Abstract
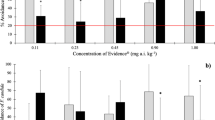
The impact of diazinon spraying in an agricultural tropical soil through the evaluation of both the habitat and retention functions of the soil system was never reported. To fill this gap, five times the recommended dose of a commercial diazinon formulation was sprayed in an agricultural area of Costa Rica, and dilution gradients of the sprayed soil were prepared in the laboratory. Avoidance and reproduction tests with soil organisms (Eisenia andrei, Enchytraeus crypticus and Folsomia candida) to evaluate losses in terrestrial habitat function, and growth and reproduction tests with aquatic organisms (Chlorella vulgaris and Daphnia magna, respectively) to evaluate the retention function of soil were performed. Results demonstrated that regarding habitat function, F. candida reproduction was the most sensitive endpoint (EC50 = 0.288 mg a.i./kg), followed by avoidance behaviour of E. andrei (EC20 = 1.75 mg a.i./kg). F. candida avoidance and the reproduction of E. andrei and E. crypticus were not affected by diazinon. The toxicity tests with aquatic organisms showed that the soil retention function was insufficient to prevent effects of diazinon either on microalgae growth (EC50 ≤ 0.742 mg/L and EC20 ≤ 0.223 mg/L) and on the reproduction of the cladoceran (EC50 ≤ 0.00771 mg/L and EC20 ≤ 0.00646 mg/L). Results suggested that diazinon exerted toxic effects even at the dilution corresponding to the recommended dose, fact which makes its misuse an issue of environmental concern. Furthermore, the present study highlighted the importance and complementary nature of the assessment of both habitat and retention functions to an ecological risk assessment in tropical systems.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhya TK, Wahid PA, Sethunathan N (1987) Persistence and biodegradation of selected organophosphorus insecticides in flooded versus non-flooded soils. Biol Fertil Soils 4:36–40
Ankley GT, Collyard SA (1995) Influence of piperonyl butoxide on the toxicity of organophosphate insecticides to three species of freshwater benthic invertebrates. Comp Biochem Physiol C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 110:149–155
Anon (2002) FAOSTAT (Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations) Database. Rome, Italy
APVMA (2003) The reconsideration of registrations of products containing diazinon and their labels. Part 1 Product cancellations. Review Series 1. R. Report. Australian Pesticides & Veterinary Medicines Authority, Canberra, Australia, pp 1–25
Arienzo M, Crisanto T, Sánchez-Martín MJ, Sánchez-Camazano M (1994) Effect of soil characteristics on adsoprtion and mobility of (14C) Diazinon. J Agric Food Chem 42:1803–1808
Arnold EG (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
ASTM (2002) Standard guide for conducting acute toxicity tests on test materials with fishes, macroinvertebrates, and amphibians. E 729–96. In: Annual book of ASTM standards, vol. 11.05. American Society for Testing and Material, Philadelphia, PA
Baicu T (1982) Toxicity of some pesticides to Trichoderma viride Pers. Crop Prot 1:349–359
Bailey HC, Elphick JR, Krassoi R, Lowell A (2001) Joint acute toxicity of diazinon and ammonia to Ceriodaphnia dubia. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2877–2882
Bisson M, Hontela A (2002) Cytotoxic and endocrine-disrupting potential of atrazine, diazinon, endosulfan, and mancozeb in adrenocortical steroidogenic cells of rainbow trout exposed in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 180:110–117
Booth LH, O’Halloran K (2001) A comparison of biomarker responses in the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa to the organophosphorus insecticides diazinon and chlorpyrifos. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2494–2502
Bouldin JL, Farris JL, Moore MT, Smith S, Cooper CM (2007) Assessment of diazinon toxicity in sediment and water of constructed wetlands using deployed Corbicula fluminea and laboratory testing. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 53:174–182
Brasel JM, Collier AC, Pritsos CA (2007) Differential toxic effects of carbofuran and diazinon on time of flight in pigeons (Columba livia): potential for pesticide effects on migration. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 219:241–246
Bustos-Obreg E, Goicochea RI (2002) Pesticide soil contamination mainly affects earthworm male reproductive parameters. Asian J Androl 4:195–199
Butler GL, Deason TR, O’Kelley JC (1975) The effect of atrazine, 2,4-D, methoxychlor, carbaryl and diazinon on the growth of planktonic algae. Br Phycol J 10:371–376
Castillo LE, De La Cruz E, Ruepert C (1997) Ecotoxicology as pesticides ni tropical aquatic ecosystems of central america. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:41–51
Chaverri F (2002) Importaciones y uso de plaguicidas en Costa Rica: análisis del perriodo 1994–1995. Universidad Nacional. Instituto Regional de Estudios en Sustancias Tóxicas, Herédia, Costa Rica, p 58
Daam MA, Leitão S, Cerejeira MJ, Sousa JP (2011) Comparing the sensitivity of soil invertebrates to pesticides with that of Eisenia andrei. Chemosphere 85:1040–1047
DIN (1984). German standard methods for the examination of water, waste and sludge: sludge and sediments, determination of leachability by water. DIN 38 414–S4. Deutsches Institut für Normung, Berlin, Germany
