Abstract
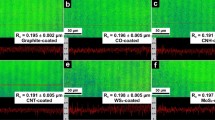
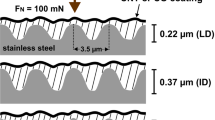
In the present study, a systematic evaluation of the influence of the surface roughness on the lubrication activity of multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) and onion-like carbon (OLC) is performed. MWCNT and OLC are chosen as they both present an sp2-hybridization of carbon atoms, show a similar layered atomic structure, and exhibit the potential to roll on top of a surface. However, their morphology (size and aspect ratio) clearly differs, allowing for a methodical study of these differences on the lubrication effect on systematically varied surface roughness. Stainless steel platelets with different surface finishing were produced and coated by electrophoretic deposition with OLC or MWCNT. The frictional behavior is recorded using a ball-on-disk tribometer, and the resulting wear tracks are analyzed by scanning electron microscopy in order to reveal the acting tribological mechanisms. It is found that the lubrication mechanism of both types of particles is traced back to a mixture between a rolling motion on the surfaces and particle degradation, including the formation of nanocrystalline graphitic layers. This investigation further highlights that choosing the suitable surface finish for a tribological application is crucial for achieving beneficial tribological effects of carbon nanoparticle lubricated surfaces.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holmberg, K., Andersson, P., Erdemir, A.: Global energy consumption due to friction in passenger cars. Tribol. Int. 47, 221–234 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2011.11.022
Donnet, C., Erdemir, A.: Solid lubricant coatings: recent developments and future trends. Tribol. Lett. 17, 389–397 (2004)
Aouadi, S.M., Gao, H., Martine, A., Scharf, T.W., Muratore, C.: Lubricious oxide coatings for extreme temperature applications: a review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 257, 266–277 (2014)
Li, Y., Li, B.X., Zou, W.J.: The relationship between nanocrystalline structure and frictional properties of nanodiamond/Ni composite coatings by brush plating. Appl. Mech. Mater. 80–81, 683–687 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.80-81.683
Hirata, A., Yoshioka, N.: Sliding friction properties of carbon nanotube coatings deposited by microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition. Tribol. Int. 37, 893–898 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2004.07.005
Miyoshi, K., Street Jr., K.W., Vander Wal, R.L., Andrews, R., Sayir, A.: Solid lubrication by multiwalled carbon nanotubes in air and in vacuum. Tribol. Lett. 19, 191–201 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-005-6146-4
Reinert, L., Suárez, S., Rosenkranz, A.: Tribo-mechanisms of carbon nanotubes: friction and wear behavior of CNT-reinforced nickel matrix composites and CNT-coated bulk nickel. Lubricants 4, 11 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants4020011
Gogotsi, Y., Presser, V.: Carbon Nanomaterials. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2014). ISBN 9781138076815
Bakshi, S.R., Lahiri, D., Agarwal, A.: Carbon nanotube reinforced metal matrix composites—a review. Int. Mater. Rev. 55, 41–64 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1179/095066009X12572530170543
Mochalin, V.N., Shenderova, O., Ho, D., Gogotsi, Y.: The properties and applications of nanodiamonds. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 11–23 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2011.209
Iijima, S.: Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354, 56–58 (1991)
Cebik, J., McDonough, J.K., Peerally, F., Medrano, R., Neitzel, I., Gogotsi, Y., Osswald, S.: Raman spectroscopy study of the nanodiamond-to-carbon onion transformation. Nanotechnology 24, 1–10 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/24/20/205703
Zeiger, M., Jäckel, N., Aslan, M., Weingarth, D., Presser, V.: Understanding structure and porosity of nanodiamond-derived carbon onions. Carbon 84, 584–598 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.12.050
Reinert, L., Lasserre, F., Gachot, C., Grützmacher, P., MacLucas, T., Souza, N., Mücklich, F., Suarez, S.: Long-lasting solid lubrication by CNT-coated patterned surfaces. Sci. Rep. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42873
