Summary
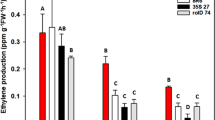
Canola, Brassica napus cv. Westar, was transformed to express a bacterial 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase (EC 4.1.99.4) gene under the transcriptional control of (a) the constitutive and strong 35S promoter from cauliflower mosaic virus, (b) the root-specific promoter of the rolD gene within the T-DNA from the Ri plasmid of Agrobacterium rhizogenes, and (c) the promoter for the pathogenesis-related prb-1b gene from tobacco. Following the growth of transformed and non-transformed canola plants in the presence of 0–200 mM NaCl, the fresh and dry weights of plants, leaf protein concentration, and leaf chlorophyll contents were measured. The data suggest that the presence of ACC deaminase provides the transgenic canola lines with tolerance to the inhibitory effects of salt stress, compared to the non-transformed canola plants, with the rolD transformants being the most effective. The improved salt tolerance of these transgenic plants is likely the consequence of the decreased synthesis of stress ethylene. This data is consistent with previous studies with transgenic tomato plants expressing bacterial ACC deaminase which showed that lowering ethylene levels partially protected plants against growth inhibition by metals, phytopathogens and flooding.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACC:
-
1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate
References
Apse M.P., Aharon G.S., Snedden W.S., Blumwald E., 1999 Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter in Arabidopsis Science 285:1256–1258
Burd G.I., Dixon D.G., Glick B.R., 1998 A plant growth promoting bacterium that decreases nickel toxicity in plant seedlings Applied and Environmental Microbiology 64:3663–3668
Burd G.I., Dixon D.G., Glick B.R., 2000 Plant growth-promoting bacteria that decrease heavy met al toxicity in plants Canadian Journal of Microbiology 46:237–245
Campbell C.R., Plank C.O., 1998 Preparation of plant tissue for laboratory analysis. In Y.P. Karla, ed. Handbook of Reference Methods for Plant Analysis CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 37–49,ISBN: 1574441248
Christopher L.S., Byrd A.D., Benzion G., Altschuler M.A., Hildebrand D., Hunt A.G 1987 Design and construction of a versatile system for the expression of foreign genes in plants Gene 61:1–11
Cushman J.C., Bohnert H.J., 2000 Genomic approaches to plant stress tolerance Current Opinions in Plant Biology 3:117–124
Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D.R., 1980 Broad host range cloning system for Gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America 177:7347–7351
Elmayan T., Tepfer M., 1995 Evaluation in tobacco of the organ specificity and strength of the rolD promoter, domain A of the 35S promoter and the 35S2 promoter Transgenic Research 4:388–396
Eyal Y., Sagee O., Fluhr R., 1992 Dark-induced accumulation of a basic pathogenesis-related (PR-1) transcript and a light requirement for its induction by ethylene Plant Molecular Biology 19:589–599
Frommer W.B., Ludewig U., Rentsch D., 1999 Taking transgenic plants with a pinch of salt Science 285:1222–1223
Glick B.R., 1995 The enhancement of plant growth by free-living bacteria Canadian Journal of Microbiology 41:109–117
Glick B.R., Karaturovic D.M., Newell P.C., 1995 A novel procedure for rapid isolation of plant growth promoting pseudomonads Canadian Journal of Microbiology 41:533–536
Glick B.R., Liu C., Ghosh S., Dumbroff E.B., 1997 The effect of the plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida GR12-2 on the development of canola seedlings subjected to various stresses Soil Biology and Biochemistry 29:1233–1239
Glick B.R., Penrose D.M., Li J., 1998 A model for the lowering of plant ethylene concentrations by plant growth-promoting bacteria Journal of Theoretical Biology 190:63–68
Glick B.R., Patten C.L., Holguin G., Penrose D.M., 1999 Biochemical and Genetic Mechanisms Used by Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria, Imperial College Press, London, ISBN 1860941524
Grichko V.P., Filby B., Glick B.R., 2000 Increased ability of transgenic plants expressing the bacterial enzyme ACC deaminase to accumulate Cd, Co, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn Journal of Biotechnology 81:45–53
Grichko V.P., Glick B.R., 2001a Amelioration of flooding stress by ACC deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting bacteria. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 39:11–17
Grichko V.P., Glick B.R., 2001b Flooding tolerance of transgenic tomato plants expressing the bacterial enzyme ACC deaminase controlled by the 35S, rolD or PRB-1b promoter Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 39:19–25
Hiscox J.D., Israelstman G.F., 1979 A method for the extraction of chlorophyll from leaf tissue without maceration Canadian Journal of Botany 57:1332–1334
Honma M., Shimomura T., 1978 Metabolism of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid Agricultural and Biological Chemistry 42:1825–1831
Hyodo H., 1991 Stress/wound ethylene. In: Mattoo A.K., Suttle J.C., eds. The Plant Hormone Ethylene, CRC Press. Boca Raton. pp. 65–80 ISBN 0849345669
Jacobson C.B., Pasternak J.J., Glick B.R., 1994 Partial purification and characterization of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase from the plant growth promoting rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida GR12–2 Canadian Journal of Microbiology 40:1019–1025
