Abstract
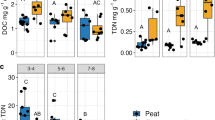
Pesticide use generates wastewaters from its handling and from washing of spraying equipment, bringing concern about punctual discharge. Biobeds are biopurification systems for pesticide residues disposal, representing safe alternatives to avoid soil contamination. Peat that composes the original biomixture is not available all around Brazil. The aim of this work was to evaluate the efficiency of two alternative, accessible biomixtures, replacing peat, for treating phosmet (organophosphate insecticide) residues in biobeds and reducing its ecotoxicological effects. We hypothesized that the new biomixtures with pine litter (PB) or vermicompost (VB) could show the same degradation and detoxification efficiency as the standard biobed’s biomixture (SB) using peat. Small size bioreactors received 35 mg kg−1 of phosmet (Imidan®) in a laboratory-scale experiment. The pesticide degradation was monitored by chemical analysis. The decrease of ecotoxicity was determined by reproduction tests with collembolans (Folsomia candida) and enchytraeids (Enchytraeus crypticus), following ISO guidelines. Degradation curves showed that all biomixtures reached almost complete degradation of phosmet after 90 days. Collembolans were more sensitive than enchytraeid, confirming their usefulness in biomonitoring insecticide degradation. This work showed that both pine litter and vermicompost are potentially substitutes for peat in alternative biomixtures, since they were efficient in degrading the pesticide and reducing its ecotoxicity. Our results contribute for the development of newly, accessible biobeds for south Brazil, bringing the first study reports involving such biobeds capacity to degrade phosmet, which is a commonly used pesticide in this region.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta-Sánchez, A., Soto-Garita, C., Masís-Mora, M., Cambronero-Heinrichs, J. C., & Rodríguez-Rodríguez, C. E. (2020). Impaired pesticide removal and detoxification by biomixtures during the simulated pesticide application cycle of a tropical agricultural system. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 195, 110460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110460.
Agrequima. (2019). Presentaciones biodep. Retrieved May, 2020, from https://agrequima.com.gt/site/presentaciones-biodep/#.
Amorim, M. J. B., Pereira, C., Menezes-Oliveira, V. B., Campos, B., Soares, A. M. V. M., & Loureiro, S. (2012). Assessing single and joint effects of chemicals on the survival and reproduction of Folsomia candida (Collembola) in soil. Environmental Pollution, 160, 145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.09.005.
Bellinger, P. F., Christiansen, K. A., Janssens, F. (2020). Checklist of the Collembola of the world. Belgium: University of Antwerp, 1996–2020. Retrieved Aug. 21 2020, from http://www.collembola.org.
Bozdogan, A. M., Yarpuz-Bozdogan, N., Aka-Sagliker, H., Oztekin, M. E., & Daglioglu, N. (2014). Determination of absorption and degradation of some pesticides in biobed. Journal Food Agriculture. and Environment, 12, 347–351.
Buch, A. C., Niemeyer, J. C., Correia, M. E. F., & Silva-Filho, E. V. (2016). Ecotoxicity of mercury to Folsomia candida and Proisotoma minuta (Collembola: Isotomidae) in tropical soils: Baseline for ecological risk assessment. Ecotoxicology Environment Safety, 127, 22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.01.009.
Carniel, L. S. C., Niemeyer, J. C., Oliveira Filho, L. C. I., Alexandre, D., Gebler, L., & Klauberg-Filho, O. (2020). Are there any risks of the disposal of pesticide effluents in soils? Biobed system meets ecotoxicology ensuring safety to soil fauna. Ecotoxicology, 29, 1409–1421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02260-x.
Castro-Gutiérrez, V., Masís-Mora, M., Diez, M. C., Tortella, G. R., & Rodríguez-Rodríguez, C. E. (2017). Aging of biomixtures: Effects on carbofuran removal and microbial community structure. Chemosphere, 168, 418–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.065.
Castillo, J. M., Beguet, J., Martin-Laurent, F., & Romero, E. (2016). Multidisciplinary assessment of pesticide mitigation in soil amended with vermicomposted agroindustrial wastes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 304, 379–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.10.056.
Castillo, M. P., & Torstensson, L. (2007). Effect of biobed composition, moisture, and temperature on the degradation of pesticides. Journal Agriculture Food Chem, 55, 5725–5733. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0707637.
Castillo, M. del P., Torstensson, L., Stenstrom, J. (2008). Biobeds for environmental protection from pesticide use - A review. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56, 6206–6219.
Chin-Pampillo, J. S., Masís-Mora, M., Ruiz-Hidalgo, K., Carazo-Rojas, E., & Rodríguez-Rodríguez, C. E. (2016). Removal of carbofuran is not affected by co-application of chlorpyrifos in a coconut fiber/compost based biomixture after aging or pre-exposure. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 46, 182–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2015.12.026.
