Abstract
Purpose
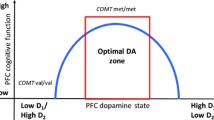
Catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) is a pivotal regulator of brain dopamine function with a region-specific role. COMT is important in dopamine elimination in the prefrontal cortex, whereas dopamine reuptake is the main mechanism for synaptic removal of dopamine in the striatum. We studied whether the functional COMT gene polymorphism (Val158Met) associates with altered dopamine D2 receptor binding characteristics in vivo hypothesizing an effect in the cortex but not in the striatum.
Procedures
Samples of 38 and 45 Finnish healthy subjects scanned previously with PET and the D2/D3 receptor radioligands [11C]FLB457 or [11C]raclopride, respectively, were genotyped for the Val158Met polymorphism.
Results
No significant associations were found between the Val158Met genotype and D2 receptor binding characteristics in the cortex or the striatum as measured with [11C]FLB457 and [11C]raclopride, respectively.
Conclusions
COMT genotype is not related with alterations in baseline D2 receptor availability in vivo in the cortex or the striatum. This information is useful for the interpretation of genetic studies on COMT in neuropsychiatry.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ciliax BJ, Drash GW, Staley JK, Haber S, Mobley CJ, Miller GW et al (1999) Immunocytochemical localization of the dopamine transporter in human brain. J Comp Neurol 409:38–56
Ciliax BJ, Heilman C, Demchyshyn LL, Pristupa ZB, Ince E, Hersch SM et al (1995) The dopamine transporter: immunochemical characterization and localization in brain. J Neurosci 15:1714–1723
Lewis DA, Melchitzky DS, Sesack SR, Whitehead RE, Auh S, Sampson A (2001) Dopamine transporter immunoreactivity in monkey cerebral cortex: regional, laminar, and ultrastructural localization. J Comp Neurol 432:119–136
Sesack SR, Hawrylak VA, Guido MA, Levey AI (1998) Cellular and subcellular localization of the dopamine transporter in rat cortex. Adv Pharmacol 42:171–174
Matsumoto M, Weickert CS, Akil M, Lipska BK, Hyde TM, Herman MM et al (2003) Catechol O-methyltransferase mRNA expression in human and rat brain: evidence for a role in cortical neuronal function. Neuroscience 116:127–137
Mazei MS, Pluto CP, Kirkbride B, Pehek EA (2002) Effects of catecholamine uptake blockers in the caudate-putamen and subregions of the medial prefrontal cortex of the rat. Brain Res 936:58–67
Moron JA, Brockington A, Wise RA, Rocha BA, Hope BT (2002) Dopamine uptake through the norepinephrine transporter in brain regions with low levels of the dopamine transporter: evidence from knock-out mouse lines. J Neurosci 22:389–395
Karoum F, Chrapusta SJ, Egan MF (1994) 3-Methoxytyramine is the major metabolite of released dopamine in the rat frontal cortex: reassessment of the effects of antipsychotics on the dynamics of dopamine release and metabolism in the frontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, and striatum by a simple two pool model. J Neurochem 63:972–979
Gogos JA, Morgan M, Luine V, Santha M, Ogawa S, Pfaff D et al (1998) Catechol-O-methyltransferase-deficient mice exhibit sexually dimorphic changes in catecholamine levels and behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:9991–9996
Huotari M, Garcia-Horsman JA, Karayiorgou M, Gogos JA, Mannisto PT (2004) D-amphetamine responses in catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) disrupted mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 172:1–10
Yavich L, Forsberg MM, Karayiorgou M, Gogos JA, Mannisto PT (2007) Site-specific role of catechol-O-methyltransferase in dopamine overflow within prefrontal cortex and dorsal striatum. J Neurosci 27:10196–10209
Lotta T, Vidgren J, Tilgmann C, Ulmanen I, Melen K, Julkunen I et al (1995) Kinetics of human soluble and membrane-bound catechol O-methyltransferase: a revised mechanism and description of the thermolabile variant of the enzyme. Biochemistry 34:4202–4210
Lachman HM, Papolos DF, Saito T, Yu YM, Szumlanski CL, Weinshilboum RM (1996) Human catechol-O-methyltransferase pharmacogenetics: description of a functional polymorphism and its potential application to neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacogenetics 6:243–250
Chen J, Lipska BK, Halim N, Ma QD, Matsumoto M, Melhem S et al (2004) Functional analysis of genetic variation in catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT): effects on mRNA, protein, and enzyme activity in postmortem human brain. Am J Hum Genet 75:807–821