Hu, J.J., Jo, S.H., Ren, Z.F., Voevodin, A., Zabinski, J.S.: Tribological behavior and graphitization of carbon nanotubes grown on 440C stainless steel. Tribol. Lett. 19, 119–125 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-005-5091-6
Tunable friction behavior of oriented carbon nanotube films: Dickrell, P.L., Pal, S.K., Bourne, G.R., Muratore, C., Voevodin, a. a., Ajayan, P.M., Schadler, L.S., Sawyer, W.G. Tribol. Lett. 24, 85–90 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-006-9162-0
Zhang, X., Luster, B., Church, A., Muratore, C., Voevodin, A.A., Kohli, P., Aouadi, S., Talapatra, S.: Carbon nanotube-MoS2 composites as solid lubricants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 1, 735–739 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/am800240e
Arai, S., Fujimori, A., Murai, M., Endo, M.: Excellent solid lubrication of electrodeposited nickel-multiwalled carbon nanotube composite films. Mater. Lett. 62, 3545–3548 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2008.03.047
Chen, W.X., Tu, J.P., Wang, L.Y., Gan, H.Y., Xu, Z.D., Zhang, X.B.: T ribological application of carbon nanotubes in a metal-based composite coating and composites. Carbon 41, 215–222 (2003)
Kim, K.T., Cha, S.I., Hong, S.H.: Hardness and wear resistance of carbon nanotube reinforced Cu matrix nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 449–451, 46–50 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.02.310
Scharf, T.W., Neira, A., Hwang, J.Y., Tiley, J., Banerjee, R.: Self-lubricating carbon nanotube reinforced nickel matrix composites. J. Appl. Phys. 106, 013508 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3158360
Chen, C.S., Chen, X.H., Xu, L.S., Yang, Z., Li, W.H.: Modification of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with fatty acid and their tribological properties as lubricant additive. Carbon 43, 1660–1666 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2005.01.044
Peng, Y., Hu, Y., Wang, H.: Tribological behaviors of surfactant-functionalized carbon nanotubes as lubricant additive in water. Tribol. Lett. 25, 247–253 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-006-9176-7
Lu, H.F., Fei, B., Xin, J.H., Wang, R.H., Li, L., Guan, W.C.: Synthesis and lubricating performance of a carbon nanotube seeded miniemulsion. Carbon 45, 936–942 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2007.01.001
Dickrell, P.L., Sinnott, S.B., Hahn, D.W., Raravikar, N.R., Schadler, L.S., Ajayan, P.M., Sawyer, W.G.: Frictional anisotropy of oriented carbon nanotube surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 18, 59–62 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-004-1752-0
Ni, B., Sinnott, S.B.: Tribological properties of carbon nanotube bundles predicted from atomistic simulations. Surf. Sci. 487, 87–96 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-6028(01)01073-1
Martin, J.M., Ohmae, N.: Nanolubricants. Wiley, New York (2008). ISBN 978-0-470-06552-5
Hirata, A., Igarashi, M., Kaito, T.: Study on solid lubricant properties of carbon onions produced by heat treatment of diamond clusters or particles. Tribol. Int. 37, 899–905 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2004.07.006
Park, S., Srivastava, D., Cho, K.: Generalized chemical reactivity of curved surfaces: carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 3, 1273–1277 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl0342747
Street, K.W., Marchetti, M., Vander Wal, R.L., Tomasek, A.J.: Evaluation of the tribological behavior of nano-onions in Krytox 143AB. Tribol. Lett. 16, 143–149 (2004)
Bucholz, E.W., Phillpot, S.R., Sinnott, S.B.: Molecular dynamics investigation of the lubrication mechanism of carbon nano-onions. Comput. Mater. Sci. 54, 91–96 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2011.09.036
Menezes, P.L., Kishore, Kailas, S.V.: Effect of surface roughness parameters and surface texture on friction and transfer layer formation in tin–steel tribo-system. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 208, 372–382 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.01.003
Persson, B.N.J., Albohr, O., Tartaglino, U., Volokitin, A.I., Tosatti, E.: On the nature of surface roughness with application to contact mechanics, sealing, rubber friction and adhesion. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/17/1/r01
