptake of Cu and Mn in Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin ex. Steudel. Ann Bot-London 86(3):647–653. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.2000.1191
Beiyuan J, Awad YM, Beckers F, Tsang DC, Ok YS, Rinklebe J (2017) Mobility and phytoavailability of As and Pb in a contaminated soil using pine sawdust biochar under systematic change of redox conditions. Chemosphere 178:110–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.022
Burke JJ, Gamble PE, Hatfield JL, Quisenberry JE (1985) Plant morphological and biochemical responses to field water deficits: I. Responses of glutathione reductase activity and paraquat sensitivity. Plant Physiol 79(2):415–419. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.79.2.415
Buschmann J, Kappeler A, Lindauer U, Kistler D, Berg M, Sigg L (2006) Arsenite and arsenate binding to dissolved humic acids: influence of pH, type of humic acid, and aluminum. Environ Sci Technol 40(19):6015–6020. https://doi.org/10.1021/es061057+
Cheng H, Wang MY, Wong MH, Ye ZH (2014) Does radial oxygen loss and iron plaque formation on roots alter Cd and Pb uptake and distribution in rice plant tissues? Plant Soil 375(1-2):137–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1945-0
Cui YS, Du X, Weng LP, Van Riemsdijk WH (2010) Assessment of in situ immobilization of lead (Pb) and arsenic (as) in contaminated soils with phosphate and iron: solubility and bioaccessibility. Water Air Soil Poll 213(1-4):95–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0370-8
Deiana S, Deiana L, Premoli A, Senette C (2009) Accumulation and mobilization of arsenate by Fe(III) polyions trapped in a Ca-polygalacturonate network. Plant Physiol Bioch 47:615–622
Dixit G, Singh AP, Kumar A, Mishra S, Dwivedi S, Kumar S, Trivedi PK, Pandey V, Tripathi RD (2016) Reduced arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) shoot involves sulfur mediated improved thiol metabolism, antioxidant system and altered arsenic transporters. Plant Physiol Bioch 99:86–96
Dixit S, Hering JG (2003) Comparison of arsenic(V) and arsenic(III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: implications for arsenic mobility. Environ Sci Technol 37(18):4182–4189. https://doi.org/10.1021/es030309t
Duan GL, Hu Y, Liu WJ, Kneer R, Zhao FJ, Zhu YG (2011) Evidence for a role of phytochelatins in regulating arsenic accumulation in rice grain. Environ Exp Bot 71:416–421
Dyer CL, Kopittke PM, Sheldon AR, Menzies NW (2008) Influence of soil moisture content on soil solution composition. Soil Sci Soc Am J 72(2):355. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2007.0124
Fan JL, ZY H, Ziadi N, Xu X (2010) Excessive sulfur supply reduces cadmium accumulation in brown rice (Oryza sativa L.) Environ Pollut 158(2):409–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.08.042
Feng H, Qian Y, Gallagher FJ, MY W, Zhang WG, LZ Y, Zhu QZ, Zhang KW, Liu CJ, Tappero R (2013) Lead accumulation and association with Fe on Typha latifolia root from an urban brownfield site. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20(6):3743–3750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1298-x
Fleming M, Tai YP, Zhuang P, McBride MB (2013) Extractability and bioavailability of Pb and As in historically contaminated orchard soil: effects of compost amendments. Environ Pollut 177:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.02.013
Gao MX, Hu ZY, Wang GD, Xia X (2010) Effect of elemental sulfur supply on cadmium uptake into rice seedlings when cultivated in low and excess cadmium soils. Commun Soil Sci Plan 41(8):990–1003. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103621003646071
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China (AQSIQ) (2008) Soil quality—analysis of total mercury, arsenic and leads contents-atomic fluorescence spectrometry-part 2: analysis of total arsenic contents in soils. GB/T 22105.2–2008 Beijing, China
Gorny J, Billon G, Lesven L, Dumoulin D, Made B, Noiriel C (2015) Arsenic behavior in river sediments under redox gradient: a review. Sci Total Environ 505:423–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.10.011
Gupta DK, Huang HG, Corpas FJ (2013) Lead tolerance in plants: strategies for phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20(4):2150–2161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1485-4
