Abstract
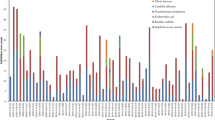
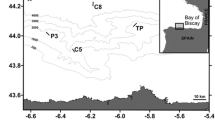
Bacteria associated with eight field-collected and five cultured soft corals of Briareum sp., Sinularia sp., Sarcophyton sp., Nephtheidae sp., and Lobophytum sp. were screened for their abilities in producing antimicrobial metabolites. Field-collected coral samples were collected from Nanwan Bay in southern Taiwan. Cultured corals were collected from the cultivating tank at National Museum of Marine Biology and Aquarium. A total of 1,526 and 1,138 culturable, heterotrophic bacteria were isolated from wild and cultured corals, respectively; seawater requirement and antimicrobial activity were then assessed. There is no significant difference between the ratio of seawater-requiring bacteria on the wild and cultured corals. The ratio of antibiotic-producing bacteria within the seawater-requiring bacteria did not differ between the corals. Nineteen bacterial strains that showed high antimicrobial activity were selected for 16S rDNA sequencing. Three strains could be assigned at the family level (Rhodobacteraceae). The remaining 16 strains belong to eight genera: Marinobacterium (2 strains), Pseudoalteromonas (1), Vibrio (5), Enterovibrio (1), Tateyamaria (1), Labrenzia (2), and Pseudovibrio (4). The crude extract from bacteria strains CGH2XX was found to have high cytotoxicity against the cancer cell line HL-60 (IC50 = 0.94 μg/ml) and CCRF-CEM (IC50 = 1.19 μg/ml). Our results demonstrate that the marine bacteria from corals have great potential in the discovery of useful medical molecules.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Bentis C, Kaufman L, Golubic S (2000) Endolithic fungi in reef-building corals (Order: Scleractinia) are common, cosmopolitan, and potentially pathogenic. Biol Bull 198:254–260
Bourne D, Iida Y, Uthicke S, Smith-Keune C (2008) Changes in coral-associated microbial communities during a bleaching event. ISME J 2:350–363
Burgess JG, Jordan EM, Bregu M, Mearns-Spragg A, Boyd KG (1999) Microbial antagonism: a neglected avenue of natural products research. J Biotechnol 70:27–32
Chen YH, Lu MC, Chang YC, Hwang TL, Wang WH, Weng CF, Kuo J, Sung PJ (2012) Pseudoalteromone A: a novel bioactive ubiquinone from a marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. CGH2XX (Pseudoalteromonadaceae). Tetrahedron Lett 53:1675–1677
Chimetto LA, Brocchi M, Thompson CC, Martins RC, Ramos HR, Thompson FL (2008) Vibrios dominate as culturable nitrogen-fixing bacteria of the Brazilian coral Mussismilia hispida. Syst Appl Microbiol 31:312–319
Chiou SF, Kuo J, Wongd TY, Fan TY, Tew KS, Liu JK (2010) Analysis of the coral associated bacterial community structures in healthy and diseased corals from off-shore of southern Taiwan. J Environ Sci Health B 45:408–415
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2009) The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D141–D145
Dharmaraj S, Sumantha A (2009) Bioactive potential of Streptomyces associated with marine sponges. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1971–1979
Ferris MJ, Muyzer G, Ward DM (1996) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiles of 16S rRNA-defined populations inhabiting a hot spring microbial mat community. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:340–346
Hong K, Gao A-H, Xie Q-Y, Gao HG, Zhuang L, Lin H-P, Yu H-P, Li J, Yao X-S, Goodfellow M, Ruan J-S (2009a) Actinomycetes for marine drug discovery isolated from mangrove soils and plants in China. Mar Drugs 7:24–44
Hong MJ, Yu YT, Chen CA, Chiang PW, Tang SL (2009b) Influence of species specificity and other factors on bacteria associated with the coral Stylophora pistillata in Taiwan. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7797–7806
Ivanitskaia LP, Singal EM, Bibikova MV, Vostrov SN (1978) Directed isolation of Micromonospora generic cultures on a selective medium with gentamycin. Antibiotiki 23:690–692
Jensen PR, Fenical W (1995) The relative abundance and seawater requirements of gram-positive bacteria in near-shore tropical marine samples. Microb Ecol 29:249–257
Jensen PR, Gontang E, Mafnas C, Mincer TJ, Fenical W (2005) Culturable marine actinomycete diversity from tropical Pacific Ocean sediments. Environ Microbiol 7:1039–1048
Kellogg CA (2004) Tropical archaea: diversity associated with the surface microlayer of corals. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 273:81–88
Kennedy J, Baker P, Piper C, Cotter PD, Walsh M, Mooij MJ, Bourke MB, Rea MC, O’Connor PM, Ross RP, Hill C, O’Gara F, Marchesi JR, Dobson ADW (2008) Isolation and analysis of bacteria with antimicrobial activities from the marine sponge Haliclona simulans collected from Irish waters. Mar Biotechnol 11:384–396
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Koren O, Rosenberg E (2008) Bacteria associated with the bleached and cave coral Oculina patagonica. Microb Ecol 55:523–529
Kushmaro A, Rosenberg E, Fine F, Ben-Haim Y, Loya Y (1998) Effect of temperature on bleaching of the coral Oculina patagonica by Vibrio AK-1. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 171:131–137