Doggett SM, Rhodes RG (1991) Effects of a dizinon formulation on unialgal growth rates and phytoplankton diversity. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 47:36–42
EC (1992) Biological test method: growth inhibition test using the freshwater alga Selenastrum capricornutum. Report EPS 1/RM/25. Environment Canada, Ottawa, ON, Canada
EC (2004) Biological test methods for measuring the survival and reproduction of springtails exposed to contaminants in soil. Reports EPS 1/RM/47. Environment Canada, Ottawa, ON, Canada
Espinoza-Navarro O, Bustos-Obreg E (2005) Effect of malathion on the male reproductive organs of earthworms, Eisenia fetida. Asian J Androl 7:97–101
FAOSTAT (2011) Pineapple production in Costa Rica in 2009. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://faostat.fao.org. Accessed 18 October 2011
Fernández-Casalderrey A, Ferrando MD, Andreu-Moliner E (1992) Filtration and ingestion rates of Brachionus calyciflorus after exposure to endosulfan and diazinon. Comp Biochem Physiol C Comp Pharmacol 103:357–361
Fernández-Casalderrey A, Ferrando MD, Andreu-Moliner E (1994) Effect of sublethal concentrations of pesticides on the feeding behavior of Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 27:82–89
Fountain MT, Brown VK, Gange AC, Symondson WOC, Murray PJ (2007) The effects of the insecticide chlorpyrifos on spider and Collembola communities. Pedobiologia 51:147–158
Frampton GK, Van den Brink PJ (2007) Collembola and macroarthropod community responses to carbamate, organophosphate and synthetic pyrethroid insecticides: direct and indirect effects. Environ Poll 147:14–25
Frampton GK, Jänsch S, Scott-Fordsmand JJ, Römbke J, Van den Brink PJ (2006) Effects of pesticides on soil invertebrates in laboratory studies: a review and analysis using species sensitivity distributions. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2480–2489
Gersich FM, Milazzo DP (1990) Evaluation of a 14-day static renewal toxicity test with Daphnia magna Straus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 19:72–76
Gokcimen A, Gulle K, Demirin H, Bayram D, Kocak A, Altuntas I (2007) Effects of diazinon at different doses on rat liver and pancreas tissues. Pest Biochem Physiol 87:103–108
Higgins J, Hohn C (2008) Effects of prevalent freshwater chemical contaminants on in vitro growth of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Environ Poll 152:259–266
Hodge S, Webster KM, Booth L, Hepplethwaite V, O’Halloran K (2000) Non-avoidance of organophosphate insecticides by the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa (lumbricidae). Soil Biol Biochem 32:425–428
HSDB (2011) Toxnet home: toxicology data network. United States national library of medicine. Diazinon. http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov. Accessed 4 October 2011
Hund-Rinke K, Wiechering H (2001) Earthworm avoidance test for soil assessment. J Soils Sediments 1:15–20
ISO (1996) Soil quality: effects of pollutants on earthworms (Eisenia fetida)—Part 2: determination of effects on reproduction. ISO 1268-2.2. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland
ISO (1999) Soil quality: inhibition of reproduction of Collembola (Folsomia candida) by soil pollutants. ISO 11269. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland
ISO (2003a) Soil quality: guidance on the ecotoxicological characterization of soils and soil materials. ISO 15799. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland
ISO (2003b) Soil quality: effects of pollutants on Enchytraeidae (Enchytraeus sp.)—Determination of effects on reproduction and survival. ISO 16387. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland
ISO (2007a) Soil quality: avoidance test for testing the quality of soils and effects of chemicals on behaviour—Part 1: test with earthworms (Eisenia fetida and Eisenia andrei). ISO 17512–1.2 (Draft). International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland
ISO (2007b) Soil quality: avoidance test for testing the quality of soils and effects of chemicals on behaviour—Part 2: test with collembolans (Folsomia candida). ISO 17512–2 (Draft). International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland
Jager T, Crommentuijn T, Van Gestel CAM, Kooijman SALM (2007) Chronic exposure to chlorpyrifos reveals two modes of action in the springtails Folsomia candida. Environ Poll 145:452–458
Jänsch S, Frampton GK, Römbke J, Van den Brink PJ, Scott-Fordsmand JJ (2006) Effects of pesticides on soil invertebrates in model ecosystem and field studies: a review and comparison with laboratory toxicity data. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:2490–2501
Jemec A, Tisler T, Drobne D, Sepcić K, Fournier D, Trebse P (2007) Comparative toxicity of imidacloprid, of its commercial liquid formulation and of diazinon to a non-target arthropod, the microcrustacean Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 68:1408–1418
Kidd H, James DR (1991) The agrochemicals handbook, 3rd edn. Royal Society of Chemistry Information Services, Cambridge, UK
Leland JE, Mullins DE, Barry DF (2001) Evaluating environmental hazards of land applying composted diazinon using earthworm bioassays. J Environ Sci Health B 36:821–834