Hansel CM, Fendorf S, Sutton S, Newville M (2001) Characterization of Fe plaque and associated metals on the roots of mine-waste impacted aquatic plants. Environ Sci Technol 35(19):3863–3868. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0105459
Hartley W, Edwards R, Lepp NW (2004) Arsenic and heavy metal mobility in iron oxide-amended contaminated soils as evaluated by short- and long-term leaching tests. Environ Pollut 131(3):495–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.02.017
Hettick BE, Canas-Carrell JE, French AD, Klein DM (2015) Arsenic: a review of the element’s toxicity, plant interactions, and potential methods of remediation. J Agric Food Chem 63(32):7097–7107. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b02487
Hossain MB, Jahiruddin M, Loeppert RH, Panaullah GM, Islam MR, Duxbury JM (2008) The effects of iron plaque and phosphorus on yield and arsenic accumulation in rice. Plant Soil 317:167–176
Hu Y, Huang YZ, Liu YX (2013) Influence of iron plaque on chromium accumulation and translocation in three rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars grown in solution culture. Chem Ecol 30:29–38
Hu ZY, Zhu YG, Li M, Zhang LG, Cao ZH, Smith FA (2007) Sulfur (S)-induced enhancement of iron plaque formation in the rhizosphere reduces arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Environ Pollut 147:387–393
Jackson MB, Armstrong W (1999) Formation of aerenchyma and the processes of plant ventilation in relation to soil flooding and submergence. Plant Biol 1(3):274–287. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.1999.tb00253.x
Jia YF, Demopoulos GP (2005) Adsorption of arsenate onto ferrihydrite from aqueous solution: influence of media (sulfate vs nitrate), added gypsum, and pH alteration. Environ Sci Technol 39:9523–9527
Lee CH, Hsieh YC, Lin TH, Lee DY (2012) Iron plaque formation and its effect on arsenic uptake by different genotypes of paddy rice. Plant Soil 363:231–241
Lee M, Lee K, Lee J, Noh EW, Lee Y (2005) AtPDR12 contributes to lead resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 138(2):827–836. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.058107
Li RY, Stroud JL, Ma JF, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2009) Mitigation of arsenic accumulation in rice with water management and silicon fertilization. Environ Sci Technol 43(10):3778–3783. https://doi.org/10.1021/es803643v
Li YY, Zhao JT, Zhang BW, Liu YJ, XH X, Li YF, Li B, Gao YX, Chai ZF (2016) The influence of iron plaque on the absorption, translocation and transformation of mercury in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings exposed to different mercury species. Plant Soil 398(1-2):87–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2627-x
Liang S, Guan DX, Ren JH, Zhang M, Luo J, Ma LQ (2014) Effect of aging on arsenic and lead fractionation and availability in soils: coupling sequential extractions with diffusive gradients in thin-films technique. J Hazard Mater 273:272–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.03.024
Liang Y, Zhu YG, Xia Y, Li Z, Ma Y (2006) Iron plaque enhances phosphorus uptake by rice (Oryza sativa) growing under varying phosphorus and iron concentrations. Ann Appl Biol 149(3):305–312. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2006.00095.x
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42(3):421–428. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1978.03615995004200030009x
Liu CP, HY Y, Liu CP, Li FB, XH X, Wang Q (2015) Arsenic availability in rice from a mining area: is amorphous iron oxide-bound arsenic a source or sink? Environ Pollut 199:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.01.025
Liu HJ, Zhang JL, Christie P, Zhang FS (2008) Influence of iron plaque on uptake and accumulation of Cd by rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings grown in soil. Sci Total Environ 394(2-3):361–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.02.004
Liu HY, Probst A, Liao BH (2005a) Metal contamination of soils and crops affected by the Chenzhou lead/zinc mine spill (Hunan, China). Sci Total Environ 339(1-3):153–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.07.030
