Abstract
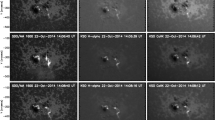
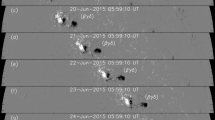
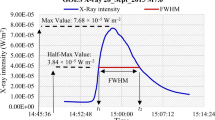
We report on a new method to compute the flare reconnection (RC) flux from post-eruption arcades (PEAs) and the underlying photospheric magnetic fields. In previous works, the RC flux has been computed using the cumulative flare ribbon area. Here we obtain the RC flux as the flux in half of the area underlying the PEA in EUV imaged after the flare maximum. We apply this method to a set of 21 eruptions that originated near the solar disk center in Solar Cycle 23. We find that the RC flux from the arcade method (\(\Phi_{\mathrm{rA}}\)) has excellent agreement with the flux from the flare-ribbon method (\(\Phi_{\mathrm{rR}}\)) according to \(\Phi_{\mathrm{rA}} = 1.24(\Phi_{\mathrm{rR}})^{0.99}\). We also find \(\Phi_{\mathrm{rA}}\) to be correlated with the poloidal flux (\(\Phi_{\mathrm{P}}\)) of the associated magnetic cloud at 1 AU: \(\Phi_{\mathrm{P}} = 1.20(\Phi_{\mathrm{rA}})^{0.85}\). This relation is nearly identical to that obtained by Qiu et al. (Astrophys. J. 659, 758, 2007) using a set of only 9 eruptions. Our result supports the idea that flare reconnection results in the formation of the flux rope and PEA as a common process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aschwanden, M.J., Alexander, D.: 2001, Flare plasma cooling from 30 MK down to 1 MK modeled from Yohkoh, GOES, and TRACE observations during the Bastille Day Event (14 July 2000). Solar Phys. 204, 91. DOI .
Baker, D.N., Pulkkinen, T.I., Li, X., Kanekal, S.G., Blake, J.B., Selesnick, R.S., et al.: 1998, A strong CME-related magnetic cloud interaction with the Earth’s Magnetosphere: ISTP observations of rapid relativistic electron acceleration on May 15, 1997. Geophys. Res. Lett. 29, 2975. DOI .
Brueckner, G.E., Howard, R.A., Koomen, M.J., Korendyke, C.M., Michels, D.J., Moses, J.D., et al.: 1995, The Large Angle Spectroscopic Coronagraph (LASCO). Solar Phys. 162, 357. DOI .
Burlaga, L., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., Schwenn, R.: 1981, Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock – Voyager, Helios, and IMP 8 observations. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 6673. DOI .
Delaboudiniére, J.-P., Artzner, G.E., Brunaud, J., Gabriel, A.H., Hochedez, J.F., Millier, F., et al.: 1995, EIT: Extreme-Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope for the SOHO mission. Solar Phys. 162, 291. DOI .
Domingo, V., Fleck, B., Poland, A.I.: 1995, The SOHO mission: An overview. Solar Phys. 162, 1. DOI .
Gibson, S.E., Fan, Y., Török, T., Kliem, B.: 2006, The evolving sigmoid: Evidence for magnetic flux ropes in the corona before, during, and after CMEs. Space Sci. Rev. 124, 131. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N.: 2009, Coronal mass ejections and space weather. In: Tsuda, T., Fujii, R., Shibata, K., Geller, M.A. (eds.) Climate and Weather of the Sun Earth System (CAWSES): Selected Papers from the 2007 Kyoto Symposium, Terrapub, Tokyo, 77.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S.: 2006, Coronal mass ejections and space weather due to extreme events. In: Gopalswamy, N., Bhattacharyya, A. (eds.) Solar Influence on the Heliosphere and Earth’s Environment: Recent Progress and Prospects, Quest Publications, Mumbai, 79.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Krucker, S., Stenborg, G., Howard, R.A.: 2004, Intensity variation of large solar energetic particle events associated with coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A12105. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Liu, Y., Michalek, G., Vourlidas, A., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A.: 2005, Coronal mass ejections and other extreme characteristics of the 2003 October–November solar eruptions. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A09S15. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Mäkelä, P., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2010, Interplanetary shocks lacking type II radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 710, 1111. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S., Mäkelä, P., Usoskin, I.G.: 2012, Properties of ground level enhancement events and the associated solar eruptions during solar cycle 23. Space Sci. Rev. 171, 23. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Akiyama, S., Xie, H., Yashiro, S., Reinard, A.A.: 2013a, The solar connection of enhanced heavy ion charge states in the interplanetary medium: Implications for the flux-rope structure of CMEs. Solar Phys. 284, 17. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Hidalgo, M., Zhang, J., Riley, P., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Mandrini, C.H.: 2013b, Preface Solar Phys. 284, 1. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Mäkelä, P.: 2015, Properties and geoeffectiveness of magnetic clouds during solar cycles 23 and 24. J. Geophys. Res. 120, 9221. DOI .