Slifstein M, Kolachana B, Simpson EH, Tabares P, Cheng B, Duvall M et al (2008) COMT genotype predicts cortical-limbic D1 receptor availability measured with [11C]NNC112 and PET. Mol Psychiatry 13:821–827
Egan MF, Goldberg TE, Kolachana BS, Callicott JH, Mazzanti CM, Straub RE et al (2001) Effect of COMT Val108/158 Met genotype on frontal lobe function and risk for schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:6917–6922
Goldberg TE, Egan MF, Gscheidle T, Coppola R, Weickert T, Kolachana BS et al (2003) Executive subprocesses in working memory: relationship to catechol-O-methyltransferase Val158Met genotype and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:889–896
Mattay VS, Goldberg TE, Fera F, Hariri AR, Tessitore A, Egan MF et al (2003) Catechol O-methyltransferase val158-met genotype and individual variation in the brain response to amphetamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:6186–6191
Kessler RM, Whetsell WO, Ansari MS, Votaw JR, de Paulis T, Clanton JA et al (1993) Identification of extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptors in post mortem human brain with [125I]epidepride. Brain Res 609:237–243
Hall H, Farde L, Halldin C, Hurd YL, Pauli S, Sedvall G (1996) Autoradiographic localization of extrastriatal D2-dopamine receptors in the human brain using [125I]epidepride. Synapse 23:115–123
Lumme V, Aalto S, Ilonen T, Nagren K, Hietala J (2007) Dopamine D2/D3 receptor binding in the anterior cingulate cortex and executive functioning. Psychiatry Res 156:69–74
Craddock N, Owen MJ, O'Donovan MC (2006) The catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) gene as a candidate for psychiatric phenotypes: evidence and lessons. Mol Psychiatry 11:446–458
Monakhov M, Golimbet V, Abramova L, Kaleda V, Karpov V (2008) Association study of three polymorphisms in the dopamine D2 receptor gene and schizophrenia in the Russian population. Schizophr Res 100:302–307
Huuhka K, Anttila S, Huuhka M, Hietala J, Huhtala H, Mononen N et al (2008) Dopamine 2 receptor C957T and catechol-o-methyltransferase Val158Met polymorphisms are associated with treatment response in electroconvulsive therapy. Neurosci Lett 448:79–83
Farde L, Suhara T, Nyberg S, Karlsson P, Nakashima Y, Hietala J et al (1997) A PET-study of [11C]FLB 457 binding to extrastriatal D2-dopamine receptors in healthy subjects and antipsychotic drug-treated patients. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 133:396–404
Sudo Y, Suhara T, Inoue M, Ito H, Suzuki K, Saijo T et al (2001) Reproducibility of [11 C]FLB 457 binding in extrastriatal regions. Nucl Med Commun 22:1215–1221
Vilkman H, Kajander J, Nagren K, Oikonen V, Syvalahti E, Hietala J (2000) Measurement of extrastriatal D2-like receptor binding with [11C]FLB 457—a test–retest analysis. Eur J Nucl Med 27:1666–1673
Pohjalainen T, Rinne JO, Nagren K, Lehikoinen P, Anttila K, Syvalahti EK et al (1998) The A1 allele of the human D2 dopamine receptor gene predicts low D2 receptor availability in healthy volunteers. Mol Psychiatry 3:256–260
Hirvonen M, Laakso A, Nagren K, Rinne JO, Pohjalainen T, Hietala J (2004) C957T polymorphism of the dopamine D2 receptor (DRD2) gene affects striatal DRD2 availability in vivo. Mol Psychiatry 9:1060–1061. Corrigendum in: Mol Psychiatry 2005;10:889
Hirvonen MM, Laakso A, Någren K, Rinne JO, Pohjalainen T, Hietala J (2009) C957T polymorphism of dopamine D2 receptor (DRD2) gene affects striatal DRD2 in vivo availability by changing the receptor affinity. Synapse 63:907–912
Hirvonen MM, Lumme V, Hirvonen J, Pesonen U, Nagren K, Vahlberg T et al (2009) C957T polymorphism of the human dopamine D2 receptor gene predicts extrastriatal dopamine receptor availability in vivo. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:630–636
Hietala J, Syvalahti E, Vuorio K, Nagren K, Lehikoinen P, Ruotsalainen U et al (1994) Striatal D2 dopamine receptor characteristics in neuroleptic-naive schizophrenic patients studied with positron emission tomography. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:116–123
Hietala J, West C, Syvalahti E, Nagren K, Lehikoinen P, Sonninen P et al (1994) Striatal D2 dopamine receptor binding characteristics in vivo in patients with alcohol dependence. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 116:285–290
Hietala J, Nagren K, Lehikoinen P, Ruotsalainen U, Syvalahti E (1999) Measurement of striatal D2 dopamine receptor density and affinity with [11C]-raclopride in vivo: a test-retest analysis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19:210–217
