Abstract
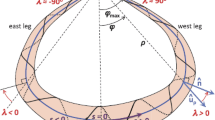
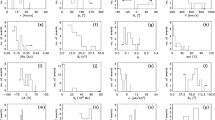
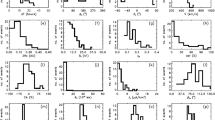
Magnetic clouds (MCs) are a subset of ejecta, launched from the Sun as coronal mass ejections. The coherent rotation of the magnetic field vector observed in MCs leads to envision MCs as formed by flux ropes (FRs). Among all the methods used to analyze MCs, Lepping’s method (Lepping, Burlaga, and Jones in J. Geophys. Res.95, 11957, 1990) is the broadest used. While this fitting method does not require the axial field component to vanish at the MC boundaries, this idea is largely spread in publications. We revisit Lepping’s method to emphasize its hypothesis and the meaning of its output parameters. As originally defined, these parameters imply a fitted FR which could be smaller or larger than the studied MC. We rather provide a re-interpretation of Lepping’s results with a fitted model limited to the observed MC interval. We find that typically the crossed FRs are asymmetric with a larger side both in size and magnetic flux before or after the FR axis. At the boundary of the largest side we find an axial magnetic field component distributed around zero which we justify by the physics of solar eruptions. In contrast, at the boundary of the smaller side the axial field distribution is shifted to positive values, as expected with erosion acting during the interplanetary travel. This new analysis of Lepping’s results has several implications. First, global quantities, such as magnetic fluxes and helicity, need to be revised depending on the aim (estimating global properties of FRs just after the solar launch or at 1 au). Second, the deduced twist profiles in MCs range quasi-continuously from nearly uniform, to increasing away from the FR axis, up to a reversal near the MC boundaries. There is no trace of outsider cases, but a continuum of cases. Finally, the impact parameter of the remaining FR crossed at 1 au is revised. Its distribution is compatible with weakly flattened FR cross-sections.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Haddad, N., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Savani, N.P., Möstl, C., Marubashi, K., Hidalgo, M.A., Roussev, I.I., Poedts, S., Farrugia, C.J.: 2013, Magnetic field configuration models and reconstruction methods for interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys.284, 129. DOI . ADS .
Asai, A., Ishii, T.T., Kurokawa, H., Yokoyama, T., Shimojo, M.: 2003, Evolution of conjugate footpoints inside flare ribbons during a great two-ribbon flare on 2001 April 10. Astrophys. J.586, 624. DOI . ADS .
Aulanier, G., Janvier, M., Schmieder, B.: 2012, The standard flare model in three dimensions. I. Strong-to-weak shear transition in post-flare loops. Astron. Astrophys.543, A110. DOI . ADS .
Berger, M.A.: 2003, In: Ferriz-Mas, A., Núñez, M. (eds.) Topological Quantities in Magnetohydrodynamics, 345. DOI . ADS .
Burlaga, L.F.: 1995, Interplanetary magnetohydrodynamics. In: Interplanetary Magnetohydrodynamics3. ADS .
Burlaga, L.F., Behannon, K.W.: 1982, Magnetic clouds – Voyager observations between 2 and 4 AU. Solar Phys.81, 181. DOI . ADS .
Burlaga, L., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., Schwenn, R.: 1981, Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock – Voyager, Helios, and IMP 8 observations. J. Geophys. Res.86, 6673. DOI . ADS .
Burlaga, L., Fitzenreiter, R., Lepping, R., Ogilvie, K., Szabo, A., Lazarus, A., Steinberg, J., Gloeckler, G., Howard, R., Michels, D., Farrugia, C., Lin, R.P., Larson, D.E.: 1998, A magnetic cloud containing prominence material – January 1997. J. Geophys. Res.103, 277. DOI . ADS .
Cho, K.-S., Park, S.-H., Marubashi, K., Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Kim, R.-S., Lim, E.-K.: 2013, Comparison of helicity signs in interplanetary CMEs and their solar source regions. Solar Phys.284(1), 105. DOI . ADS .
Dasso, S., Mandrini, C.H., Démoulin, P., Farrugia, C.J.: 2003, Magnetic helicity analysis of an interplanetary twisted flux tube. J. Geophys. Res.108, 1362. DOI . ADS .