Hanaoka, Y., Kurokawa, H., Enome, S., Nakajima, H., Shibasaki, K., Nishio, M., et al.: 1994, Simultaneous observations of a prominence eruption followed by a coronal arcade formation in radio, soft X-rays, and H(alpha). Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 46, 205.
Hu, Q., Qiu, J., Dasgupta, B., Khare, A., Webb, G.M.: 2014, Structures of interplanetary magnetic flux ropes and comparison with their solar sources. Astrophys. J. 793, 53. DOI .
Leamon, R.J., Canfield, R.C., Jones, S.L., Lambkin, K., Lundberg, B.J., Pevtsov, A.A.: 2004, Helicity of magnetic clouds and their associated active regions. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A05106. DOI .
Lepping, R.P., Burlaga, L.F., Jones, J.A.: 1990, Magnetic field structure of interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 95, 11957. DOI .
Lepri, S.T., Zurbuchen, T.H., Fisk, L.A., Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V., Gloeckler, G.: 2001, Iron charge state distributions as an identifier of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 29231. DOI .
Lin, J., Raymond, J.C., van Ballegooijen, A.A.: 2004, The role of magnetic reconnection in the observable features of solar eruptions. Astrophys. J. 602, 422. DOI .
Linton, M.G., Moldwin, M.B.: 2009, A comparison of the formation and evolution of magnetic flux ropes in solar coronal mass ejections and magnetotail plasmoids. J. Geophys. Res. 114, A00B09. DOI .
Longcope, D.W., Beveridge, C.: 2007, Quantitative, topological model of reconnection and flux rope formation in a two-ribbon flare. Astrophys. J. 669, 621. DOI .
Longcope, D., Beveridge, C., Qiu, J., Ravindra, B., Barnes, G., Dasso, S.: 2007, Modeling and measuring the flux reconnected and ejected by the two-ribbon flare/CME event on 7 November 2004. Solar Phys. 244, 45. DOI .
Mäkelä, P., Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Mohamed, A.A., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S.: 2013, Coronal hole influence on the observed structure of interplanetary CMEs. Solar Phys. 284, 59. DOI .
Marubashi, K.: 1997, Interplanetary magnetic flux ropes and solar filaments. In: Crooker, N., Joselyn, J.A., Feynman, J. (eds.) Coronal Mass Ejections, Geophysical Monograph Series 99, American Geophysical Union, Washington DC, 147. DOI .
Marubashi, K., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Cho, K.-S., Park, Y.-D.: 2015, Geometrical relationship between interplanetary flux ropes and their solar sources. Solar Phys. 290, 137. DOI .
Mewaldt, R.A., Looper, M.D., Cohen, C.M.S., Haggerty, D.K., Labrador, A.W., Leske, R.A., Mason, G.M., Mazur, J.E., von Rosenvinge, T.T., et al.: 2012, Energy spectra, composition, and other properties of ground-level events during solar cycle 23. Space Sci. Rev. 171, 97. DOI .
Moore, R.L., Sterling, A.C., Suess, S.T.: 2007, The width of a solar coronal mass ejection and the source of the driving magnetic explosion: A test of the standard scenario for CME production. Astrophys. J. 668, 1221. DOI .
Mouschovias, T.Ch., Poland, A.I.: 1978, Expansion and broadening of coronal loop transients – a theoretical explanation. Astrophys. J. 220, 675. DOI .