Slifstein M, Laruelle M (2001) Models and methods for derivation of in vivo neuroreceptor parameters with PET and SPECT reversible radiotracers. Nucl Med Biol 28:595–608
Lammertsma AA, Hume SP (1996) Simplified reference tissue model for PET receptor studies. Neuroimage 4:153–158
Innis RB, Cunningham VJ, Delforge J, Fujita M, Gjedde A, Gunn RN et al (2007) Consensus nomenclature for in vivo imaging of reversibly binding radioligands. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1533–1539
Woo JM, Yoon KS, Yu BH (2002) Catechol O-methyltransferase genetic polymorphism in panic disorder. Am J Psychiatry 159:1785–1787
Kaasinen V, Vilkman H, Hietala J, Nagren K, Helenius H, Olsson H et al (2000) Age-related dopamine D2/D3 receptor loss in extrastriatal regions of the human brain. Neurobiol Aging 21:683–688
Pohjalainen T, Rinne JO, Nagren K, Syvalahti E, Hietala J (1998) Sex differences in the striatal dopamine D2 receptor binding characteristics in vivo. Am J Psychiatry 155:768–773
Syvanen AC, Tilgmann C, Rinne J, Ulmanen I (1997) Genetic polymorphism of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT): correlation of genotype with individual variation of S-COMT activity and comparison of the allele frequencies in the normal population and parkinsonian patients in Finland. Pharmacogenetics 7:65–71
Tunbridge EM, Bannerman DM, Sharp T, Harrison PJ (2004) Catechol-o-methyltransferase inhibition improves set-shifting performance and elevates stimulated dopamine release in the rat prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 24:5331–5335
Slifstein M, Kegeles LS, Gonzales R, Frankle WG, Xu X, Laruelle M et al (2007) [11C]NNC 112 selectivity for dopamine D1 and serotonin 5-HT(2A) receptors: a PET study in healthy human subjects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1733–1741
Ekelund J, Slifstein M, Narendran R, Guillin O, Belani H, Guo NN et al (2007) In vivo DA D(1) receptor selectivity of NNC 112 and SCH 23390. Mol Imaging Biol 9:117–125
Laruelle M (2000) Imaging synaptic neurotransmission with in vivo binding competition techniques: a critical review. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:423–451
Olsson H, Halldin C, Farde L (2004) Differentiation of extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptor density and affinity in the human brain using PET. Neuroimage 22:794–803
Montgomery AJ, Asselin MC, Farde L, Grasby PM (2007) Measurement of methylphenidate-induced change in extrastriatal dopamine concentration using [11C]FLB 457 PET. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:369–377
Aalto S, Hirvonen J, Kaasinen V, Hagelberg N, Kajander J, Nagren K et al (2009) The effects of d-amphetamine on extrastriatal dopamine D2/D3 receptors: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled PET study with [11C]FLB 457 in healthy subjects. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36:475–483
Landwehrmeyer B, Mengod G, Palacios JM (1993) Dopamine D3 receptor mRNA and binding sites in human brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 18:187–192
Meador-Woodruff JH, Damask SP, Wang J, Haroutunian V, Davis KL, Watson SJ (1996) Dopamine receptor mRNA expression in human striatum and neocortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 15:17–29
Murray AM, Ryoo HL, Gurevich E, Joyce JN (1994) Localization of dopamine D3 receptors to mesolimbic and D2 receptors to mesostriatal regions of human forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:11271–11275
Suzuki M, Hurd YL, Sokoloff P, Schwartz JC, Sedvall G (1998) D3 dopamine receptor mRNA is widely expressed in the human brain. Brain Res 779:58–74
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the staff of Turku PET Centre (Turku, Finland), the Radiopharmaceutical Chemistry Laboratory of University of Turku (Turku, Finland), and the Department of Pharmacology, Drug Development, and Therapeutics of University of Turku (Turku, Finland). This study has been supported financially by EVO-funding, Turku University Central Hospital (13649 to J.H. and 13464 for J.O.R.) and by personal research grants from Oy H. Lundbeck Ab (to M.M.H.) and from Research and Science Foundation of Farmos (to M.M.H.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirvonen, M.M., Någren, K., Rinne, J.O. et al. COMT Val158Met Genotype Does Not Alter Cortical or Striatal Dopamine D2 Receptor Availability In Vivo . Mol Imaging Biol 12, 192–197 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-009-0257-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-009-0257-5