Liu JG, Ma XM, Wang MX, Sun XW (2013) Genotypic differences among rice cultivars in lead accumulation and translocation and the relation with grain Pb levels. Ecotox Environ Safe 90:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.12.007
Liu WJ, Zhu YG, Smith FA (2005b) Effects of iron and manganese plaques on arsenic uptake by rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) grown in solution culture supplied with arsenate and arsenite. Plant Soil 277(1-2):127–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-005-6453-4
Liu WJ, Zhu YG, Smith FA, Smith SE (2004) Do iron plaque and genotypes affect arsenate uptake and translocation by rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) grown in solution culture? J Exp Bot 55(403):1707–1713. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh205
Luo GB (2012) Determination of total arsenic in wastewater and sewage sludge samples by ssing sydride-generation atomic fluorescence spectrometryunder the pptimized analytical conditions. Anal Lett 45(17):2493–2507. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2012.694131
Martinez CE, McBride MB (2001) Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn coprecipitates in Fe oxide formed at different pH: aging effects on metal solubility and extractability by citrate. Environ Toxicol Chem 20(1):122–126. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620200112
Mele E, Donner E, Juhasz AL, Brunetti G, Smith E, Betts AR, Castaldi P, Deiana S, Scheckel KG, Lombi E (2015) In situ fixation of metal(loid)s in contaminated soils: a comparison of conventional, opportunistic, and engineered soil amendments. Environ Sci Technol 49(22):13501–13509. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01356
Moore TJ, Rightmire CM, Vempati RK (2000) Ferrous iron treatment of soils contaminated with arsenic-containing wood-preserving solution. Soil Sediment Contam 9(4):375–405. https://doi.org/10.1080/10588330091134310
Moyer CE, Tappero R, Bais H, Sparks DL (2012) Role of iron plaques in immobilizing arsenic in the rice-root environment. Abstr Pap Am Chem S 244
Norton GJ, Adomako EE, Deacon CM, Carey AM, Price AH, Meharg AA (2013) Effect of organic matter amendment, arsenic amendment and water management regime on rice grain arsenic species. Environ Pollut 177:38–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.01.049
Patra M, Bhowmik N, Bandopadhyay B, Sharma A (2004) Comparison of mercury, lead and arsenic with respect to genotoxic effects on plant systems and the development of genetic tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 52(3):199–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2004.02.009
Rahman MA, Rahman MM, Kadohashi K, Maki T, Hasegawa H (2011) Effect of external iron and arsenic species on chelant-enhanced iron bioavailability and arsenic uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Chemosphere 84(4):439–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.03.046
Reddy CN, Patrick WH (1977) Effect of redox potential and pH on the uptake of cadmium and lead by rice plants. J Environ Qual 6(3):259. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1977.00472425000600030005x
Seyfferth AL, Webb SM, Andrews JC, Fendorf S (2011) Defining the distribution of arsenic species and plant nutrients in rice (Oryza sativa L.) from the root to the grain. Geochimi Cosmochim 75(21):6655–6671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2011.06.029
Shih YH, Lien HL, Yan W, Ok YS (2016) Special issue on thermodynamics and kinetics of emerging contaminants in the environment. Chemosphere 155:257–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.021
Silvetti M, Garau G, Demurtas D, Marceddu S, Deiana S, Castaldi P (2017) Influence of lead in the sorption of arsenate by municipal solid waste composts: metal(loid) retention, desorption and phytotoxicity. Bioresour Technol 225:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.11.057
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568
Somenahally AC, Hollister EB, Yan W, Gentry TJ, Loeppert RH (2011) Water management impacts on arsenic speciation and iron-reducing bacteria in contrasting rice-rhizosphere compartments. Environ Sci Technol 45(19):8328–8335. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2012403
