Abstract
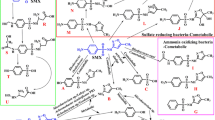
Antibiotic ciprofloxacin is ubiquitous in the environment. However, little is known about ciprofloxacin dissipation by microbial community. The present study investigated the biodegradation potential of ciprofloxacin by mixed culture and the influential factors and depicted the structure of ciprofloxacin-degrading microbial community. Both the original microbiota from drinking water biofilter and the microbiota previously acclimated to high levels of ciprofloxacin could utilize ciprofloxacin as sole carbon and nitrogen sources, while the acclimated microbiota had a much stronger removal capacity. Temperature rise and the presence of carbon or nitrogen sources favored ciprofloxacin biodegradation. Many novel biotransformation products were identified, and four different metabolic pathways for ciprofloxacin were proposed. Bacterial community structure illustrated a profound shift with ciprofloxacin biodegradation. The ciprofloxacin-degrading bacterial community was mainly composed of classes Gammaproteobacteria, Bacteroidia, and Betaproteobacteria. Microorganisms from genera Pseudoxanthomonas, Stenotrophomonas, Phenylobacterium, and Leucobacter might have links with the dissipation of ciprofloxacin. This work can provide some new insights towards ciprofloxacin biodegradation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amorim CL, Moreira IS, Maia AS, Tiritan ME, Castro PML (2014) Biodegradation of ofloxacin, norfloxacin, and ciprofloxacin as single and mixed substrates by Labrys portucalensis F11. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:3181–3190
Baginska E, Haiss A, Kummerer K (2015) Biodegradation screening of chemicals in an artificial matrix simulating the water-sediment interface. Chemosphere 119:1240–1246
Calza P, Medana C, Carbone F, Giancotti V, Baiocchi C (2008) Characterization of intermediate compounds formed upon photoinduced degradation of quinolones by high-performance liquid chromatography/high-resolution multiple-stage mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22:1533–1552
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Conkle JL, White JR (2012) An initial screening of antibiotic effects on microbial respiration in wetland soils. J Environ Sci Health Part A Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 47:1381–1390
Cortes-Lorenzo C, Sanchez-Peinado MD, Oliver-Rodriguez B, Vilchez JL, Gonzalez-Lopez JJ, Rodriguez-Diaz M (2013) Two novel strains within the family Caulobacteraceae capable of degradation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates as pure cultures. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 85:62–65
Dai Y, Li NN, Zhao Q, Xie SG (2015) Bioremediation using Novosphingobium strain DY4 for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-contaminated soil and influence on microbial community structure. Biodegradation 26:161–170
Dorival-Garcia N, Zafra-Gomez A, Navalon A, Gonzalez J, Vilchez JL (2013) Removal of quinolone antibiotics from wastewaters by sorption and biological degradation in laboratory-scale membrane bioreactors. Sci Total Environ 442:317–328
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE, highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998
Fuentes S, Mendez V, Aguila P, Seeger M (2014) Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons, catabolic genes, microbial communities, and applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:4781–4794
Gao LH, Shi YL, Li WH, Liu JM, Cai YQ (2015) Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in urban soil in Beijing and Shanghai, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:11360–11371
Girardi C, Greve J, Lamshoft M, Fetzer I, Miltner A, Schaffer A, Kastner M (2011) Biodegradation of ciprofloxacin in water and soil and its effects on the microbial communities. J Hazard Mater 198:22–30
Gonzalez-Martinez A, Rodriguez-Sanchez A, Martinez-Toledo MV, Garcia-Ruiz MJ, Hontoria E, Osorio-Robles F, Gonzalez-Lopez J (2014) Effect of ciprofloxacin antibiotic on the partial-nitritation process and bacterial community structure of a submerged biofilter. Sci Total Environ 476:276–287
Guan W, Yin M, He T, Xie SG (2015a) Influence of substrate type on microbial community structure in vertical-flow constructed wetland treating polluted river water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16202–16209
Guan XY, Xie YX, Wang JF, Wang J, Liu F (2015b) Electron donors and co-contaminants affect microbial community composition and activity in perchlorate degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:6057–6067