Dasso, S., Mandrini, C.H., Démoulin, P., Luoni, M.L., Gulisano, A.M.: 2005a, Large scale MHD properties of interplanetary magnetic clouds. Adv. Space Res.35, 711. DOI . ADS .
Dasso, S., Mandrini, C.H., Gulisano, A.M., Démoulin, P.: 2005b, A direct method to estimate magnetic helicity in magnetic clouds. In: Dere, K., Wang, J., Yan, Y. (eds.) Coronal and Stellar Mass Ejections, IAU Symposium226, 403. DOI . ADS .
Dasso, S., Mandrini, C.H., Démoulin, P., Luoni, M.L.: 2006, A new model-independent method to compute magnetic helicity in magnetic clouds. Astron. Astrophys.455, 349. DOI . ADS .
Dasso, S., Nakwacki, M.S., Démoulin, P., Mandrini, C.H.: 2007, Progressive transformation of a flux rope to an ICME. Comparative analysis using the direct and fitted expansion methods. Solar Phys.244, 115. DOI . ADS .
Démoulin, P., Dasso, S.: 2009, Causes and consequences of magnetic cloud expansion. Astron. Astrophys.498, 551. DOI . ADS .
Démoulin, P., Dasso, S., Janvier, M.: 2013, Does spacecraft trajectory strongly affect detection of magnetic clouds? Astron. Astrophys.550, A3. DOI . ADS .
Démoulin, P., Nakwacki, M.S., Dasso, S., Mandrini, C.H.: 2008, Expected in situ velocities from a hierarchical model for expanding interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys.250, 347. DOI . ADS .
Farrugia, C.J., Janoo, L.A., Torbert, R.B., Quinn, J.M., Ogilvie, K.W., Lepping, R.P., Fitzenreiter, R.J., Steinberg, J.T., Lazarus, A.J., Lin, R.P., Larson, D., Dasso, S., Gratton, F.T., Lin, Y., Berdichevsky, D.: 1999, A uniform-twist magnetic flux rope in the solar wind. In: Habbal, S.R., Esser, R., Hollweg, J.V., Isenberg, P.A. (eds.) American Institute of Physics Conference Series471, 745. DOI . ADS .
Gold, T., Hoyle, F.: 1960, On the origin of solar flares. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc.120, 89. DOI . ADS .
Goldstein, H.: 1983, On the field configuration in magnetic clouds. In: NASA Conference Publication, 228. 0.731. ADS .
Good, S.W., Kilpua, E.K.J., LaMoury, A.T., Forsyth, R.J., Eastwood, J.P., Möstl, C.: 2019, Self-similarity of ICME flux ropes: Observations by radially aligned spacecraft in the inner heliosphere. J. Geophys. Res.124(7), 4960. DOI . ADS .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S., Xie, H.: 2017, Estimation of reconnection flux using post-eruption arcades and its relevance to magnetic clouds at 1 AU. Solar Phys.292, 65. DOI . ADS .
Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Xie, H.: 2018, Coronal flux ropes and their interplanetary counterparts. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys.180, 35. DOI . ADS .
Gosling, J.T.: 1990, Coronal Mass Ejections and Magnetic Flux Ropes in Interplanetary Space, Washington DC American Geophysical Union Geophysical Monograph Series58, 343. DOI . ADS .
Gulisano, A.M., Démoulin, P., Dasso, S., Ruiz, M.E., Marsch, E.: 2010, Global and local expansion of magnetic clouds in the inner heliosphere. Astron. Astrophys.509, A39. DOI . ADS .
Hidalgo, M.A., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Cid, C.: 2002, Elliptical cross-section model for the magnetic topology of magnetic clouds. Geophys. Res. Lett.29, 1637. DOI . ADS .
Hu, Q., Qiu, J., Krucker, S.: 2015, Magnetic field line lengths inside interplanetary magnetic flux ropes. J. Geophys. Res.120(7), 5266. DOI . ADS .
Hu, Q., Qiu, J., Dasgupta, B., Khare, A., Webb, G.M.: 2014, Structures of interplanetary magnetic flux ropes and comparison with their solar sources. Astrophys. J.793, 53. DOI . ADS .