Lampert Y, Kelman D, Dubinsky Z, Nitzan Y, Hill RT (2006) Diversity of culturable bacteria in the mucus of the Red Sea coral Fungia scutaria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 58:99–108
Lampert Y, Kelman D, Nitzan Y, Dubinsky Z, Behar A, Hill RT (2008) Phylogenetic diversity of bacteria associated with the mucus of Red Sea corals. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 64:187–198
Li Z (2009) Advances in narine microbial symbionts in the China Sea and related pharmaceutical metabolites. Mar Drugs 7:113–129
Littman RA, Willis BL, Pfeffer C, Bourne DG (2009) Diversities of coral-associated bacteria differ with location, but not species, for three Acroporid corals on the Great Barrier Reef. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 68:152–163
Lombo F, Velasco A, Castro A, de la Calle F, Brana AF, Sanchez-Puelles JM, Mendez C, Salas JA (2006) Deciphering the biosynthesis pathway of the antitumor thiocoraline from a marine actinomycete and its expression in two Streptomyces species. Chem Bio Chem 7:366–376
Long RA, Azam F (2001) Antagonistic interactions among marine pelagic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4975–4983
Lu M-C, Du Y-C, Chuu J–J, Hwang S-L, Hsieh P-C, Hung C-S, Chang F-R, Wu Y-C (2009) Active extracts of wild fruiting bodies of Antrodia camphorata (EEAC) induce leukemia HL 60 cells apoptosis partially through histone hypoacetylation and synergistically promote anticancer effect of trichostatin A. Arch Toxicol 83:121–129
Luna GM, Biavasco F, Danovaro R (2007) Bacteria associated with the rapid tissue necrosis of stony corals. Environ Microbiol 9:1851–1857
Mincer TJ, Jensen PR, Kauffman CA, Fenical W (2002) Widespread and persistent populations of a major new marine actinomycete taxon in ocean sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5005–5011
Nikaido H (1996) Multidrug efflux pumps of gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol 178:5853–5859
Nissimov J, Rosenberg E, Munn CB (2009) Antimicrobial properties of resident coral mucus bacteria of Oculina patagonica. FEMS Microbiol Lett 292:210–215
Nithyanand P, Thenmozhi R, Rathna J, Pandian SK (2010) Inhibition of Streptococcus pyogenes biofilm formation by coral-associated actinomycetes. Curr Microbiol 60:454–460
Nithyanand P, Manju S, Karutha Pandian S (2011) Phylogenetic characterization of culturable actinomycetes associated with the mucus of the coral Acropora digitifera from Gulf of Mannar. FEMS Microbiol Lett 314:112–118
Penesyan A, Marshall-Jones Z, Holmstrom C, Kjelleberg S, Egan S (2009) Antimicrobial activity observed among cultured marine epiphytic bacteria reflects their potential as a source of new drugs. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 69:113–124
Radjasa OK, Wises J, Sabdono A, Imhoff JF (2008) Corals as source of bacteria with antimicrobial activity. J Coast Dev 11:121–130
Reshef L, Koren O, Loya Y, Zilber-Rosenberg I, Rosenberg E (2006) The coral probiotic hypothesis. Environ Microbiol 8:2068–2073
Ritchie KB (2006) Regulation of microbial populations by coral surface mucus and mucus-associated bacteria. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 322:1–14
Rohwer F, Breitbart M, Jara J, Azam F, Knowlton N (2001) Diversity of bacteria associated with the Caribbean coral Montastraea franksi. Coral Reefs 20:85–91
Rohwer F, Seguritan V, Azam F, Knowlton N (2002) Diversity and distribution of coral-associated bacteria. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 243:1–10
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Shnit-Orland M, Kushmaro A (2009) Coral mucus-associated bacteria: a possible first line of defense. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 67:371–380
Stern NJ, Svetoch EA, Eruslanov BV, Perelygin VV, Mitsevich EV, Mitsevich IP, Pokhilenko VD, Levchuk VP, Svetoch OE, Seal BS (2006) Isolation of a Lactobacillus salivarius strain and purification of Its bacteriocin, which is inhibitory to Campylobacter jejuni in the chicken gastrointestinal system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:3111–3116
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Wegley L, Edwards R, Rodriguez-Brito B, Liu H, Rohwer F (2007) Metagenomic analysis of the microbial community associated with the coral Porites astreoides. Environ Microbiol 9:2707–2719
Wilson GS, Raftos DA, Corrigan SL, Nair SV (2010) Diversity and antimicrobial activities of surface-attached marine bacteria from Sydney Harbour, Australia. Microbiol Res 165:300–311
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by intramural funding from the National Museum of Marine Biology and Aquarium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, YH., Kuo, J., Sung, PJ. et al. Isolation of marine bacteria with antimicrobial activities from cultured and field-collected soft corals. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28, 3269–3279 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1138-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1138-7