Steinmaus C, Ferreccio C, Acevedo J, Balmes JR, Liaw J, Troncoso P, Dauphiné DC, Nardone A, Smith AH (2016) High risks of lung disease associated with early-life and moderate lifetime arsenic exposure in northern Chile. Toxicol appl pharm 313:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2016.10.006
Syu CH, Lee CH, Jiang PY, Chen MK, Lee DY (2013) Comparison of As sequestration in iron plaque and uptake by different genotypes of rice plants grown in As-contaminated paddy soils. Plant Soil 374:411–422
Tack FM (2017) Watering regime influences Cd concentrations in cultivated spinach. J Environ Manag 186(Pt 2):201–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.05.056
Talukder A, Mahmud S, Shaon S, Tanvir R, Saha M, Imran A, Islam M (2015) Arsenic detoxification by phytoremediation. Int J Basic Clin Pharmacol:822–846. https://doi.org/10.18203/2319-2003.ijbcp20150853
Talukder AS, Meisner CA, Sarkar MA, Islam MS (2011) Effect of water management, tillage options and phosphorus status on arsenic uptake in rice. Ecotox Environ Safe 74(4):834–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.11.004
Talukder AS, Meisner CA, Sarkar MA, Islam MS, Sayre KD, Duxbury JM, Lauren JG (2012) Effect of water management, arsenic and phosphorus levels on rice in a high-arsenic soil-water system: II. Arsenic uptake. Ecotox Environ Safe 80:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.02.020
Tripathi RD, Tripathi P, Dwivedi S, Kumar A, Mishra A, Chauhan PS, Norton GJ, Nautiyal CS (2014) Roles for root iron plaque in sequestration and uptake of heavy metals and metalloids in aquatic and wetland plants. Metallomics 6(10):1789–1800. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4MT00111G
Verbruggen N, Hermans C, Schat H (2009) Mechanisms to cope with arsenic or cadmium excess in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12(3):364–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2009.05.001
Vromman D, Lutts S, Lefèvre I, Somer L, De Vreese O, Šlejkovec Z, Quinet M (2013) Effects of simultaneous arsenic and iron toxicities on rice (Oryza sativa L.) development, yield-related parameters and As and Fe accumulation in relation to As speciation in the grains. Plant Soil 371(1-2):199–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1676-2
Wang SS, Gao B, Li YC, Mosa A, Zimmerman AR, Ma LQ, Harris WG, Migliaccio KW (2015) Manganese oxide-modified biochars: preparation, characterization, and sorption of arsenate and lead. Bioresour Technol 181:13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.044
Warren GP, Alloway BJ (2003) Reduction of arsenic uptake by lettuce with ferrous sulfate applied to contaminated soil. J Environ Qual 32(3):767–772. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2003.7670
Warren GP, Alloway BJ, Lepp NW, Singh B, Bochereau FJM, Penny C (2003) Field trials to assess the uptake of arsenic by vegetables from contaminated soils and soil remediation with iron oxides. Sci Total Environ 311(1-3):19–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00096-2
Wenzel WW, Kirchbaumer N, Prohaska T, Stingeder G, Lombi E, Adriano DC (2001) Arsenic fractionation in soils using an improved sequential extraction procedure. Anal Chim Acta 436(2):309–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(01)00924-2
Wolz S, Fenske RA, Simcox NJ, Palcisko G, Kissel JC (2003) Residential arsenic and lead levels in an agricultural community with a history of lead arsenate use. Environ Res 93(3):293–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-9351(03)00064-1
Wu Z, Ren H, McGrath SP, Wu P, Zhao FJ (2011) Investigating the contribution of the phosphate transport pathway to arsenic accumulation in rice. Plant Physiol 157(1):498–508. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.178921
Xenidis A, Stouraiti C, Papassiopi N (2010) Stabilization of Pb and As in soils by applying combined treatment with phosphates and ferrous iron. J Hazard Mater 177(1-3):929–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.006
Xu XY, McGrath SP, Meharg AA, Zhao FJ (2008) Growing rice aerobically markedly decreases arsenic accumulation. Environ Sci Technol 42:5574–5579