Guo QW, Zhang JX, Wan R, Xie SG (2014) Impacts of carbon sources on simazine biodegradation by Arthrobacter strain SD3-25 in liquid culture and soil microcosm. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 89:1–6
He K, Blaney L (2015) Systematic optimization of an SPE with HPLC-FLD method for fluoroquinolone detection in wastewater. J Hazard Mater 282:SI 96–SI 105
Horemans B, Vandermaesen J, Breugelmans P, Hofkens J, Smolders E, Springael D (2014) The quantity and quality of dissolved organic matter as supplementary carbon source impacts the pesticide-degrading activity of a triple-species bacterial biofilm. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:931–943
Jayamani I, Cupples AM (2015) Stable isotope probing reveals the importance of Comamonas and Pseudomonadaceae in RDX degradation in samples from a navy detonation site. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:10340–10350
Ju F, Zhang T (2014) Novel microbial populations in ambient and mesophilic biogas-producing and phenol-degrading consortia unraveled by high-throughput sequencing. Microb Ecol 68:235–246
Kummerer K, Al-Ahmad A, Mersch-Sundermann V (2000) Biodegradability of some antibiotics, elimination of the genotoxicity and affection of wastewater bacteria in a simple test. Chemosphere 40:701–710
Lei XN, Lu JJ, Liu ZL, Tong YB, Li SM (2015) Concentration and distribution of antibiotics in water-sediment system of Bosten Lake, Xinjiang. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1670–1678
Li B, Zhang T (2010) Biodegradation and adsorption of antibiotics in the activated sludge process. Environ Sci Technol 44:3468–3473
Liao XB, Zhang XJ, Wang J, Li XB, Wang CK, Chen C (2013) Application of conventional and O3-BAC processes to treat organic matter and antibiotic pollutants in a lake in East China. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 13:1470–1477
Liao XB, Chen C, Zhang JX, Dai Y, Zhang XJ, Xie SG (2015a) Dimethylamine biodegradation by mixed culture enriched from drinking water biofilter. Chemosphere 119:935–940
Liao XB, Li BX, Zou RS, Xie SG, Yuan BL (2015b) Antibiotic sulfanilamide biodegradation by acclimated microbial populations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-7133-9
Liu ZG, Sun PZ, Pavlostathis SG, Zhou XF, Zhang YL (2013a) Adsorption, inhibition, and biotransformation of ciprofloxacin under aerobic conditions. Bioresour Technol 144:644–651
Liu ZG, Sun PZ, Pavlostathis SG, Zhou XF, Zhang YL (2013b) Inhibitory effects and biotransformation potential of ciprofloxacin under anoxic/anaerobic conditions. Bioresour Technol 150:28–35
Liu RH, Jiang H, Xu P, Qiao CL, Zhou QX, Yang C (2014) Engineering chlorpyrifos-degrading Stenotrophomonas sp. YC-1 for heavy metal accumulation and enhanced chlorpyrifos degradation. Biodegradation 25:903–910
Ma JW, Lin H, Sun WC, Wang Q, Yu QG, Zhao YH, Fu JR (2014) Soil microbial systems respond differentially to tetracycline, sulfamonomethoxine, and ciprofloxacin entering soil under pot experimental conditions alone and in combination. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:7436–7448
Mutiyar PK, Mittal AK (2014) Risk assessment of antibiotic residues in different water matrices in India: key issues and challenges. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:7723–7736
Nguyen LH, Chong NM (2015) Conditions for supplemental biogenic substrates to enhance activated sludge degradation of xenobiotic. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:8247–8257
Nopcharoenkul W, Netsakulnee P, Pinyakong O (2013) Diesel oil removal by immobilized Pseudoxanthomonas sp. RN402. Biodegradation 24:387–397
Olapade OA, Ronk AJ (2015) Isolation, characterization and community diversity of indigenous putative toluene-degrading bacterial populations with catechol-2,3-dioxygenase genes in contaminated soils. Microb Ecol 69:59–65
Patel V, Cheturvedula S, Madamwar D (2012) Phenanthrene degradation by Pseudoxanthomonas sp. DMVP2 isolated from hydrocarbon contaminated sediment of Amlakhadi Canal, Gujarat, India. J Hazard Mater 201:43–51
Reis I, Almeida CMR, Magalhaes CM, Cochofel J, Guedes P, Basto MCP, Bordalo AA, Mucha AP (2014) Bioremediation potential of microorganisms from a sandy beach affected by a major oil spill. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:3634–3645
Rodgers-Vieira EA, Zhang ZF, Adrion AC, Gold A, Aitken MD (2015) Identification of anthraquinone-degrading bacteria in soil contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:3775–3781
Salam LB, Ilori MO, Amund OO, Numata M, Horisaki T, Nojiri H (2014) Carbazole angular dioxygenation and mineralization by bacteria isolated from hydrocarbon-contaminated tropical African soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9311–9324
