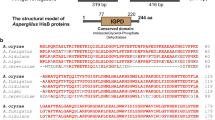
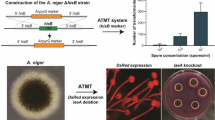
Abstract
Aspergillus oryzae is a filamentous fungus widely used in food industry and as a microbial cell factory for recombinant protein production. Due to the inherent resistance of A. oryzae to common antifungal compounds, genetic transformation of this mold usually requires auxotrophic mutants. In this study, we show that Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation (ATMT) method is very efficient for deletion of the pyrG gene in different Aspergillus oryzae wild-type strains to generate uridine/uracil auxotrophic mutants. Our data indicated that all the obtained uridine/uracil auxotrophic transformants, which are 5- fluoroorotic acid (5-FOA) resistant, exist as the pyrG deletion mutants. Using these auxotrophic mutants and the pyrG selectable marker for genetic transformation via A. tumefaciens, we could get about 1060 transformants per 106 fungal spores. In addition, these A. oryzae mutants were also used successfully for expression of the DsRed fluorescent reporter gene under control of the A. oryzae amyB promoter by the ATMT method, which resulted in obvious red transformants on agar plates. Our work provides a new and effective approach for constructing the uridine/uracil auxotrophic mutants in the importantly industrial fungus A. oryzae. This strategy appears to be applicable to other filamentous fungi to develop similar genetic transformation systems based on auxotrophic/nutritional markers for food-grade recombinant applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arentshorst M, Lagendijk EL, Ram AF (2015) A new vector for efficient gene targeting to the pyrG locus in Aspergillus niger. Fungal Biol Biotechnol 2:2
Bhumiratana A, Flegel TW, Glinsukon T, Somporan W (1980) Isolation and analysis of molds from soy sauce koji in Thailand. Appl Environ Microbiol 39:430–435
Covert S, Kapoor P, Lee M, Briley A, Nairn C (2001) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Fusarium circinatum. Mycol Res 105:259–264
d’Enfert C (1996) Selection of multiple disruption events in Aspergillus fumigatus using the orotidine-5′-decarboxylase gene, pyrG, as a unique transformation marker. Curr Genet 30:76–82
de Boer P, Bronkhof J, Dukismall kje Macedonian K, Kerkman R, Touw H, van den Berg M, Offringa R (2013) Efficient gene targeting in Penicillium chrysogenum using novel Agrobacterium-mediated transformation approaches. Fungal Genet Biol 61:9–14
de Groot MJA, Bundock P, Hooykaas PJJ, Beijersbergen AGM (1998) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of filamentous fungi. Nat Biotechnol 16:840–842
de Ruiter-Jacobs YM, Broekhuijsen M, Unkles SE, Campbell EI, Kinghorn JR, Contreras R, Pouwels PH, van den Hondel CA (1989) A gene transfer system based on the homologous pyrG gene and efficient expression of bacterial genes in Aspergillus oryzae. Curr Genet 16:159–163
Du Y, Xie G, Yang C, Fang B, Chen H (2014) Construction of brewing-wine Aspergillus oryzae pyrG- mutant by pyrG gene deletion and its application in homology transformation. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 46:477–483
Fitzgerald AM, Mudge AM, Gleave AP, Plummer KM (2003) Agrobacterium and PEG-mediated transformation of the phytopathogen Venturia inaequalis. Mycol Res 107:803–810
Frandsen RJ (2011) A guide to binary vectors and strategies for targeted genome modification in fungi using Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. J Microbiol Methods 87:247–262
Frandsen RJ, Frandsen M, Giese H (2012) Targeted gene replacement in fungal pathogens via Agrobacterium tumefaciens- mediated transformation. Methods Mol Biol 835:17–45
Gouka RJ, Hessing JG, Stam H, Musters W, van den Hondel CA (1995) A novel strategy for the isolation of defined pyrG mutants and the development of a site-specific integration system for Aspergillus awamori. Curr Genet 27:536–540
Gouka RJ, Gerk C, Hooykaas PJ, Bundock P, Musters W, Verrips CT, de Groot MJ (1999) Transformation of Aspergillus awamori by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated homologous recombination. Nat Biotechnol 17:598–601
Grant SG, Jessee J, Bloom FR, Hanahan D (1990) Differential plasmid rescue from transgenic mouse DNAs into Escherichia coli methylation-restriction mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4645–4649