Sahin, M., Çetinarslan, C.S., Akata, H.E.: Effect of surface roughness on friction coefficients during upsetting processes for different materials. Mater. Des. 28, 633–640 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2005.07.019
Svahn, F., Kassman-Rudolphi, Å., Wallén, E.: The influence of surface roughness on friction and wear of machine element coatings. Wear 254, 1092–1098 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(03)00341-7
Komvopoulos, K.: Adhesion and friction forces in microelectromechanical systems: mechanisms, measurement, surface modification techniques, and adhesion theory. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 17, 477–517 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1163/15685610360554384
Bowden, F.P., Tabor, D.: Mechanism of metallic friction. Nature 3798, 197–199 (1942). https://doi.org/10.1038/150197a0
Czichos, H., Habig, K.: Tribologie-Handbuch. Vieweg + Teubner, Wiesbaden (2010). ISBN 978-3-8348-0017-6
Hirano, M., Shinjo, K., Kaneko, R., Murata, Y.: Anisotropy of frictional forces in muscovite mica. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 2642–2646 (1991)
Dienwiebel, M., Verhoeven, G., Pradeep, N., Frenken, J., Heimberg, J., Zandbergen, H.: Superlubricity of graphite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 126101 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.126101
Tomlinson, G.A.: A molecular theory of friction. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 7, 905–939 (1929). https://doi.org/10.1080/14786440608564819
Weiss, M., Elmer, F.: Dry friction in the Frenkel–Kontorova–Tomlinson model: static properties. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 53, 7539–7549 (1996)
Etsion, I.: State of the art in laser surface texturing. J. Tribol. Trans. ASME 127, 248 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1828070
Rapoport, L., Moshkovich, A., Perfilyev, V., Gedanken, A., Koltypin, Y., Sominski, E., Halperin, G., Etsion, I.: Wear life and adhesion of solid lubricant films on laser-textured steel surfaces. Wear 267, 1203–1207 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2009.01.053
Gachot, C., Rosenkranz, A., Reinert, L., Ramos-Moore, E., Souza, N., Müser, M.H., Mücklich, F.: Dry friction between laser-patterned surfaces: role of alignment, structural wavelength and surface chemistry. Tribol. Lett. 9, 193–202 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-012-0057-y
Rosenkranz, A., Reinert, L., Gachot, C., Mücklich, F.: Alignment and wear debris effects between laser-patterned steel surfaces under dry sliding conditions. Wear 318, 49–61 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2014.06.016
Sondhauß, J., Fuchs, H., Schirmeisen, A.: Frictional properties of a mesoscopic contact with engineered surface roughness. Tribol. Lett. 42, 319–324 (2011)
Persson, B.N.J.: Contact mechanics for randomly rough surfaces. Surf. Sci. Rep. 61, 201–227 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfrep.2006.04.001
Greenwood, J., Williamson, J.: Contact of nominally flat surfaces. R. Soc. Publ. 295, 300–319 (1966)
Jackson, R.L., Green, I.: A statistical model of elasto-plastic asperity contact between rough surfaces. Tribol. Int. 39, 906–914 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2005.09.001
Akbulut, M.: Nanoparticle-based lubrication systems. J. Powder Metall. Min. 1, 377–411 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118483961.ch17
Wu, Y.Y., Tsui, W.C., Liu, T.C.: Experimental analysis of tribological properties of lubricating oils with nanoparticle additives. Wear 262, 819–825 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2006.08.021
Ivanov, M.G., Ivanov, D.M., Pavlyshko, S.V., Petrov, I., Vargas, A., McGuire, G., Shenderova, O.: Nanodiamond-based nanolubricants. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 20, 606–610 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/1536383x.2012.657010
Joly-Pottuz, L., Vacher, B., Ohmae, N., Martin, J.M., Epicier, T.: Anti-wear and friction reducing mechanisms of carbon nano-onions as lubricant additives. Tribol. Lett. 30, 69–80 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-008-9316-3
Khalilpourazary, S., Meshkat, S.S.: Investigation of the effects of alumina nanoparticles on spur gear surface roughness and hob tool wear in hobbing process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 71, 1599–1610 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5591-8
