Abstract
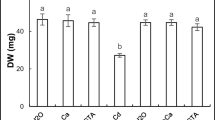
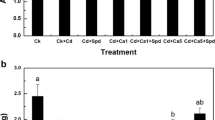
Cadmium (Cd) toxicity in plants leads to serious disturbances of physiological processes, such as inhibition of chlorophyll synthesis, oxidative injury to the plant cells and water and nutrient uptake. Response of Matricaria chamomilla L. to calcium chloride (CaCl2) enrichment in growth medium for reducing Cd toxicity were studied in this study. Hydroponically cultured seedlings were treated with 0, 0.1, 1, and 5 mM CaCl2, under 0, 120, and 180 μM CdCl2 conditions, respectively. The study included measurements pertaining to physiological attributes such as growth parameters, Cd concentration and translocation, oxidative stress, and accumulation of phenolics. Addition of CaCl2 to growth media decreased the Cd concentration, activity of antioxidant enzymes, and reactive oxygen species accumulation in the plants treated with different CdCl2, but increased the growth parameters. Malondialdehyde and total phenolics in shoots and roots were not much affected when plants were treated only with different CaCl2 levels, but it showed a rapid increase when the plants were exposed to 120 and 180 CdCl2 levels. CaCl2 amendment also ameliorated the CdCl2-induced stress by reducing oxidative injury. The beneficial effects of CaCl2 in ameliorating CdCl2 toxicity can be attributed to the Ca-induced reduction of Cd concentration, by reducing the cell-surface negativity and competing for Cd2+ ion influx, activity enhancement of antioxidant enzymes, and biomass accumulation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aidid SB, Okamoto H (1993) Responses of elongation growth rate, turgor pressure and cell wall extensibility of stem cells of Impatiens balsamina to lead, cadmium and zinc. Biometals 6:245–249
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantization of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cakmak I, Horst W (1991) Effect of aluminium on lipid peroxidation, superoxide dismutase, catalase and peroxidase activities in root tip of soybean (Glysine max L.). Plant Physiol 83:463–468
Chance B, Maehly AC (1955) Assay of catalase and peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 2:764–775
Chizzola R, Mitteregger U (2005) Cadmium and zinc interactions in trace element accumulation in chamomile. J Plant Nutr 28:1383–1396
De Vos C, Schat HM, De Waal MA, Vooijs R, Ernst W (1991) Increased to copper-induced damage of the root plasma membrane in copper tolerant Silene cucubalus. Plant Physiol 82:523–528
Elstner EF, Heupel A (1976) Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxylammoniumchloride: a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Anal Biochem 70:616–620
Garnier L, Simon-Plas F, Thuleau P, Agnel JP, Blein JP, Ranjeva R, Montillet JL (2006) Cadmium affects tobacco cells by a series of three waves of reactive oxygen species that contribute to cytotoxicity. Plant Cell Environ 29:1956–1969
Ghnaya T, Slama I, Messedi D, Grignon C, Ghorbel MH, Abdelly C (2007) Cd-induced growth reduction in the halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum is significantly improved by NaCl. J Plant Res 120:309–316
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Hall JL (2002) Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J Exp Bot 53(366):1–11
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif Exp Sta Circ 347:1–32
Hojati M, Modarres-Sanavy SAM, Ghanati F, Panahi M (2011) Hexaconazole induces antioxidant protection and apigenin-7-glucoside accumulation in Matricaria chamomilla plants subjected to drought stress. J Plant Physiol 168:782–791
Ismai MA (2008) Involvement of Ca2+ in alleviation of Cd2+ toxicity in common bean (Phaseolas vulgaris L.). Plants Res J Agric Biol Sci 4(3):203–209
Jana S, Choudhuri MA (1981) Glycolate metabolism of three submerged aquatic angiosperm during aging. Aquat Bot 12:345–354
Kabata-Pendias A (2004) Soil-plant transfer of trace elements—an environmental issue. Geoderma 122:143–149
Kinraide TB (1998) Three mechanisms for the calcium alleviation of mineral toxicities. Plant Physiol 118:513–520
Kováčik J, Tomko J, Bačkor M, Repcák M (2006) Matricaria chamomilla is not a hyperaccumulator, but tolerant to cadmium stress. Plant Growth Regul 50:239–247