Delgado-Moreno, L., Nogales, R., & Romero, E. (2017). Biodegradation of high doses of commercial pesticide products in pilot-scale biobeds using olive-oil agroindustry wastes. Journal of Environmental Management, 204, 160–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.08.032.
De Wilde, T., Mertens, J., Simunek, J., Sniegowksi, K., Ryckeboer, J., Jaeken, P., Springael, D., Spanoghe, P. (2009). Characterizing pesticide sorption and degradation in microscale biopurification systems using column displacement experiments. Environmental Pollution, 157, 463–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.09.008.
Dias, L. A., Gebler, L., Niemeyer, J. C., Itako, A. T. (2020). Destination of pesticide residues on biobeds: State of the art and future perspectives in Latin America. Chemosphere, 248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126038.
Diaz, J. M. C., Martin-Laurent, F., Beguet, J., Nogales, R., & Romero, E. (2017). Fate and effect of imidacloprid on vermicompost-amended soils under dissimilar conditions: Risk for soil functions, structure, and bacterial abundance. Science of the Total Environment, 579, 1111–1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.082.
Diez, M. C., Levio, M., Briceño, G., Rubilar, O., Tortella, G., & Gallardo, F. (2013). Biochar as a partial replacement of peat in pesticide-degrading biomixtures formulated with different soil types. Journal of Biobased Materials and Bioenergy, 7, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbmb.2013.1376.
FAO - Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. (2015). World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, update 2015 - International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. World Soil Resources Reports No. 106, Rome.
FAO. (2020). FAO specifications for agricultural pesticides in agriculture - New specifications list. Phosmet (evaluation report only). Retrieved may/2021, from http://www.fao.org/agriculture/crops/thematic-sitemap/theme/pests/jmps/ps-new/en/.
Fernández-Alberti, S., Rubilar, O., Tortella, G. R., & Diez, M. C. (2012). Chlorpyrifos degradation in a Biomix: Effect of pre-incubation and water holding capacity. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 12(4), 785–799. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162012005000032.
Fogg, P., & Boxall, A. B. A. (2004). Effect of different soil textures on leaching potential and degradation of pesticides in biobeds. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 52, 5643–5652. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf040023n.
Frouz, J., Livečková, M., Albrechtová, J., Chroňáková, A., Cajthaml, T., Pižl, V., Háněl, L., Starý, J., Baldrian, P., Lhotáková, Z., Šimáčková, H., & Cepáková, Š. (2013). Is the effect of trees on soil properties mediated by soil fauna? A case study from post-mining sites. Food Policy, 309, 87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2013.02.013.
Garcia, M.V.B. (2004). Effects of pesticides on soil fauna: Development of ecotoxicological test methods for tropical regions, Ecology and. Development Series No. 19, Zentrum für Entwicklungsforschung, University of Bonn, 281 p.
Gainer, A., Cousins, M., Hogan, N., & Siciliano, S. D. (2018). Petroleum hydrocarbon mixture toxicity and a trait based approach to soil invertebrate species for site specific risk assessments. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 37, 2222–2234. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4164.
Gebler, L. (2017). Orientações para o Dimensionamento e Operação de Biobeds no Brasil. Comunicado Técnico, 204. Bento Gonçalves: Embrapa Uva e Vinho, 5p
Gebler, L., Pelizza, T. R., & Almeida, D. L. (2006). Variáveis ambientais e toxicológicas de agroquímicos utilizados na Produção Integrada de Maçãs (PIM) visando modelagem matemática. Revista de Ciências Agrovet. Lages, 5, 169–184.
Góngora-Echeverría, V. R., Quintal-Franco, C., Arena-Ortiz, M. L., Gi acoman-Vallejos, G., Ponce-Caballero, C. (2018). Identification of microbial species present in a pesticide dissipation process in biobed systems using typical substrates from southeastern Mexico as a biomixture at a laboratory scale. Science of The Total Environment, 528-538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.082.
Huete-Soto, A., Castillo-González, H., Masís-Mora, M., Chin-Pampillo, J. S., & Rodríguez-Rodríguez, C. E. (2017). Effects of oxytetracycline on the performance and activity of biomixtures: Removal of herbicides and mineralization of chlorpyrifos. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 321, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.08.078.
Hund-Rinke, K., Baun, A., Cupi, D., Fernandes, T. F., Handy, R., Kinross, J. H., Navas, J. M., Peijnenburg, J., Schlich, K., Shaw, B. J., & Scott-Fordsmand, S. (2016). Regulatory ecotoxicity testing of nanomaterials – Proposed modifications of OECD test guidelines based on laboratory experience with silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology, 10, 1442–1447. https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2016.1229517.