Karuna Stree B., Chadalavanda S.V., Rajendrakumar A., Reddy R., 2000 Aldose reductase in rice (Oryza sativa L.): stress response and developmental specificity Plant Science 160:149–157
Kasuga M., Liu Q., Miura S., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Shinozaki K., 1999 Improving plant drought, salt, and freezing tolerance by gene transfer of a single stress-inducible transcription factor Nature Biotechnology 17:287–291
Leary J.J., Brigati D.J., Ward D.C., 1983 Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labelled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America 80:4045–4049
Lund S.T., Stall R.E., Klee H.J., 1998 Ethylene regulates the susceptible response to pathogen infection in tomayo Plant Cell 10:371–382
Mayak S., Tirosh T., Glick B.R., 2004a Plant growth-promoting bacteria that confer resistance to water stress in tomato and pepper Plant Science 166:525–530
Mayak S., Tirosh T., Glick B.R., 2004b Plant growth-promoting bacteria that confer resistance in tomato to salt stress Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 42:565–572
Moloney M., Walker J.M., Sharma K.K., 1989 High efficiency transformation of Brassica napus using Agrobacterium vectors Plant Cell Reports 8:238–242
Nie L., Shah S., Rashid A., Burd G.I., Dixon D.G., Glick B.R., 2002 Phytoremediation of arsenate contaminated soil by transgenic canola and the plant growth-promoting bacterium Enterobacter cloacae CAL2 Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 40:355–361
Patten C.L., Glick B.R., 2002 The role of bacterial indoleacetic acid in the development of the host plant root system Applied and Environmental Microbiology 68:3795–3801
Penrose D.M., Glick B.R., 2003 Methods for isolating and characterizing ACC deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria Physiologia Plantarum 118: 10–15
Penrose D.M., Moffatt B.A., Glick B.R., 2001 Determination of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) to assess the effects of ACC deaminase-containing bacteria on roots of canola seedlings Canadian Journal of Microbiology 47:77–80
Robison M.M., Shah S., Tamot B., Pauls K.P., Moffatt B.A., Glick B.R., 2001 Reduced symptoms of Verticillium wilt in transgenic tomato expressing a bacterial ACC deaminase Molecular Plant Pathology 2:135–145
Sambrook J., Fritsch E.F., Maniatis T., 1989 Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, ISBN 0879695773
Schardl C.L., Byrd A.D., Benzion G., Altschuler M.A., Hildebrand D.F., Hunt A.G., 1987 Design and construction of a versatile system for the expression of foreign genes in plants Gene 61:1–11
Shah S., Li J., Moffatt B.A., Glick B.R., 1998 Isolation and characterization of ACC deaminase genes from two different plant growth promoting rhizobacteria Canadian Journal of Microbiology 44:833–843
Shi H., Ishitani M., Kim C., Zhu J.-K., 2000 The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America 97:6896–6901
Stearns J.C., Glick B.R., 2003 Transgenic plants with altered ethylene biosynthesis or perception Biotechnology Advances 21:193–210
Stearns, J.C., Shah, S., Dixon, D.G., Greenberg, B.M. & Glick, B.R. 2005 Tolerance of transgenic canola expressing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase to growth inhibition by nickel. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, in press
Tabaei-Aghdaei S.R., Harrison P., Pearce R.S., 2000 Expression of dehydration-stress genes in the crowns of wheatgrass species (Lophopyrum elongatum (host) A. Love and Agropyron desertorum (Fisch Ex Link Schult.) having contrasting acclimation to salt, cold and drought Plant, Cell and Environment 23:561–571
Tamot B.K., Pauls K.P., Glick B.R., 2003 Regulation of expression of the prb-1b/ACC deaminase gene by UV-B in transgenic tomatoes Journal of Plant Biochemistry and Biotechnology 12:25–29
Wang C., Knill E., Glick B.R., Défago G., 2000 Effect of transferring 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) deaminase genes into Pseudomonas fluorescens strain CHA0 and its gacA derivative CHA96 on their growth-promoting and disease-suppressive capacities Canadian Journal of Microbiology 46:898–907
Watson B., Currie T.C., Gordon M.P., Chilton M.D., Nester E.W., 1975 Plasmids required for virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Journal of Bacteriology 123:255–264
Zhang H.-X., Blumwald E., 2001 Transgenic salt tolerant tomato plants accumulate salt in the foliage but not in the fruits Nature Biotechnology 19:765–768
Zhang H.-X., Hodson J., Williams J.P., Blumwald E., 2001 Engineering salt-tolerant Brassica plants: characterization of yield and seed oil quality in transgenic plants with increased vacuolar sodium accumulation Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America 98:12832–12836
Zhu J.-K., 2002 Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants Annual Review of Plant Biology 53:247–273
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada for providing funds in support of this research. We thank Ms Lynn Hoyles for assistance in growing the plants. We thank Ms Saleema Saleh and Dr Hilda Rodriguez for critically reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sergeeva, E., Shah, S. & Glick, B.R. Growth of transgenic canola (Brassica napus cv. Westar) expressing a bacterial 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase gene on high concentrations of salt. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22, 277–282 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-005-9032-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-005-9032-1