Kováčik J, Klejdus B, Hedbavny J, Bačkor M (2009a) Salicylic acid alleviates NaCl-induced changes in the metabolism of Matricaria chamomilla plants. Ecotoxicology 18:544–554
Kováčik J, Grúz J, Hedbavny J, Klejdus B, Strnad M (2009b) Cadmium and nickel uptake are differentially modulated by salicylic acid in Matricaria chamomilla plants. J Agric Food Chem 57:9848–9855
Kováčik J, Klejdus B, Hedbavny J, Štork F, Bačkor M (2009c) Comparison of cadmium and copper effect on phenolic metabolism, mineral nutrients and stress-related parameters in Matricaria chamomilla plants. Plant Soil 320:231–242
Kováčik J, Klejdus B, Kaduková J, Bačkor M (2009d) Physiology of Matricaria chamomilla exposed to nickel excess. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:603–609
Kováčik J, Klejdus B, Hedbavny J, Zon J (2011a) Significance of phenols in cadmium and nickel uptake. J Plant Physiol 168:576–584
Kováčik J, Klejdus B, Štork F, Hedbavny J (2011b) Nitrate deficiency reduces cadmium and nickel accumulation in chamomile plants. J Agric Food Chem 59:5139–5149
Kováčik J, Grúz J, Klejdus B, Štork F, Hedbavny J (2012) Accumulation of metals and selected nutritional parameters in the field-grown chamomile anthodia. Food Chem 131:55–62
Kummerová M, Zezulka Š, Král'ová K, Masarovičová E (2010) Effect of zinc and cadmium on physiological and production characteristics in Matricaria recutita. Biol Plant 54(2):308–314
Lynch JA (1989) Salinity stresses increases cytoplasmic activity in maize root protoplasts. Plant Physiol 90:127–180
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Najeeb U, Jilani G, Ali S, Sarwar M, Xu L, Zhou WJ (2011) Insight into cadmium induced physiological and ultra-structural disorders in Juncus effusus L. and its remediation through exogenous citric acid. J Hazard Mater 186:565–574
Rodríguez-Serrano M, Romero-Puertas MC, Pazmiño DM, Testillano PS, Risueño MC, Del Río LA, Sandalio LM (2009) Cellular response of pea plants to cadmium toxicity: cross talk between reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide, and calcium. Plant Physiol 150:229–243
Schilcher H, Imming P, Goeters S (2005) Pharmacology and toxicology. In: Franke R, Schilcher H (eds) Chamomile industrial profiles. CRCPress, Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, pp 245–263
Sharma SS, Dietz KJ (2006) The significance of amino acids and amino acid-derived molecules in plant response and adaptation to heavy metal stress. J Exp Bot 57:711–726
Singleton V, Orthofer R, Lamuela-Raventós R (1999) Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent. In: Packer L (ed) Oxidants and antioxidants, part A, methods in enzymology, vol 299. Academic, New York, pp 152–178
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D, Hassoun E, Bagchi M (2000) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of chromium and cadmium ions. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 19:201–213
Sudha G, Ravishankar GA (2003) The role of calcium channels in anthocyanin production in callus cultures of Daucus carota. Plant Growth Regul 40:163–169
Wan G, Najeeb U, Jilani G, Naeem MS, Zhou W (2011) Calcium invigorates the cadmium-stressed Brassica napus L. plants by strengthening their photosynthetic system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:1478–1486
Wang CQ, Song H (2009) Calcium protects Trifolium repens L. seedlings against cadmium stress. Plant Cell Rep 28:1341–1349
Xavier V, Fabienne L, Stephanie K, Vitrac X, Larronde F, Krisa S, Decendit A, Deffieux G (2000) Sugar sensing and Ca2+–calmodulin requirement in Vitis vinifera cells producing anthocyanins. Phytochem 53:659–665
Yan F, Schubert S, Mengel K (1992) Effect of low root medium pH on net proton release, root respiration, and root growth of corn (Zea mays L.) and broad bean (Vicia faba L.). Plant Physiol 99:415–421
Yoo KM, Lee CH, Lee H, Moon B, Lee CY (2008) Relative antioxidant and cytoprotective activities of common herbs. Food Chem 106:929–936
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farzadfar, S., Zarinkamar, F., Modarres-Sanavy, S.A.M. et al. Exogenously applied calcium alleviates cadmium toxicity in Matricaria chamomilla L. plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 1413–1422 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1181-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1181-9