ISO - International Organization For Standardization. (2008). ISO 17512–1. Soil quality - Avoidance test for determining the quality of soils and effects on behavior - Part 1: Test with earthworms (Eisenia fetida and Eisenia andrei). ISO, Geneva. https://www.iso.org/standard/38402.html.
ISO. (2014a). ISO 11267. Soil quality - Inhibition of reproduction of Collembola (Folsomia candida) by soil contaminants. ISO, Geneva. https://www.iso.org/standard/57582.html.
ISO. (2014b). ISO 16387. Soil quality - Effects of contaminants on Enchytraeidae (Enchytraeus sp.) — Determination of effects on reproduction. ISO, Geneva. https://www.iso.org/standard/57067.html.
IUPAC - International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. (2021). Pesticide Properties Database. Retrieved jan/2021, from https://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/iupac/atoz.htm.
Karanasios, E., Tsiropoulos, G., & Karpouzas, D. (2012). On-farm biopurification systems for the depuration of pesticide wastewaters: Recent biotechnological advances and future perspectives. Biodegradation, 23, 787–802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9571-8.
Karanasios, E., Karpouzas, D., & Tsiropoulos, N. (2012). Key parameters and practices controlling pesticide degradation efficiency of biobed substrates. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part b: Pesticides, Food Contaminants, and Agricultural Wastes, 47, 589–598. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2012.665753.
Khan, M. A. I., Biswas, B., Smith, E., Naidu, R., & Megharaj, M. (2018). Toxicity assessment of fresh and weathered petroleum hydrocarbons in contaminated soil- A review. Chemosphere, 212, 755–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.08.094.
Kravvariti, K., Tsiropoulos, N. G., & Karpouzas, D. G. (2010). Degradation and adsorption of terbuthylazine and chlorpyrifos in biobed biomixtures from composted cotton crop residues. Pest Management Science, 66, 1122–1128. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1990.
Masin, C. E., Lescano, M. R., Rodríguez, A. R., Godoy, J. L., & Zalazar, C. S. (2018). Earthworms to assess the innocuousness of spent biomixtures employed for glyphosate degradation. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part b: Pesticides, Food Contaminants, and Agricultural Wastes. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2018.1462922.
Masís-Mora, M., Lizano-Fallas, V., Tortella, G., Beita-Sandí, W., & Rodríguez-Rodríguez, C. E. (2019). Removal of triazines, triazoles and organophophates in biomixtures and application of a biopurification system for the treatment of laboratory wastewaters. Chemosphere, 233, 733–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.001.
Menta, C. (2012). Soil fauna diversity – Function, soil degradation, biological indices, soil restoration. In: LAMEED, G. A. Biodiversity Conservation and Utilization in a Diverse World. Ed. IntechOpen, 296 p. https://doi.org/10.5772/51091.
Natal-da-Luz, T., Moreira-Santos, M., Ruepert, C., Castillo, L. E., Ribeiro, R., & Sousa, J. P. (2012). Ecotoxicological characterization of a tropical soil after diazinon Spraying. Ecotoxicology, 21, 2163–2176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0970-8.
Niemeyer, J. C., Chelinho, S., & Sousa, J. P. (2017). Soil ecotoxicology in Latin America: Current research and perspectives. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 36, 1795–1810. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3792.
Niva, C. C., Brown, G. G. (2019). Ecotoxicologia terrestre: métodos e aplicações dos ensaios com oligoquetas. Embrapa. 258 p.
OECD - The Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development. (1984). Test No. 208: Terrestrial plant test: Seedling emergence and seedling growth test. OECD Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals Section 2: Effects on Biotic Systems. OECD.
Owojori, O. J., Waszak, K., & Roembke, J. (2014). Avoidance and reproduction tests with the predatory mite Hypoaspis aculeifer: Effects of different chemical substances. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 33, 230–237. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2421.
Papazlatani, C. V., Karas, P. A., Tucat, G., Karpouzas, D. G. (2019). Expanding the use of biobeds: Degradation and adsorption of pesticides contained in effluents from seed-coating, bulb disinfestation and fruit-packaging activities. Journal of Environmental Management, 248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.06.122.
Pesaro, M., Widmer, F., Nicollier, G., & Zeyer, J. (2003). Effects of freeze-thaw stress during soil storage on microbial communities and methidathion degradation. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 35, 1049–1061. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(03)00147-0.
Pelosi, C., & Römbke, J. (2016). Are Enchytraeidae (Oligochaeta, Annelida) good indicators of agricultural management practices? Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 100, 255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.06.030.
Quatrin, G. D., Pizzutti, I. R., Gebler, L., Dias, J. V., & Cardoso, C. D. (2020). New analytical method for chlorpyrifos determination in biobeds constructed in Brazil: Development and validation. Journal of Chromatography B, 1157, 122285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2020.122285.