LNEC (1970) Solos—Análise granulométrica por peneiração húmida. LNEC-E 239, Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia Civil, Lisbon, Portugal
Matson PA, Parton WJ, Power AG, Swift M (1997) Agricultural intensification and ecosystem properties. Science 277:504–509
Natal-da-Luz T, Tidona S, Jesus B, Morais PV, Sousa JP (2009) The use of sewage sludge as soil amendment. The need for an ecotoxicological evaluation. J Soils Sediments 9:246–260
NPTN (1998) Diazinon. National Pesticide Telecommunications Network, <http://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/diazinon.pdf.>. Accessed 4 October 2011
NRA (2002) The NRA review of diazinon, vol 1. National Registration Authority for Agricultural and Veterinary Chemicals, Canberra, Australia
OECD (1984a) Algal growth inhibition test. OECD guidelines for testing of chemicals 201. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris, France
OECD (1984b) Daphnia sp., acute immobilization test and reproduction test. OECD guidelines for testing of chemicals 202. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris, France
Rodríguez G, Jordán P (1993) Guía práctica para el cultivo de la piña. CORDEP, Cochabamba, Bolivia, p 31
Sakuma M (1998) Probit analysis of preference data. Appl Entomol Zool 33:339–347
Sánchez M, Ferrando MD, Sancho E, Andreu E (2000) Physiological perturbations in several generations of Daphnia magna Straus exposed to diazinon. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 46:87–94
Schuler LJ, Trimble AJ, Belden JB, Lydy MJ (2005) Joint toxicity of triazine herbicides and organophosphate insecticides to the midge Chironomus tentans. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 49:173–177
Slimak KM (1997) Avoidance response as a sublethal effect of pesticides on Lumbricus terrestris (Oligochaeta). Soil Biol Biochem 29:713–715
Smith LH, Liyanage JA, Watawala RC, Aravinna AGP, Kookana RS (2006) Degradation of the pesticides carbofuran and diazinon in tropical soils from Sri Lanka. CSIRO Land and Water Science Report 67/06, pp 26
Smith S, Lizotte RE, Moore MT (2007) Toxicity assessment of diazinon in a constructed wetland using Hyalella azteca. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:58–61
Stephenson GL, Wren CD, Middelraad ICJ, Warner JE (1997) Exposure of the earthworm, Lumbricus terrestris, to diazinon, and relative risk to passerine birds. Soil Biol Biochem 29:717–720
Sucahyo D, Van Straalen NM, Krave A, Van Gestel CAM (2008) Acute toxicity of pesticides to the tropical freshwater shrimp Caridina laevis. Ecotox Envon Safe 69:421–427
USEPA (1986) Pesticide fact sheet: diazinon. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
USEPA (2004) Economic and environmental benefit analysis of the final effluent limitations guidelines and standards for the concentrated aquatic animal production point source category. Office of water, United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
USEPA (2005) Aquatic life ambient water quality criteria: diazinon. Final Report EPA-822-R-05-006. Office of water, United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Vink K, Van Straalen NM (1999) Effects of benomyl and diazinon on isopod-mediated leaf litter decomposition in microcosms. Pedobiologia 43:345–359
Wauchope RD, Buttler TM, Hornsby AG, Augustijn-Beckers PWM, Burt JP (1992) The SCS ARS CES Pesticide properties database for environmental decision-making. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 123:1–155
Weber JB, Wilkerson GG, Reinhardt CF (2004) Calculating pesticide sorption coefficient (K d ) using selected soil properties. Chemosphere 55:157–166
Werner I, Deanovic A, Hinton DE, Henderson JD, Oliveira GH, Wilson BW, Krueger W, Wallender WW, Oliver MN, Zalom FG (2002) Toxicity of stormwater runoff after dormant spray application of diazinon and esfenvalerate (Asana®) in a french prune orchard, Glenn County, California, USA. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 68:29–36
Wilcox D, Dove B, McDavid D, Greer D (2002) UTHSCSA ImageTool Version 3.0. Copyright 1995-2002, The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. http://ddsdx.uthscsa.edu/dig/itdesc.html. Accessed 21 October 2011
Yeardley JRB, Lazorchak JM, Gast LC (1996) The potential of an earthworm avoidance test for evaluation of hazardous waste sites. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:1532–1537
Zar J (1999) Biostatistical analysis. Hall International, London, UK
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Irene Campos and Johnny Campos for making available the agricultural field and for all field assistance, Fernando Mojica for characterizing the soil texture, Andrea Suárez for supporting in laboratory tests, and the Laboratorio de Estudios Ecotoxicológicos (ECOTOX) team for assistance. This research was partially funded by a postdoctoral grant of M. Moreira-Santos from the Portuguese institution “Fundacão para a Ciência e a Tecnologia” (SFRH/BPD/7196/2001) and by Ciência 2007-FSE and POPH funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Natal-da-Luz, T., Moreira-Santos, M., Ruepert, C. et al. Ecotoxicological characterization of a tropical soil after diazinon spraying. Ecotoxicology 21, 2163–2176 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0970-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0970-8