Kanamasa S, Yamaoka K, Kawaguchi T, Sumitani J, Arai M (2003) Transformation of Aspergillus aculeatus using the drug resistance gene of Aspergillus oryzae and the pyrG gene of Aspergillus nidulans. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:2661–2663
Kitamoto K (2015) Cell biology of the Koji mold Aspergillus oryzae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 79:863–869
Kunitake E, Tani S, Sumitani J, Kawaguchi T (2011) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Aspergillus aculeatus for insertional mutagenesis. AMB Expr 1:46
Kwon MJ, Arentshorst M, Fiedler M, de Groen FL, Punt PJ, Meyer V, Ram AF (2014) Molecular genetic analysis of vesicular transport in Aspergillus niger reveals partial conservation of the molecular mechanism of exocytosis in fungi. Microbiology 160:316–329
Lazo GR, Stein PA, Ludwig RA (1991) A DNA transformation-competent Arabidopsis genomic library in Agrobacterium. Nat Biotechnol 9:963–967
Lee LY, Gelvin SB (2008) T-DNA binary vectors and systems. Plant Physiol 146:325–332
Liu Z, Friesen TL (2012) Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-mediated transformation in filamentous fungal pathogens. Methods Mol Biol 835:365–375
Machida M, Asai K, Sano M, Tanaka T, Kumagai T, Terai G, Kusumoto K, Arima T, Akita O, Kashiwagi Y, Abe K, Gomi K, Horiuchi H, Kitamoto K, Kobayashi T, Takeuchi M, Denning DW, Galagan JE, Nierman WC, Yu J, Archer DB, Bennett JW, Bhatnagar D, Cleveland TE, Fedorova ND, Gotoh O, Horikawa H, Hosoyama A, Ichinomiya M, Igarashi R, Iwashita K, Juvvadi PR, Kato M, Kato Y, Kin T, Kokubun A, Maeda H, Maeyama N, Maruyama J, Nagasaki H, Nakajima T, Oda K, Okada K, Paulsen I, Sakamoto K, Sawano T, Takahashi M, Takase K, Terabayashi Y, Wortman JR, Yamada O, Yamagata Y, Anazawa H, Hata Y, Koide Y, Komori T, Koyama Y, Minetoki T, Suharnan S, Tanaka A, Isono K, Kuhara S, Ogasawara N, Kikuchi H (2005) Genome sequencing and analysis of Aspergillus oryzae. Nature 438:1157–1161
Machida M, Yamada O, Gomi K (2008) Genomics of Aspergillus oryzae: learning from the history of Koji mold and exploration of its future. DNA Res 15:173–183
Maruyama J, Kitamoto K (2008) Multiple gene disruptions by marker recycling with highly efficient gene-targeting background (∆ligD) in Aspergillus oryzae. Biotechnol Lett 30:1811–1817
Mattern IE, Unkles S, Kinghorn JR, Pouwels PH, van den Hondel CA (1987) Transformation of Aspergillus oryzae using the A. niger pyrG gene. Mol Gen Genet 210:460–461
Michielse CB, Arentshorst M, Ram AF, van den Hondel CA (2005a) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation leads to improved gene replacement efficiency in Aspergillus awamori. Fungal Genet Biol 42:9–19
Michielse CB, Hooykaas PJ, van den Hondel CA, Ram AF (2005b) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation as a tool for functional genomics in fungi. Curr Genet 48:1–17
Michielse CB, Hooykaas PJ, van den Hondel CA, Ram AF (2008) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of the filamentous fungus Aspergillus awamori. Nat Protoc 3:1671–1678
Mizutani O, Kudo Y, Saito A, Matsuura T, Inoue H, Abe K, Gomi K (2008) A defect of LigD (human Lig4 homolog) for nonhomologous end joining significantly improves efficiency of gene-targeting in Aspergillus oryzae. Fungal Genet Biol 45:878–889
Mullins ED, Chen X, Romaine P, Raina R, Geiser DM, Kang S (2001) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Fusarium oxysporum: an efficient tool for insertional mutagenesis and gene transfer. Phytopathology 91:173–180
Nguyen LA (2015) Health-promoting microbes in traditional Vietnamese fermented foods: a review. Food Sci Hum Wellness 4:147–161
Nguyen KT, Ho QN, Pham TH, Phan TN, Tran VT (2016) The construction and use of versatile binary vectors carrying pyrG auxotrophic marker and fluorescent reporter genes for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Aspergillus oryzae. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32:204
Oakley BR, Rinehart JE, Mitchell BL, Oakley CE, Carmona C, Gray GL, May GS (1987) Cloning, mapping and molecular analysis of the pyrG (orotidine-5′-phosphate decarboxylase) gene of Aspergillus nidulans. Gene 61:385–399
Shin D, Jeong D (2015) Korean traditional fermented soybean products: Jang. J Ethn Foods 2:2–7