Yadav SK (2010) Heavy metals toxicity in plants: an overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. S Afr J Bot 76(2):167–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2009.10.007
Yamaguchi N, Nakamura T, Dong D, Takahashi Y, Amachi S, Makino T (2011) Arsenic release from flooded paddy soils is influenced by speciation, Eh, pH, and iron dissolution. Chemosphere 83(7):925–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.044
Yamaguchi N, Ohkura T, Takahashi Y, Maejima Y, Arao T (2014) Arsenic distribution and speciation near rice roots influenced by iron plaques and redox conditions of the soil matrix. Environ Sci Technol 48(3):1549–1556. https://doi.org/10.1021/es402739a
Yang JX, Guo QJ, Yang J, Zhou XY, Ren HY, Zhang HZ, RX X, Wang XD, Peters M, Zhu GX, Wei RF, Tian LY, Han XK (2016b) Red mud (RM)-induced enhancement of iron plaque formation reduces arsenic and metal accumulation in two wetland plant species. Int J Phytoremediat 18(3):269–277. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2015.1085830
Yang JX, Liu ZY, Wan XM, Zheng GD, Yang J, Zhang HZ, Guo L, Wang XD, Zhou XY, Guo QJ, RX X, Zhou GD, Peters M, Zhu GX, Wei RF, Tian LY, Han XK (2016a) Interaction between sulfur and lead in toxicity, iron plaque formation and lead accumulation in rice plant. Ecotox Environ Safe 128:206–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.02.021
Yang JX, Zheng GD, Yang J, Wan XM, Song B, Cai W, Guo JM (2017) Phytoaccumulation of heavy metals (Pb, Zn, and cd) by 10 wetland plant species under different hydrological regimes. Ecol Eng 107:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.06.052
Yang QW, Shu WS, Qiu JW, Wang HB, Lan CY (2004) Lead in paddy soils and rice plants and its potential health risk around Lechang Lead/Zinc Mine, Guangdong, China. Environ Int 30(7):883–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2004.02.002
Ye ZH, Baker AJM, Wong MH, Willis AJ (1998) Zinc, lead and cadmium accumulation and tolerance in Typha latifolia as affected by iron plaque on the root surface. Aquat Bot 61(1):55–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3770(98)00057-6
Yu HY, Wang XQ, Li FB, Li B, Liu CP, Wang Q, Lei J (2017) Arsenic mobility and bioavailability in paddy soil under iron compound amendments at different growth stages of rice. Environ Pollut 224:136–147
Yuan ZD, Zhang DN, Wang SF, LY X, Wang KL, Song Y, Xiao F, Jia YF (2016) Effect of hydroquinone-induced iron reduction on the stability of scorodite and arsenic mobilization. Hydrometallurgy 164:228–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2016.06.001
Zhao F, McGrath SP (1994) Extractable sulphate and organic sulphur in soils and their availability to plants. Plant Soil 164(2):243–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010076
Zhao CF, Liu XJ, Lü SH, Zhang FS (2003) Effects of water and fertilization conditions on Fe movement and its uptake by rice (in Chinese). J China Agr Univer 8:74–78
Zhao FJ, Ma JF, Meharg AA, McGrath SP (2009) Arsenic uptake and metabolism in plants. New Phytol 181(4):777–794. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02716.x
Zheng SN, Zhang MK (2011) Effect of moisture regime on the redistribution of heavy metals in paddy soil. J Environ Sci 23(3):434–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60428-7
Zhu YG, Sun GX, Lei M, Teng M, Liu YX, Chen NC, Wang LH, Carey AM, Deacon C, Raab A, Meharg AA, Williams PN (2008) High percentage inorganic arsenic content of mining impacted and nonimpacted Chinese rice. Environ Sci Technol 42(13):5008–5013. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8001103
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0800401), Natural Science foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY16D030001), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (41422107 and 41671312).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Roberto Terzano
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, L., Zhang, S., Duan, D. et al. Effects of ferrous sulfate amendment and water management on rice growth and metal(loid) accumulation in arsenic and lead co-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 8888–8902 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1175-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1175-8