Romero, E., Delgado-Moreno, L., Nogales, R. (2019). Pesticide dissipation and enzyme activities in ungrassed and grassed biomixtures, composed of winery wastes, used in biobed bioremediation systems. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 230-233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.087.
Ruiz-Hidalgo, K., Chin-Pampillo, J. S., Masís-Mora, M., Carazo-Rojas, E., & Rodríguez Rodríguez, C. E. (2016). Optimization of a fungally bioaugmented biomixture for carbofuran removal in on-farm biopurification systems. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 227, 3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2681-2.
RSTUDIO© Desktop. (2009–2020). Version 1.1.423: RStudio.
Saez, J. M., Bigliardo, A. L., Raimondo, E. E., Brice~no, G. E., Polti, E. A., & Benimeli, C. S. (2018). Lindane dissipation in a biomixture: Effect of soil properties and bioaugmentation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 156, 97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.011.
Santos, M. J., Ferreira, M. F., Cachada, A., Duarte, A. C., & Sousa, J. P. (2012). Pesticide application to agricultural fields: Effects on the reproduction and avoidance behaviour of Folsomia candida and Eisenia andrei. Ecotoxicology, 21, 2113–2122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0963-7.
Schneider, C. A., Rasband, W. S., Eliceiri, K.W. (2012). NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nature Methods 9, 671–675.
Sinclair, C. J., Boxall, A. B. (2003). Assessing the ecotoxicity of pesticide transformation products. Environmental Science & Technology 37, 4617–4625. https://doi.org/10.1021/es030038m.
Sniegowski, K., Bers, K., Van Goetem, K., Ryckeboer, J., Jaeken, P., Spanoghe, P., Springael, D. (2011). Improvement of pesticide mineralization in on-farm biopurification systems by bioaugmentation with pesticide-primed soil. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 76, 64–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2010.01031.x.
Torstensson, L., & Castillodel, M. P. (1997). Use of biobeds in Sweden to minimize environmental spillages from agricultural spray equipment. Pesticide Outlook, 8, 24–27.
Tortella, G. R., Rubilar, O., Castillo, M. P., Cea, M., Mella-Herrera, R., & Diez, M. C. (2012). Chlorpyrifos degradation in a biomixture of biobed at different maturity stages. Chemosphere, 88, 224–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.02.072.
Tortella, G. R., Rubilar, O., Cea, M., Briceño, G., Quiroz, A., Diez, M. C., & Parra, L. (2013). Natural wastes rich in terpenes and their relevance in the matrix of an on-farm biopurification system for the biodegradation of atrazine. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 85, 8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.06.003.
Tortella, G. R., Mella-Herrera, R. A., Sousa, D. Z., Rubilar, O., Acuña, J. J., Briceño, G., & Diez, M. C. (2013). Atrazine dissipation and its impact on the microbial communities and community level physiological profiles in a microcosm simulating the biomixture of on-farm biopurification system. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 260, 459–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.05.059.
Urrutia, C., Rubilar, O., Tortella, G. R., & Diez, M. C. (2013). Degradation of pesticide mixture on modified matrix of a biopurification system with alternatives lignocellulosic wastes. Chemosphere, 92, 1361–1366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.04.088.
Vareli, C.S., Pizzutti, I. R., Gebler, L., Cardoso, C. D., Fontana, M. E., Reichert, B., Jänisch, B. D. (2019). Evaluation of two extraction approaches for pesticide residue determination in biobed using GC-MS/MS. In: Anal. Methods. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ay01746a.
Vischetti, C., Monaci, E., Cardinali, A., Casucci, C., & Perucci, P. (2008). The effect of initial concentration, co-application and repeated applications on pesticide degradation in a biobed mixture. Chemosphere, 72, 1739–1743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.04.065.
Zhang, X., Luo, Y., & Goh, K. S. (2018). Modeling spray drift and runoffrelated inputs of pesticides to receiving water. Environmental Pollution, 234, 48–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.032.
Zhu, D., KE, X., Wu, L., Li, Z., Christie, P., & Luo, Y. (2016). Ecotoxicity of cadmium in a soil collembolan-predatory mite food chain: Can we use the 15N labeled litter addition method to assess soil functional change? Environmental Pollution, 219, 37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.051.
Zortéa, T., Reis, T. R., Serafini, S., Sousa, J. P., Silva, A. S., & Baretta, D. (2018). Ecotoxicological effect of fipronil and its metabolites on Folsomia candida in tropical soils. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 62, 203–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2018.07.011.
Funding
This study was financed by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES)—Brazil – Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dias, L.d., Itako, A.T., Gebler, L. et al. Pine Litter and Vermicompost as Alternative Substrates for Biobeds: Efficiency in Pesticide Degradation. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 283 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05231-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05231-y