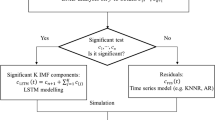
Abstract
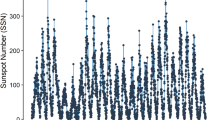
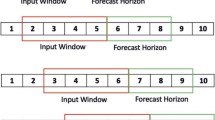
Solar activity directly influences the heliospheric environment and lives on the Earth. Sunspot number (SN) is one of the most crucial and commonly predicted solar activity indices. The prediction of SN time series is a challenging problem owing to its non-stationary, non-Gaussian and nonlinear nature. Therefore, improving the forecasting accuracy of SN time series is an important and challenging task. Motivated from this, in this paper, we have proposed a hybridization of the autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA); exponential smoothing with error, trend and seasonality (ETS); and support vector machine (SVM) to predict monthly and yearly SN time series. In this method, first ARIMA, ETS and SVM with linear kernel function are applied to the SN time series and the maximum of forecasts are determined to obtain the forecasts on linear component. Then the residual series is obtained by subtracting the forecasts on linear component from SN time series. The residual series is considered as nonlinear and modeled using SVM with Gaussian kernel function. Then the forecasts on linear component are added with the forecasts on nonlinear component to obtain the final forecasts. To evaluate the efficiency of the proposed method, three constituent models, one of the most popular deep learning models long short-term memory (LSTM), four hybrid methods, four ensemble methods are considered. Furthermore, two horizons, monthly and yearly sunspot time series are considered to evaluate the robustness of the proposed method. Results indicate the statistical superiority of the proposed methods over different horizons considering different accuracy measures.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arlt, R., Weiss, N.: 2014, Solar activity in the past and the chaotic behaviour of the dynamo. Space Sci. Rev. 186(1–4), 525. DOI.
Attia, A., Ismail, H.A., Basurah, H.M.: 2013, A neuro-fuzzy modeling for prediction of Solar Cycles 24 and 25. Astrophys. Space Sci. 344, 5. DOI.
Babu, C.N., Reddy, B.E.: 2014, A moving-average filter based hybrid ARIMA–ANN model for forecasting time series data. Appl. Soft Comput. 23,pp, 27. DOI.
Bisoi, S.K., Janardhan, P., Ananthakrishnan, S.: 2020, Another mini solar maximum in the offing: a prediction for the amplitude of solar Cycle 25. J. Geophys. Res. 125(7), e2019JA027508. DOI.
Box, G.E., Jenkins, G.M., Reinsel, G.C., Ljung, G.M.: 2015, Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, Wiley, New York.
Demsar, J.: 2006, Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 7, 1.
Gardner, E.S.: 1985, Exponential smoothing: the state of the art. J. Forecast. 4, 1. DOI.
Hollander, M., Wolfe, D.A., Chicken, E.: 1999, Nonparametric Statistical Methods, Wiley, Hoboken.
Holt, C.E.: 2004, Forecasting seasonals and trends by exponentially weighted averages. Int. J. Forecast. 20(1), 5. DOI.
Hyndman, R.J., Khandakar, Y.: 2008, Automatic time series forecasting: the forecast package for R. J. Stat. Softw. 26(3), 1. DOI.
Hyndman, R.J., Koehler, R., Ord, A.B., Snyder, R.D.: 2008, Forecasting with Exponential Smoothing: The State Space Approach, Springer, Berlin.
Hyndman, R.J., Koehler, A.B.: 2006, Another look at measures of forecast accuracy. Int. J. Forecast. 22(4), 679. DOI.
Jiang, C., Song, F.: 2011, Sunspot forecasting by using chaotic time series analysis and NARX network. J. Comput. 6(7), 1424. DOI.
Kane, R.P.: 2013, An estimate for the size of sunspot Cycle 24. Solar Phys. 282(1), 87. DOI.
