Abstract
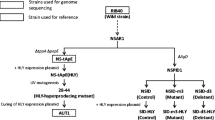
The filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae is used as one of the most favored hosts for heterologous protein production due to its ability to secrete large amounts of proteins into the culture medium. We previously generated a hyper-producing mutant strain of A. oryzae, AUT1, which produced 3.2- and 2.6-fold higher levels of bovine chymosin (CHY) and human lysozyme (HLY), respectively, compared with the wild-type strain. However, further enhancement of heterologous protein production by multiple gene disruption is difficult because of the low gene-targeting efficiency in strain AUT1. Here, we disrupted the ligD gene, which is involved in nonhomologous recombination, and the pyrG gene to create uridine/uracil auxotrophy in strain AUT1, to generate a hyper-producing mutant applicable to pyrG marker recycling with highly efficient gene targeting. We generated single and double disruptants of the tripeptidyl peptidase gene AosedD and vacuolar sorting receptor gene Aovps10 in the hyper-producing mutant background, and found that all disruptants showed significant increases in heterologous protein production. Particularly, double disruption of the Aovps10 and AosedD genes increased the production levels of CHY and HLY by 1.6- and 2.1-fold, respectively, compared with the parental strain. Thus, we successfully generated a fungal host for further enhancing the heterologous protein production ability by combining mutational and molecular breeding techniques.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleißner A, Dersch P (2010) Expression and export: recombinant protein production systems for Aspergillus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:1255–1270
Higuchi Y, Shoji JY, Arioka M, Kitamoto K (2009) Endocytosis is crucial for cell polarity and apical membrane recycling in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae. Eukaryot Cell 8:37–46
Holkeri H, Makarow M (1998) Different degradation pathways for heterologous glycoproteins in yeast. FEBS Lett 429:162–166
Hong E, Davidson AR, Kaiser CA (1996) A pathway for targeting soluble misfolded proteins to the yeast vacuole. J Cell Biol 135:623–633
Idiris A, Tohda H, Sasaki M, Okada K, Kumagai H, Giga-Hama Y, Takegawa K (2009) Enhanced protein secretion from multiprotease-deficient fission yeast by modification of its vacuolar protein sorting pathway. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:667–677
Ito K, Asakura T, Morita Y, Nakajima K, Koizumi A, Shimizu-Ibuka A, Masuda K, Ishiguro M, Terada T, Maruyama J, Kitamoto K, Misaka T, Abe K (2007) Microbial production of sensory-active miraculin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 360:407–411
Jin FJ, Watanabe T, Juvvadi PR, Maruyama J, Arioka M, Kitamoto K (2007) Double disruption of the proteinase genes, tppA and pepE, increases the production level of human lysozyme by Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:1059–1068
Kimura S, Maruyama J, Takeuchi M, Kitamoto K (2008) Monitoring global gene expression of proteases and improvement of human lysozyme production in the nptB gene disruptant of Aspergillus oryzae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72:499–505
Kitamoto K (2002) Molecular biology of the Koji molds. Adv Appl Microbiol 51:129–153
Kubodera T, Yamashita N, Nishimura A (2000) Pyrithiamine resistance gene (ptrA) of Aspergillus oryzae: cloning, characterization and application as a dominant selectable marker for transformation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:1416–1421
Machida M, Asai K, Sano M, Tanaka T, Kumagai T, Terai G, Kusumoto K, Arima T, Akita O, Kashiwagi Y, Abe K, Gomi K, Horiuchi H, Kitamoto K, Kobayashi T, Takeuchi M, Denning DW, Galagan JE, Nierman WC, Yu J, Archer DB, Bennett JW, Bhatnagar D, Cleveland TE, Fedorova ND, Gotoh O, Horikawa H, Hosoyama A, Ichinomiya M, Igarashi R, Iwashita K, Juvvadi PR, Kato M, Kato Y, Kin T, Kokubun A, Maeda H, Maeyama N, Maruyama J, Nagasaki H, Nakajima T, Oda K, Okada K, Paulsen I, Sakamoto K, Sawano T, Takahashi M, Takase K, Terabayashi Y, Wortman JR, Yamada O, Yamagata Y, Anazawa H, Hata Y, Koide Y, Komori T, Koyama Y, Minetoki T, Suharnan S, Tanaka A, Isono K, Kuhara S, Ogasawara N, Kikuchi H (2005) Genome sequencing and analysis of Aspergillus oryzae. Nature 438:1157–1161
Maruyama J, Kitamoto K (2008) Multiple gene disruptions by marker recycling with highly efficient gene-targeting background (ΔligD) in Aspergillus oryzae. Biotechnol Lett 30:1811–1817
Maruyama J, Kitamoto K (2011) Targeted gene disruption in koji mold Aspergillus oryzae. Methods Mol Biol 765:447–456
Nakajima K, Asakura T, Maruyama J, Morita Y, Oike H, Shimizu-Ibuka A, Misaka T, Sorimachi H, Arai S, Kitamoto K, Abe K (2006) Extracellular production of neoculin, a sweet-tasting heterodimeric protein with taste-modifying activity, by Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3716–3723
Nemoto T, Watanabe T, Mizogami Y, Maruyama J, Kitamoto K (2009) Isolation of Aspergillus oryzae mutants for heterologous protein production from a double proteinase gene disruptant. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:1105–1114
Ohno A, Maruyama J, Nemoto T, Arioka M, Kitamoto K (2011) A carrier fusion significantly induces unfolded protein response in heterologous protein production by Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:1197–1206
Tsuchiya K, Tada S, Gomi K, Kitamoto K, Kumagai C, Jigami Y, Tamura G (1992) High-level expression of the synthetic human lysozyme gene in Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:109–114
Tsuchiya K, Nagashima T, Yamamoto Y, Gomi K, Kitamoto K, Kumagai C, Tamura G (1994) High-level secretion of calf chymosin using a glucoamylase-prochymosin fusion gene in Aspergillus oryzae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58:895–899
Yoon J, Aishan T, Maruyama J, Kitamoto K (2010a) Enhanced production and secretion of heterologous proteins by the filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae via disruption of vacuolar protein sorting receptor gene Aovps10. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:5718–5727
Yoon J, Maruyama J, Kitamoto K (2010b) Disruption of ten protease genes in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae highly improves production of heterologous proteins. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:747–759
Zhang B, Chang A, Kjeldsen TB, Arvan P (2001) Intracellular retention of newly synthesized insulin in yeast is caused by endoproteolytic processing in the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol 153:1187–1198
Zhu L, Nemoto T, Yoon J, Maruyama J, Kitamoto K (2012) Improved heterologous protein production by a tripeptidyl peptidase gene (AosedD) disruptant of the filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae. J Gen Appl Microbiol 58:199–209
Acknowledgments
We thank Toshiko Tanaka for help with the experiments. This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (S) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 248 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, L., Maruyama, Ji. & Kitamoto, K. Further enhanced production of heterologous proteins by double-gene disruption (ΔAosedD ΔAovps10) in a hyper-producing mutant of Aspergillus oryzae . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 6347–6357 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4795-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4795-z