Abstract
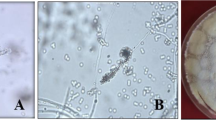
A survey for natural entomopathogenic fungi of two spotted spider mite (Tetranychus urticae) adults was made in Erzurum, Turkey, during the period 2006. Tetranychus urticae (65.8%) infected with a strain of the fungus Cladosporium cladosporioides were found. Thirteen isolates of C. cladosporioides were assessed against T. urticae, in a single dose (8 × 106 conidia ml −1), laboratory bioassay on bean leaflets. The total mortality percentage caused by C. cladosporioides isolates varied from 50.95 to 74.76% and LT50 values ranged from 2.34 to 3.90 days. The results revealed that isolates of C. cladosporioides were effective against two spotted spider mite. This is the first record of natural infection of T. urticae by C. cladosporioides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Baky NF (2000) Cladosporium spp. an entomopathogenic fungus for controlling whiteflies and aphids in Egypt. Pak J Biol Sci 3:1662–1667
Abdel-Baky NF, Abdel-Salam AH (2003) Natural incidence of Cladosporium spp. as a bio-control agent against whiteflies and aphids in Egypt. J Appl Entomol 127:228–235. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0418.2003.00662.x
Abdel-Baky NF, Arafat NS, Abdel-Salam AH (1998) Three Cladosporium spp. as promising biological control candidates for controlling whiteflies (Bemisia spp.) in Egypt. Pak J Biol Sci 1:188–195
Aghajanzadeh S, Mallik B, Chandrashekar SC (2006) Bioefficacy of six isolates of Hirsutella thompsonii Fisher against citrus rust mite, Phyllocoptruta oleivora Ashmead (Acari: Eriophyidae) and two spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae). Pak J Biol Sci 9:871–875
Alves SB, Rossi LS, Lopes RB, Tamai MA, Pereira RM (2002) Beauveria bassiana yeast on agar medium and its pathogenicity against Diatraea saccharalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) and Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). J Invertebr Pathol 81:70–77. doi:10.1016/S0022-2011(02)00147-7
Anonymous (2002) Plant protection handbook. Publication of Ministry of Agricultural and Rural Affairs, Publication No: 352, İzmir, Turkey, 536 pp (in Turkish)
Berón CM, Diaz BM (2005) Pathogenicity of hyphomycetous fungi against Cyclocephala signaticollis. Biocontrol 50:143–150. doi:10.1007/s10526-004-0586-x
Butt TM, Jackson C, Magan N (2001) Introduction—fungal biological control agents: progress, problems and potential. In: Butt TM, Jackson C, Magan N (eds) Fungi as biocontrol agents: progress problems and potential. CABI, New York, pp 1–8
Cabrera RI, Garcia A, Otero-Colina G, Almaguel L, Ginarte A (2005) Hirsutella nodulosa and other fungus species associated to the rice tarsonemid mite Steneotarsonemus spinki (Acari: Tarsonemidae) in Cuba. Folia Entomol Mex 44:115–121
Chandler D, Davidson G, Pell JK, Ball BV, Shaw K, Sunderland KD (2000) Fungal biocontrol of acari. Biocontrol Sci Technol 10:357–384. doi:10.1080/09583150050114972
Chandler D, Davidson G, Jacobson RJ (2005) Laboratory and glasshouse evaluation of entomopathogenic fungi against the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae), on tomato, Lycopersicon esculentum. Biocontrol Sci Technol 15:37–54. doi:10.1080/09583150410001720617
Dick GL, Buschman LL (1995) Seasonal occurrence of a fungal pathogen, Neozygites adjarica (Entomophthorales: Neozygitaceae), infecting Banks grass mites, Oligonychus pratensis, and two-spotted spider mites, Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae), in field corn. J Kans Entomol Soc 68:425–436
Eken C, Demirci E (1997) Use of fungi in biological control. Ataturk Univ J Fac Agric 28:138–152 (in Turkish)
Ellis MB (1971) Dematiaceous hyphomycetes. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew, Surrey
