Abstract
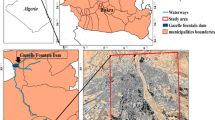
In recent years, uneven distribution of available water resources as well as increasing water demands and overexploiting the water resources have brought severe need for transferring water from basins having sufficient water to basins facing water shortages. Therefore, optimal allocation of shared water resources in water transfer projects, considering the utilities of different stakeholders, physical limitations of the system and socioeconomic criteria is an important task. In this paper, a new methodology based on crisp and fuzzy Shapley games is developed for optimal allocation of inter-basin water resources. In the proposed methodology, initial water allocations are obtained using an optimization model considering an equity criterion. In the second step, the stakeholders form crisp coalitions to increase the total net benefit of the system as well as their own benefits and a crisp Shapley Value game is used to reallocate the benefits produced in the crisp coalitions. Lastly, to provide maximum total net benefit, fuzzy coalitions are constituted and the participation rates of water users to fuzzy coalitions are optimized. Then, the total net benefit is reallocated to water users in a rational and equitable way using Fuzzy Shapley Value game. The effectiveness of this method is examined by applying it to a large scale case study of water transfer from the Karoon river basin in southern Iran to the Rafsanjan plain in central Iran.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubin JP (1974) Coeur et Valeur des jeux Flous à Paiements Latéraux. C R Hebd Séances Acad Sci 279-A:891–894
Butnariu D (1980) Stability and shapley value for an n-persons fuzzy game. Fuzzy Sets Syst 4:63–72
Butnariu D, Kroupa T (2008) Shapley mappings and the cumulative value for n-person game with fuzzy coalitions. Eur J Oper Res 186:288–299
Carvalho RC, Magrini A (2006) Conflicts over water resource management in Brazil: a case study of inter-basin transfers. Water Resour Manag 20(2):193–213
Kucukmehmetoglu M (2009) A game theoretic approach to assess the impacts of major investments on transboundary water resources: the case of the Euphrates and Tigris. Water Resour Manag 23:3069–3099
Li S, Zhang Q (2009) A simplified expression of the shapley function for fuzzy game. Eur J Oper Res 196:234–245
Luss H (1999) On equitable resource allocation problems: a lexicographic minimax approach. Oper Res 47(3):361–378
Ma J, Hipel KW, De M, Cai J (2008) Transboundary water policies: assessment, comparison and enhancement. Water Resour Manag 22(2008):1069–1087
Mahab-Ghods Consulting Engineers (2004) Environmental impact assessment of water transfer project from the Karoon river to the Rafsanjan region. Technical report
Mahjouri N, Ardestani M (2009) A game theoretic approach for interbasin water resources allocation considering the water quality issues. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-1070-y
Mylopoulos Y, Kolokytha E, Kampragou E, Vagiona D (2008) A combined methodology for transboundary river basin management in Europe. Application in The Nestos–Mesta Catchment Area. Water Resour Manag 22:1101–1112
Niksokhan MH, Kerachian R, Karamouz M (2009) A game theoretic approach for trading discharge permits in rivers. Water Sci Technol 60(3):793–804. doi:10.2166/wst.2009.394
Rahnama MR (2007) Assessment of the land subsidence in the Rafsanjan plain. Technical Report
Shapley LS (1953) A value for n-person game. Ann Math Stud 28:307–318
Tisdell JG, Harrison SR (1992) Estimating an optimal distribution of water entitlements. Water Resour Res 28:3111–3117
Tsurumi M, Tanino T, Inuiguchi M (2001) Theory and methodology-a shapley function on a class of cooperative fuzzy games. Eur J Oper Res 129:596–618
Von Neumann J, Morgenstern O (1944) Theory of games and economic behavior, 3rd edn. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Wang L, Fang L, Hipel KW (2007) Mathematical programming approaches for modeling water rights allocation. J Water Resour Plan Manage 133(1):50–59
Wang L, Fang L, Hipel KW (2008) Basin-wide cooperative water resources allocation. Eur J Oper Res, Elsevier 190(3):798–817
Winter E (2002) The Shapley value. In: Aumann RJ, Hart S (ed) Handbook of game theory with economic applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 2025–2054
Xuesen L, Bende W, Mehrotra R, Sharma A, Guoli W (2009) Consideration of trends in evaluating inter-basin water transfer alternatives within a fuzzy decision making framework. Water Resour Manag 23:3207–3220
Young HP, Okada N, Hashimoto T (1982) Cost allocation in water resources development. Water Resour Res 18:463–475
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadegh, M., Mahjouri, N. & Kerachian, R. Optimal Inter-Basin Water Allocation Using Crisp and Fuzzy Shapley Games. Water Resour Manage 24, 2291–2310 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9552-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9552-9