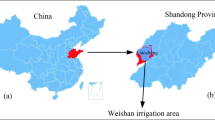
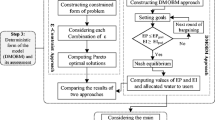
Abstract
The planning and management decisions often involve multiple objectives and multiple parties with conflicting interests due to the complexity of inter-basin water transfer systems. In this paper, the objectives, the groups involved and the corresponding conflicting interests that characterize water transfer decisions are analyzed. A multi-party, multi-objective decision/bargaining model based on the “satisfaction principle” is developed for inter-basin water transfer system decision-making. In order to obtain an ideal multi-party decision, bargaining is first broken down into two stages, and then decision alternatives are chosen using fuzzy pattern recognition. This model is simple, and it is more adaptable for solving practical multi-objective and multi-party decision problems. Finally, an inter-basin water transfer scheme optimization example is demonstrated by using the developed model.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen SY (1997) Relative membership function and new frame of fuzzy sets theory for pattern recognition. J Fuzzy Math 5(2):401–411 (in Chinese)
Chen SY (1998) Engineering fuzzy set theory and application State Security Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
Chen SY (2002) Fuzzy recognition theory and application for complex water resources system optimization. Jilin University Press, Changchun, China Comment. (in Chinese)
Cheng CT, Chau KW (2002) Three-person multi-objective conflict decisions in reservoir flood control. Eur J Oper Res 142:625–631
Cohon JL, Marks DH (1973) Multiobjective screening models and water resource investment. Water Resour Res 9(4):826–836. doi:10.1029/WR009i004p00826
El-Baroudy I, Simonovic SP (2004) Fuzzy criteria for the evaluation of water resource systems performance. Water Resour Res 40:W10503. doi:10.1029/2003WR002828
Fontane DG, Gates TK, Moncada E (1997) Planning reservoir operations with imprecise objectives. J Water Resour Plan Manag 123(3):154–162
Gu M (2006) A study for an operation mechanism of inter-basin water transfer projects. Hehai University doctoral thesis, Nanjing, China. (in Chinese)
Haimes YY (1998) Risk modeling, assessment, and management. Wiley, New York
Kung H, Ying L, Liu Y (1992) A complementary tool to water quality index: fuzzy clustering analysis. Water Resour Bull 28(3):525–533
Lee YW, Dahab MF, Bogardi I (1994) Fuzzy decision making in groundwater nitrate risk management. Water Resour Bull 30(1):135–148
Lejano RP, Davos CA (1995) Cost allocation of multiagency water resource projects: game theoretic approaches and case study. Water Resour Res 31(5):1387–1393. doi:10.1029/95WR00322
Maass A, Hufschmidt MM, Dorfman HA, Jr T, Marglin SA, Fair GM (1962) Design of water resources systems. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Mohammad RN, Reza K, Hamed P (2012) An interval parameter model for cooperative inter-basin water resources allocation considering the water quality issues. Water Resour Manag. doi:10.1007/s11269-012-0074-5
Mojtaba S, Najmeh M, Reza K (2010) Optimal inter-basin water allocation using crisp and fuzzy shapley games. Water Resour Manag 24:2291–2310
Nakas MD, Wichelns D, Montgomery L (2002) Game theory analysis of competition for groundwater involving El Paso, Texas and Ciudad Juarez, Mexico. In: Paper presented at moving with the speed of change, the 2002 annual meeting of the American agricultural economics association, Long Beach, CA, pp 18–31
Prodanovic P, Simonovic SP (2002) Comparison of fuzzy set ranking methods for implementation in water resources decision-making. Can J Civil Eng 29:692–701
Raiffa H (1968) Decision analysis. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Razavi Toosi SL, Samani JMV (2012) Evaluating water transfer projects using analytic network process (ANP). Water Resour Manag 26(7):1999–2014
Ren BH, Huang P (2006) Application of quadratic planning on water transfer and allocation. Clim Environ Res 11(3):361–370 (in Chinese)
Salazar MR, Szidarovszky F, Coppola E, Rojano AA (2007) Application of game theory for a groundwater conflict in Mexico. J Environ Manag 84:560–571
Shao DG (1994) Study on optimization decision models for inter-basin water transfer engineering. J Wuhan Univ 27(05):500–505 (in Chinese)
Shao DG (2000) Planning and operation theory and application of inter-basin water transfer system. Wuhan University Press, China (in Chinese)
Wang GL (1998) Theoretic research and application of fuzzy sets theory in complex groundwater resources system. Dalian University of Technology doctoral thesis, Dalian, China, pp 94–103 (in Chinese)
Xuesen L, Wang B, Mehrotra R, Sharma A, Guoli W (2009) Consideration of trends in evaluating inter-basin water transfer alternatives within a fuzzy decision making framework. Water Resour Manag 23:3207–3220
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51079015, 50979011). Cordial gratitude is extended to the editor and reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions used to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Wang, G., Peng, Y. et al. A Negotiation-Based Multi-Objective, Multi-Party Decision-Making Model for Inter-Basin Water Transfer Scheme Optimization. Water Resour Manage 26, 4029–4038 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0127-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0127-9