Kane, R.P.: 2007, A preliminary estimate of the size of the coming solar Cycle 24, based on Ohl’s precursor method. Solar Phys. 243, 205. DOI.
Li, K., Feng, W., Li, F.: 2015, Predicting the maximum amplitude of Solar Cycle 25 and its timing. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 135, 72. DOI.
Labonville, F., Charbonneau, P., Lemerle, A.: 2019, A dynamo-based forecast of solar Cycle 25. Solar Phys. 294, 82. DOI.
Noyes, R.W.: 1982, The Sun, Our Star, Harvard University Press, Cambridge.
Okoh, D., Seemala, G., Rabiu, A., Uwamahoro, J., Habarulema, J., Aggarwal, M.: 2018, A hybrid regression-neural network (HR-NN) method for forecasting the solar activity. Space Weather 16, 1424. DOI.
Oliveira, J.F., Ludermir, T.B.: 2016, A hybrid evolutionary decomposition system for time series forecasting. Neurocomputing 180, 27. DOI.
Pala, Z., Atici, R.: 2019, Forecasting sunspot time series using deep learning methods. Solar Phys. 294, 1. DOI.
Panigrahi, S., Behera, H.S., Abraham, A.: 2018, A fuzzy filter based hybrid ARIMA-ANN model for time series forecasting. In: Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Soft Computing and Pattern Recognition (SoCPaR 2016), Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing 614, Springer, Cham, 592. DOI.
Panigrahi, S., Behera, H.S.: 2017, A hybrid ETS-ANN model for time series forecasting. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 66, 49. DOI.
Pegels, C.C.: 1969, Exponential forecasting: some new variations. Manag. Sci. 15(5), 311. https://www.jstor.org/stable/2628137.
Pesnell, W.D., Schatten, K.H.: 2018, An early prediction of the amplitude of Solar Cycle 25. Solar Phys. 293, 112. DOI.
Pishkalo, M.I.: 2014, Prediction of Solar Cycle 24 using sunspot number near the cycle minimum. Solar Phys. 289, 1815. DOI.
Quassim, M.S., Attia, A., Elminir, H.K.: 2007, Forecasting the peak amplitude of the 24th and 25th sunspot cycles and accompanying geomagnetic activity. Solar Phys. 243, 253. DOI.
Rigozo, N., Echer, M.S., Evangelista, H., Nordemann, D., Echer, E.: 2011, Prediction of sunspot number amplitude and solar cycle length for Cycles 24 and 25. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 73, 1294. DOI.
Sabarinath, A., Anilkumar, A.K.: 2018, Sunspot cycle prediction using multivariate regression and binary mixture of Laplace distribution model. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 127, 84. DOI.
Tang, J., Zhang, X.: 2012, Prediction of smoothed monthly mean sunspot number based on chaos theory. Acta Phys. Sin. 61(16), 169601. DOI.
Taylor, J.W.: 2003, Exponential smoothing with a damped multiplicative trend. Int. J. Forecast. 19, 715. DOI.
Vapnik, V.N.: 1995, The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory, Springer, Berlin.
Vapnik, V.N.: 1998, Statistical Learning Theory, Wiley, New York.
Wang, L., Zou, H., Su, J., Li, L., Chaudhry, S.: 2013, An ARIMA-ANN hybrid model for time series forecasting. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 30(3), 244. DOI.
Winters, P.R.: 1960, Forecasting sales by exponentially weighted moving averages. Manag. Sci. 6, 324. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2627346.
Zhang, G.: 2003, Time series forecasting using a hybrid ARIMA and neural network model. Neurocomputing 50, 159. DOI.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions which significantly improved the quality of the paper. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Prabhat Kumar Sahu, Reader, Sambalpur University, Odisha, India for providing the computational resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panigrahi, S., Pattanayak, R.M., Sethy, P.K. et al. Forecasting of Sunspot Time Series Using a Hybridization of ARIMA, ETS and SVM Methods. Sol Phys 296, 6 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01757-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01757-2