Gardner WA, Oetting RD, Storey GK (1982) Susceptibility of the twospotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch, to the fungal pathogen Hirsutella thompsonii Fisher. Fla Entomol 65:458–465. doi:10.2307/3494680
Hajek AE, Leger RJ (1994) Interactions between fungal pathogens and insects hosts. Annu Rev Entomol 39:293–322. doi:10.1146/annurev.en.39.010194.001453
Inglis GD, Goettel MS, Butt TM, Strasser H (2001) Use of hyphomycetous fungi for managing insect pests. In: Butt TM, Jackson C, Magan N (eds) Fungi as biocontrol agents: progress problems and potential. CABI, New York, pp 23–69
Irigaray FJSC, Marco-Mancebón V, Pérez-Moreno I (2003) The entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana and its compatibility with triflumuron: effects on the twospotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae. Biol Control 26:168–173. doi:10.1016/S1049-9644(02)00123-8
Lagowska B (1995) The biological control perspective of scale insects (Homoptera, Coccinea) on ornamental plants in glasshouses. Wiadomosci Entomol 14:5–10
Mietkiewski R, Balazy S, Van Der Geest LPS (1993) Observations on a mycosis of spider mites (Acari: Tetranychidae) caused by Neozygites floridana in Poland. J Invertebr Pathol 61:317–319. doi:10.1006/jipa.1993.1059
Nauen R, Stumpf N, Elbert A, Zebitz CPW, Kraus W (2001) Acaricide toxicity and resistance in larvae of different strains of Tetranychus urticae and Panonychus ulmi (Acari: Tetranychidae). Pest Manag Sci 57:253–261. doi:10.1002/ps.280
Özbek H, Hayat R (2003) Cereal, vegetable, fodder and ındustrial crop pests. Publications of Ataturk University, Faculty of Agriculture Publication No: 340, Erzurum, Turkey, 320 pp (in Turkish)
Pan WY, Chen SL, Lian JH, Qiu HZ, Lan G (1989) A preliminary report on control of Hemiberlesia pitysophila using Cladosporium cladosporioides. For Pest Dis 3:22–23
Perea AEI, Rojas ME, Pineda VYA (2003) Evaluation of different media for isolation of Trialeurodes vaporariorum (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) molds. Rev Colomb Entomol 29:13–19
Rojas T, Pons N, Arnal E (1998) Cladosporium herbarum on whiteflies (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae), in Venezuela. Bol Entomol Venez 13:57–65
Tamai MA, Alves SB, Neves PJ (1999) Pathogenicity of Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. against Tetranychus urticae Koch. Sci Agric 56:285–288. doi:10.1590/S0103-90161999000200004
Thumar RK, Kapadia MN (1994) Ovicidal control of Aleurolobus barodensis (Maskell) and its suppression by the entomophagous fungus. Indian Sugar 44:501–502
Ulusoy MR, Ulgenturk S (2003) The natural enemies of whiteflies (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) in southern Anatolia. Zool Middle East 28:119–124
Van der Geest LPS, Elliot SL, Breeuwer JAJ, Beerling EAM (2000) Diseases of mites. Exp Appl Acarol 24:497–560. doi:10.1023/A:1026518418163
Van der Geest LPS, de Moraes GJ, Navia D, Tanzini MR (2002) New records of pathogenic fungi in mites (Arachnida: Acari) from Brazil. Neotrop Entomol 31:493–495. doi:10.1590/S1519-566X2002000300025
Zhang ZQ (2003) Mites of greenhouses: identification, biology and control. CABI, New York, p 240
Acknowledgments
We wish to express our cordial thanks to Dr. A. Eşitken (Department of Horticulture) for his valuable comments on statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eken, C., Hayat, R. Preliminary evaluation of Cladosporium cladosporioides (Fresen.) de Vries in laboratory conditions, as a potential candidate for biocontrol of Tetranychus urticae Koch. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25, 489–492 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9914-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9914-0