Janvier, M.: 2017, Three-dimensional magnetic reconnection and its application to solar flares. J. Plasma Phys.83(1), 535830101. DOI . ADS .
Janvier, M., Démoulin, P., Dasso, S.: 2013, Global axis shape of magnetic clouds deduced from the distribution of their local axis orientation. Astron. Astrophys.556, A50. DOI . ADS .
Janvier, M., Dasso, S., Démoulin, P., Masías-Meza, J.J., Lugaz, N.: 2015, Comparing generic models for interplanetary shocks and magnetic clouds axis configurations at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res.120, 3328. DOI . ADS .
Jian, L., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Skoug, R.M.: 2008, Evolution of solar wind structures from 0.72 to 1 AU. Adv. Space Res.41(2), 259. DOI . ADS .
Kilpua, E.K.J., Liewer, P.C., Farrugia, C., Luhmann, J.G., Möstl, C., Li, Y., Liu, Y., Lynch, B.J., Russell, C.T., Vourlidas, A., Acuna, M.H., Galvin, A.B., Larson, D., Sauvaud, J.A.: 2009, Multispacecraft observations of magnetic clouds and their solar origins between 19 and 23 May 2007. Solar Phys.254, 325. DOI .
Kliem, B., Török, T., Thompson, W.T.: 2012, A parametric study of erupting flux rope rotation. Modeling the “cartwheel CME” on 9 April 2008. Solar Phys.281(1), 137. DOI . ADS .
Lavraud, B., Ruffenach, A., Rouillard, A.P., Kajdic, P., Manchester, W.B., Lugaz, N.: 2014, Geo-effectiveness and radial dependence of magnetic cloud erosion by magnetic reconnection. J. Geophys. Res.119(1), 26. DOI . ADS .
Leitner, M., Farrugia, C.J., Möstl, C., Ogilvie, K.W., Galvin, A.B., Schwenn, R., Biernat, H.K.: 2007, Consequences of the force-free model of magnetic clouds for their heliospheric evolution. J. Geophys. Res.112, A06113. DOI . ADS .
Lepping, R.P., Berdichevsky, D.B., Ferguson, T.J.: 2003, Estimated errors in magnetic cloud model fit parameters with force-free cylindrically symmetric assumptions. J. Geophys. Res.108(A10), 1356. DOI . ADS .
Lepping, R.P., Burlaga, L.F., Jones, J.A.: 1990, Magnetic field structure of interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res.95, 11957. DOI . ADS .
Lepping, R.P., Wu, C.-C.: 2007, On the variation of interplanetary magnetic cloud type through solar cycle 23: Wind events. J. Geophys. Res.112(A11), 10103. DOI . ADS .
Lepping, R.P., Wu, C.C.: 2010, Selection effects in identifying magnetic clouds and the importance of the closest approach parameter. Ann. Geophys.28, 1539. DOI . ADS .
Lepping, R.P., Berdichevsky, D.B., Szabo, A., Arqueros, C., Lazarus, A.J.: 2003, Profile of an average magnetic cloud at 1 au for the quiet solar phase: Wind observations. Solar Phys.212, 425. DOI . ADS .
Lepping, R.P., Berdichevsky, D.B., Wu, C.C., Szabo, A., Narock, T., Mariani, F., Lazarus, A.J., Quivers, J.: 2006, A summary of Wind magnetic clouds for years 1995–2003: Model-fitted parameters, associated errors and classifications. Ann. Geophys.24, 215. DOI . ADS .
Lepping, R.P., Wu, C.-C., Berdichevsky, D.B., Szabo, A.: 2018, Wind magnetic clouds for the period 2013–2015: Model fitting, types, associated shock waves, and comparisons to other periods. Solar Phys.293(4), 65. DOI . ADS .
Liu, Y., Luhmann, J.G., Müller-Mellin, R., Schroeder, P.C., Wang, L., Lin, R.P., Bale, S.D., Li, Y., Acuña, M.H., Sauvaud, J.-A.: 2008, A comprehensive view of the 2006 December 13 CME: From the Sun to interplanetary space. Astrophys. J.689, 563. DOI . ADS .