Sanuth HA, Yadav A, Fagade OE, Shouche Y (2013) Epsilon-caprolactam utilization by Proteus sp. and Bordetella sp. isolated from solid waste dumpsites in Lagos State, Nigeria, first report. Indian J Microbiol 53:221–226
Su XM, Zhang Q, Hu JX, Hashmi MZ, Ding LX, Shen CF (2015) Enhanced degradation of biphenyl from PCB-contaminated sediments: the impact of extracellular organic matter from Micrococcus luteus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:1989–2000
Thuy HTT, Loan TTC (2014) Degradation of selected pharmaceuticals in coastal wetland water and sediments. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1940
Wan R, Yang YY, Sun WM, Wang Z, Xie SG (2014) Simazine biodegradation and community structures of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in bioaugmented soil: impact of ammonia and nitrate nitrogen sources. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:3175–3181
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Wang WP, Wang LP, Shao ZZ (2010) Diversity and abundance of oil-degrading bacteria and alkane hydroxylase (alkB) genes in the subtropical seawater of Xiamen Island. Microb Ecol 60:429–439
Wang GL, Bi M, Liang B, Jiang JD, Li SP (2011) Pseudoxanthomonas jiangsuensis sp. Nov., a DDT-degrading bacterium isolated from a long-term DDT-polluted soil. Curr Microbiol 62:1760–1766
Wang Z, Yang YY, Sun WM, Xie SG (2014) Biodegradation of nonylphenol by two alphaproteobacterial strains in liquid culture and sediment microcosm. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 92:1–5
Wang Z, Yang YY, Dai Y, Xie SG (2015a) Anaerobic biodegradation of nonylphenol in river sediment under nitrate- or sulfate-reducing conditions and associated bacterial community. J Hazard Mater 286:306–314
Wang Z, Yang YY, He T, Xie SG (2015b) Change of microbial community structure and functional gene abundance in nonylphenol degrading sediment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:3259–3268
Wang Z, Dai Y, Zhao Q, Li NN, Zhou QH, Xie SG (2015c) Nonylphenol biodegradation, functional gene abundance and bacterial community in bioaugmented sediment: effect of external carbon source. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:12083–12091
Wang YS, Zheng XC, Hu QW, Zheng YG (2015d) Degradation of abamectin by newly isolated Stenotrophomonas maltophilia ZJB-14120 and characterization of its abamectin-tolerance mechanism. Res Microbiol 66:408–418
Wu CX, Spongberg AL, Witter JD (2009) Sorption and biodegradation of selected antibiotics in biosolids. J Environ Sci Health Part A Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 44:454–461
Yang YY, Wang Z, Xie SG (2014) Aerobic biodegradation of bisphenol A in river sediment and associated bacterial community change. Sci Total Environ 470:1184–1188
Yang YY, Wang Z, He T, Dai Y, Xie SG (2015) Sediment bacterial communities associated with anaerobic biodegradation of bisphenol A. Microb Ecol 70:97–104
Zhang Z, Lo IMC (2015) Biostimulation of petroleum-hydrocarbon-contaminated marine sediment with co-substrate: involved metabolic process and microbial community. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:5683–5696
Zhang HB, Luo YM, Wu LH, Huang YJ, Christie P (2015a) Residues and potential ecological risks of veterinary antibiotics in manures and composts associated with protected vegetable farming. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:5908–5918
Zhang Y, Hu M, Li PF, Wang X, Meng QJ (2015b) Trichloroethylene removal and bacterial variations in the up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor in response to temperature shifts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:6091–6102
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51508209, 51178117), China Post-Doctoral Funding (No. 145723), Natural Science Foundation of Fujian province (No. 2015J05102), Scientific Research project for Young teachers supported by Education Department of Fujian Province (No. JA15033), the Science Research Foundation of Huaqiao University (No. 15BS105), and Key Project of International Cooperation of Science and Technology of Fujian (No. 2014I0013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
The work has not been published previously and not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerald Thouand
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, X., Li, B., Zou, R. et al. Biodegradation of antibiotic ciprofloxacin: pathways, influential factors, and bacterial community structure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 7911–7918 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6054-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6054-1