Nakai, Y., Hattori, A.: 1985, Domeless solar tower telescope at the Hida Observatory. Mem. Fac. Sci., Kyoto Univ. 36(3), 385.
Nindos, A., Zhang, J., Zhang, H.: 2003, The magnetic helicity budget of solar active regions and coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 594, 1033. DOI .
Qiu, J., Hu, Q., Howard, T.A., Yurchyshyn, V.B.: 2007, On the magnetic flux budget in low-corona magnetic reconnection and interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 659, 758. DOI .
Reinard, A.A.: 2008, analysis of interplanetary coronal mass ejection parameters as a function of energetics, source location, and magnetic structure. Astrophys. J. 682, 1289. DOI .
Reiner, M.J., Kaiser, M.L., Karlický, M., Jiřička, K., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2001, Bastille day event: A radio perspective. Solar Phys. 204, 121. DOI .
Scherrer, P.H., Bogart, R.S., Bush, R.I., Hoeksema, J.T., Kosovichev, A.G., Schou, J., et al.: 1995, The solar oscillations investigation – Michelson Doppler Imager. Solar Phys. 162, 129. DOI .
Strong, K., Bruner, M., Tarbell, T., Title, A., Wolfson, C.J.: 1994, Trace – the transition region and coronal explorer. Space Sci. Rev. 70, 119. DOI .
Thompson, B.J., Plunkett, S.P., Gurman, J.B., Newmark, J.S., St. Cyr, O.C., Michels, D.J.: 1998, SOHO/EIT observations of an Earth-directed coronal mass ejection on May 12, 1997. Geophys. Res. Lett. 24, 2465. DOI .
Titov, V.S., Mikic, Z., Linker, J.A., Lionello, R.: 2008, 1997 May 12 coronal mass ejection event. I. A simplified model of the preeruptive magnetic structure. Astrophys. J. 675, 1614. DOI .
Webb, D.F., Lepping, R.P., Burlaga, L.F., DeForest, C.E., Larson, D.E., Martin, E.F., Plunkett, S.F., Rust, D.M.: 2000, The origin and development of the May 1997 magnetic cloud. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 27251. DOI .
Xie, H., Gopalswamy, N., St. Cyr, O.C.: 2013, Near-Sun flux rope structure of CMEs. Solar Phys. 284, 47. DOI .
Yan, Y., Huang, G.: 2003, Reconstructed 3-d magnetic field structure and hard X-ray two ribbons for 2000 Bastille-day event. Space Sci. Rev. 107, 111. DOI .
Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Akiyama, S., Gopalswamy, N., Howard, R.A.: 2008, Spatial relationship between solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 673, 1174. DOI .
Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Akiyama, S.: 2013, Post-eruption arcades and interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys. 284, 5. DOI .
Zhang, J., Dere, K.P.: 2006, A statistical study of main and residual accelerations of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 649, 1100. DOI .
Zhang, J., Dere, K.P., Howard, R.A., Kundu, M.R., White, S.M.: 2001, On the temporal relationship between coronal mass ejections and flares. Astrophys. J. 559, 452. DOI .
Zhang, J., Richardson, I.G., Webb, D.F., Gopalswamy, N., Huttunen, E., Kasper, J.C., et al.: 2007, Solar and interplanetary sources of major geomagnetic storms (\(\mathit{Dst} < = - 100~\mbox{nT}\)) during 1996–2005. J. Geophys. Res. 112, A10102. DOI .
Acknowledgements
We thank the ACE, Wind and SOHO teams for providing the data on line. SOHO is a project of international collaboration between ESA and NASA. We thank C. Möstl for providing the poloidal flux of 13 magnetic clouds using the Grad–Shafranov method. Our work was supported by NASA’s Living with a Star Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Earth-affecting Solar Transients
Guest Editors: Jie Zhang, Xochitl Blanco-Cano, Nariaki Nitta, and Nandita Srivastava
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S. et al. Estimation of Reconnection Flux Using Post-eruption Arcades and Its Relevance to Magnetic Clouds at 1 AU. Sol Phys 292, 65 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-017-1080-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-017-1080-9