Liu, R., Liu, C., Wang, S., Deng, N., Wang, H.: 2010, Sigmoid-to-flux-rope transition leading to a loop-like coronal mass ejection. Astrophys. J. Lett.725, L84. DOI . ADS .
Lundquist, S.: 1950, Magnetohydrostatic fields. Ark. Fys.2, 361.
Lynch, B.J., Zurbuchen, T.H., Fisk, L.A., Antiochos, S.K.: 2003, Internal structure of magnetic clouds: Plasma and composition. J. Geophys. Res.108(A6), A01239. DOI . ADS .
Lynch, B.J., Gruesbeck, J.R., Zurbuchen, T.H., Antiochos, S.K.: 2005, Solar cycle-dependent helicity transport by magnetic clouds. J. Geophys. Res.110, A08107. DOI . ADS .
Marubashi, K., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Cho, K.-S., Park, Y.-D.: 2015, Geometrical relationship between interplanetary flux ropes and their solar sources. Solar Phys.290(5), 1371. DOI . ADS .
Masías-Meza, J.J., Dasso, S., Démoulin, P., Rodriguez, L., Janvier, M.: 2016, Superposed epoch study of ICME sub-structures near Earth and their effects on Galactic cosmic rays. Astron. Astrophys.592, A118. DOI . ADS .
Möstl, C., Farrugia, C.J., Biernat, H.K., Leitner, M., Kilpua, E.K.J., Galvin, A.B., Luhmann, J.G.: 2009, Optimized Grad–Shafranov reconstruction of a magnetic cloud using STEREO-Wind observations. Solar Phys.256, 427. DOI . ADS .
Nakwacki, M., Dasso, S., Démoulin, P., Mandrini, C.H., Gulisano, A.M.: 2011, Dynamical evolution of a magnetic cloud from the Sun to 5.4 AU. Astron. Astrophys.535, A52. DOI . ADS .
Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Hidalgo, M.A., Sequeiros, J.: 2005, Magnetic clouds observed at 1 au during the period 2000–2003. Solar Phys.232(1–2), 105. DOI . ADS .
Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Linton, M.G., Hidalgo, M.A., Vourlidas, A.: 2018, Elliptic-cylindrical analytical flux rope model for magnetic clouds. Astrophys. J.861(2), 139. DOI . ADS .
Nishimura, N., Marubashi, K., Tokumaru, M.: 2019, Comparison of cylindrical interplanetary flux-rope model fitting with different boundary pitch-angle treatments. Solar Phys.294(4), 49. DOI . ADS .
Pal, S., Gopalswamy, N., Nandy, D., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Makela, P., Xie, H.: 2017, A Sun-to-Earth analysis of magnetic helicity of the 2013 March 17–18 interplanetary coronal mass ejection. Astrophys. J.851(2), 123. DOI . ADS .
Qiu, J., Hu, Q., Howard, T.A., Yurchyshyn, V.B.: 2007, On the magnetic flux budget in low-corona magnetic reconnection and interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J.659, 758. DOI . ADS .
Rodriguez, L., Zhukov, A.N., Dasso, S., Mandrini, C.H., Cremades, H., Cid, C., Cerrato, Y., Saiz, E., Aran, A., Menvielle, M., Poedts, S., Schmieder, B.: 2008, Magnetic clouds seen at different locations in the heliosphere. Ann. Geophys.26, 213. DOI . ADS .
Ruffenach, A., Lavraud, B., Farrugia, C.J., Démoulin, P., Dasso, S., Owens, M.J., Sauvaud, J.-A., Rouillard, A.P., Lynnyk, A., Foullon, C., Savani, N.P., Luhmann, J.G., Galvin, A.B.: 2015, Statistical study of magnetic cloud erosion by magnetic reconnection. J. Geophys. Res.120, 43. DOI . ADS .
Schrijver, C.J., Title, A.M.: 2011, Long-range magnetic couplings between solar flares and coronal mass ejections observed by SDO and STEREO. J. Geophys. Res.116(A4), A04108. DOI . ADS .
Shimazu, H., Vandas, M.: 2002, A self-similar solution of expanding cylindrical flux ropes for any polytropic index value. Earth Planets Space54, 783. ADS .