Rahmati, B., Sarhan, A.A.D., Sayuti, M.: Investigating the optimum molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanolubrication parameters in CNC milling of AL6061-T6 alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 70, 1143–1155 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5334-x
Hwang, Y., Lee, C., Choi, Y., Cheong, S., Kim, D., Lee, K., Lee, J., Kim, S.H.: Effect of the size and morphology of particles dispersed in nano-oil on friction performance between rotating discs. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 25, 2853–2857 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-011-0724-1
Kogovšek, J., Remškar, M., Mrzel, A., Kalin, M.: Influence of surface roughness and running-in on the lubrication of steel surfaces with oil containing MoS2 nanotubes in all lubrication regimes. Tribol. Int. 61, 40–47 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2012.12.003
Tevet, O., Von-Huth, P., Popovitz-Biro, R., Rosentsveig, R., Wagner, H.D., Tenne, R.: Friction mechanism of individual multilayered nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 108, 19901–19906 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1106553108
Majumder, M., Rendall, C., Li, M., Behabtu, N., Eukel, J.A., Hauge, R.H., Schmidt, H.K., Pasquali, M.: Insights into the physics of spray coating of SWNT films. Chem. Eng. Sci. 65, 2000–2008 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2009.11.042
Mirri, F., Ma, A.W.K., Hsu, T.T., Behabtu, N., Eichmann, S.L., Young, C.C., Tsentalovich, D.E., Pasquali, M.: High-performance carbon nanotube transparent conductive films by scalable dip coating. ACS Nano 6, 9737–9744 (2012)
De Nicola, F., Castrucci, P., Scarselli, M., Nanni, F., Cacciotti, I., De Crescenzi, M.: Super-hydrophobic multi-walled carbon nanotube coatings for stainless steel. Nanotechnology 26, 145701 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/26/14/145701
Boccaccini, A.R., Cho, J., Roether, J.A., Thomas, B.J.C., Jane Minay, E., Shaffer, M.S.P.: Electrophoretic deposition of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 44, 3149–3160 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2006.06.021
Besra, L., Liu, M.: A review on fundamentals and applications of electrophoretic deposition (EPD). Prog. Mater Sci. 52, 1–61 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2006.07.001
Reinert, L., Zeiger, M., Suarez, S., Presser, V., Mücklich, F.: Dispersion analysis of carbon nanotubes, carbon onions, and nanodiamonds for their application as reinforcement phase in nickel metal matrix composites. RSC Adv. 5, 95149–95159 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA14310A
De Riccardis, M.F., Carbone, D., Rizzo, A.: A novel method for preparing and characterizing alcoholic EPD suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 307, 109–115 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2006.10.037
Yen, B.K., Ishihara, T.: Effect of humidity on friction and wear of Al–Si eutectic alloy and Al–Si alloy-graphite composites. Wear 198, 169–175 (1996)
Savage, R.H.: Graphite lubrication. J. Appl. Phys. 19, 1 (1948). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1697867
Berman, D., Erdemir, A., Sumant, A.V.: Graphene: a new emerging lubricant. Mater. Today 17, 31–42 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2013.12.003
Blau, P.J.: On the nature of running-in. Tribol. Int. 38, 1007–1012 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2005.07.020
Dogan, H., Findik, F., Morgul, O.: Friction and wear behaviour of implanted AISI 316L SS and comparison with a substrate. Mater. Des. 23, 605–610 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-3069(02)00066-3
Acknowledgements
The present work is supported by funding from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, project: MU 959/38-1 and SU 911/1-1). L. R., S.S., and F. M. wish to acknowledge the EFRE Funds of the European Commission for support of activities within the AMELab project. This work was supported by the CREATe-Network Project, Horizon 2020 of the European Commission (RISE Project No. 644013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reinert, L., Schütz, S., Suárez, S. et al. Influence of Surface Roughness on the Lubrication Effect of Carbon Nanoparticle-Coated Steel Surfaces. Tribol Lett 66, 45 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-018-1001-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-018-1001-6