Silva R, Aguiar TQ, Domingues L (2015) Blockage of the pyrimidine biosynthetic pathway affects riboflavin production in Ashbya gossypii. J Biotechnol 193:37–40
Skory CD, Horng JS, Pestka JJ, Linz JE (1990) Transformation of Aspergillus parasiticus with a homologous gene (pyrG) involved in pyrimidine biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:3315–3320
Sugui JA, Chang YC, Kwon-Chung KJ (2005) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Aspergillus fumigatus: an efficient tool for insertional mutagenesis and targeted gene disruption. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1798–1802
Suzuki S, Tada S, Fukuoka M, Taketani H, Tsukakoshi Y, Matsushita M, Oda K, Kusumoto K, Kashiwagi Y, Sugiyama M (2009) A novel transformation system using a bleomycin resistance marker with chemosensitizers for Aspergillus oryzae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 383:42–47
Talhinhas P, Muthumeenakshi S, Neves-Martins J, Oliveira H, Sreenivasaprasad S (2008) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and insertional mutagenesis in Colletotrichum acutatum for investigating varied pathogenicity lifestyles. Mol Biotechnol 39:57–67
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tran VT, Braus-Stromeyer SA, Kusch H, Reusche M, Kaever A, Kuhn A, Valerius O, Landesfeind M, Asshauer K, Tech M, Hoff K, Pena-Centeno T, Stanke M, Lipka V, Braus GH (2014) Verticillium transcription activator of adhesion Vta2 suppresses microsclerotia formation and is required for systemic infection of plant roots. New Phytol 202:565–581
van Hartingsveldt W, Mattern IE, van Zeijl CM, Pouwels PH, van den Hondel CA (1987) Development of a homologous transformation system for Aspergillus niger based on the pyrG gene. Mol Gen Genet 206:71–75
Weidner G, d’Enfert C, Koch A, Mol PC, Brakhage AA (1998) Development of a homologous transformation system for the human pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus based on the pyrG gene encoding orotidine 5′-monophosphate decarboxylase. Curr Genet 33:378–385
Wicklow DT, McAlpin CE, Yeoh QL (2007) Diversity of Aspergillus oryzae genotypes (RFLP) isolated from traditional soy sauce production within Malaysia and Southeast Asia. Mycoscience 48:373–380
Woloshuk CP, Seip ER, Payne GA, Adkins CR (1989) Genetic transformation system for the aflatoxin-producing fungus Aspergillus flavus. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:86–90
Xu Y (1990) Advances in the soy sauce industry in China. J Ferment Bioeng 70:434–439
Zhong Y, Yu H, Wang X, Lu Y, Wang T (2011) Towards a novel efficient T-DNA-based mutagenesis and screening system using green fluorescent protein as a vital reporter in the industrially important fungus Trichoderma reesei. Mol Biol Rep 38:4145–4151
Zhu Y, Tramper J (2013) Koji—where East meets West in fermentation. Biotechnol Adv 31:1448–1457
Zhu L, Maruyama J, Kitamoto K (2013) Further enhanced production of heterologous proteins by double-gene disruption (∆AosedD ∆Aovps10) in a hyper-producing mutant of Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:6347–6357
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Jun-ichi Maruyama (The University of Tokyo, Japan) for kindly providing the A. oryzae AUT1-PlD strain and Prof. Dr. Ursula Kües (Georg-August-University Göttingen, Germany) for helpful comments to improve the manuscript. We are grateful to Prof. Dr. Tuan-Nghia Phan (VNU University of Science, Hanoi, Vietnam) for his valuable support and inspiration. We thank the members of the Genomics Unit, National Key Laboratory of Enzyme and Protein Technology (VNU University of Science, Hanoi, Vietnam) for their helpful discussions and technical assistance. This work was funded by the National Foundation for Science and Technology Development of Vietnam (NAFOSTED) under grant 106-NN.04-2014.75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, K.T., Ho, Q.N., Do, L.T.B.X. et al. A new and efficient approach for construction of uridine/uracil auxotrophic mutants in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae using Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33, 107 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2275-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2275-9