Su, Y.N., Golub, L., van Ballegooijen, A.A., Gros, M.: 2006, Analysis of magnetic shear in an X17 solar flare on October 28, 2003. Solar Phys.236, 325. DOI . ADS .
Thernisien, A.F.R., Howard, R.A., Vourlidas, A.: 2006, Modeling of flux rope coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J.652(1), 763. DOI . ADS .
van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Green, L.M.: 2015, Evolution of active regions. Living Rev. Solar Phys.12(1), 1. DOI . ADS .
van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Baker, D., Török, T., Pariat, E., Green, L.M., Williams, D.R., Carlyle, J., Valori, G., Démoulin, P., Kliem, B., Long, D.M., Matthews, S.A., Malherbe, J.-M.: 2014, Coronal magnetic reconnection driven by CME expansion – The 2011 June 7 event. Astrophys. J.788(1), 85. DOI . ADS .
Vandas, M., Geranios, A.: 2001, November 17–18, 1975, event: A clue to an internal structure of magnetic clouds? J. Geophys. Res.106, 1849. DOI . ADS .
Vandas, M., Romashets, E.P.: 2003, A force-free field with constant alpha in an oblate cylinder: A generalization of the Lundquist solution. Astron. Astrophys.398, 801. DOI . ADS .
Vandas, M., Romashets, E., Geranios, A.: 2015, Modeling of magnetic cloud expansion. Astron. Astrophys.583, A78. DOI . ADS .
Vandas, M., Romashets, E., Watari, S.: 2005, Magnetic clouds of oblate shapes. Planet. Space Sci.53, 19. DOI . ADS .
Vandas, M., Romashets, E.P., Watari, S., Geranios, A., Antoniadou, E., Zacharopoulou, O.: 2006, Comparison of force-free flux rope models with observations of magnetic clouds. Adv. Space Res.38(3), 441. DOI . ADS .
Vemareddy, P., Démoulin, P.: 2017, Successive injection of opposite magnetic helicity in solar active region NOAA 11928. Astron. Astrophys.597, A104. DOI . ADS .
Wang, Y., Zhou, Z., Shen, C., Liu, R., Wang, S.: 2015, Investigating plasma motion of magnetic clouds at 1 AU through a velocity-modified cylindrical force-free flux rope model. J. Geophys. Res.120(3), 1543. DOI . ADS .
Wang, Y., Zhuang, B., Hu, Q., Liu, R., Shen, C., Chi, Y.: 2016, On the twists of interplanetary magnetic flux ropes observed at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res.121, 9316. DOI . ADS .
Wang, Y., Shen, C., Liu, R., Liu, J., Guo, J., Li, X., Xu, M., Hu, Q., Zhang, T.: 2018, Understanding the twist distribution inside magnetic flux ropes by anatomizing an interplanetary magnetic cloud. J. Geophys. Res.123(5), 3238. DOI . ADS .
Welsch, B.T.: 2018, Flux accretion and coronal mass ejection dynamics. Solar Phys.293(7), 113. DOI . ADS .
Wood, B.E., Wu, C.-C., Lepping, R.P., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Howard, R.A., Linton, M.G., Socker, D.G.: 2017, A STEREO survey of magnetic cloud coronal mass ejections observed at Earth in 2008–2012. Astrophys. J. Suppl.229, 29. DOI . ADS .
Zurbuchen, T.H., Richardson, I.G.: 2006, In-situ solar wind and magnetic field signatures of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Space Sci. Rev.123, 31. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgements
We thank the referee for his/her comments which broaden the potential audience of the paper. S.D. acknowledges partial support from the Argentinian grants UBACyT (UBA), and PIP-CONICET-11220130100439CO. This work was partially supported by a one-month invitation of P.D. to the Instituto de Astronomía y Física del Espacio, and by a one-month invitation of S.D. to the Observatoire de Paris. This work was supported by the Programme National PNST of CNRS/INSU co-funded by CNES and CEA. S.D. is member of the Carrera del Investigador Científico, CONICET.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Démoulin, P., Dasso, S., Janvier, M. et al. Re-analysis of Lepping’s Fitting Method for Magnetic Clouds: Lundquist Fit Reloaded. Sol Phys 294, 172 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1564-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1564-x