Abstract
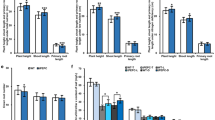
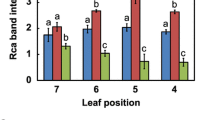
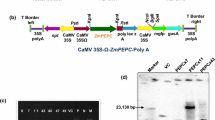
Metabolome analyses have indicated an accumulation of sedoheptulose 7-phosphate in transgenic rice plants with overproduction of Rubisco (Suzuki et al. in Plant Cell Environ 35:1369–1379, 2012. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2012.02494.x). Since Rubisco overproduction did not quantitatively enhance photosynthesis even under CO2-limited conditions, it is suspected that such an accumulation of sedoheptulose 7-phosphate hampers the improvement of photosynthetic capacity. In the present study, the gene of transketolase, which is involved in the metabolism of sedoheptulose 7-phosphate, was co-overexpressed with the Rubisco small subunit gene in rice. Rubisco and transketolase were successfully overproduced in comparison with those in wild-type plants by 35–53 and 39–84 %, respectively. These changes in the amounts of the proteins were associated with those of the mRNA levels. However, the rate of CO2 assimilation under high irradiance and different [CO2] did not differ between co-overexpressed plants and wild-type plants. Thus, co-overproduction of Rubisco and transketolase did not improve photosynthesis in rice. Transketolase was probably not a limiting factor of photosynthesis as overproduction of transketolase alone by 80–94 % did not affect photosynthesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrivault S, Guenther M, Ivakov A, Feil R, Vosloh D, van Dongen JT, Sulpice R, Stitt M (2009) Use of reverse-phase liquid chromatography, linked to tandem mass spectrometry, to profile the Calvin cycle and other metabolic intermediates in Arabidopsis rosettes at different carbon dioxide concentrations. Plant J 59:824–839. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03902.x
Benson AA (2002) Paving the path. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:1–25. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.091201.142547
Calvin M (1989) Forty years of photosynthesis and related activities. Photosynth Res 21:3–16. doi:10.1007/BF00047170
Candiano G, Bruschi M, Musante L, Santucci L, Ghiggeri GM, Carnemolla B, Orecchia P, Zardi L, Righetti PG (2004) Blue silver: a very sensitive colloidal Coomassie G-250 staining for proteome analysis. Electrophoresis 25:1327–1333. doi:10.1002/elps.200305844
Cruz JA, Emery C, Wüst M, Kramer DM, Lange BM (2008) Metabolite profiling of Calvin cycle intermediates by HPLC-MS using mixed-mode stationary phases. Plant J 55:1047–1060. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03563.x
Dong W, Thomas N, Ronald PC, Goyer A (2016) Overexpression of thiamin biosynthesis genes in rice increases leaf and unpolished grain thiamin content but not resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Front Plant Sci 7:616. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00616
Dyballa N, Metzger S (2012) Fast and sensitive Coomassie staining in quantitative proteomics. In: Marcus K (ed) Quantitative methods in proteomics. Methods in molecular biology, vol 893. Springer, Berlin, pp 47–59. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-885-6_4
Emanuelsson O, Nielsen H, von Heijne G (1999) ChloroP, a neural network-based method for predicting chloroplast transit peptides and their cleavage sites. Protein Sci 8:978–984. doi:10.1110/ps.8.5.978
Evans JR (1986) The relationship between CO2-limited photosynthetic rate and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate-carboxylase content in two nuclear-cytoplasm substitution lines of wheat, and the coordination of ribulose-bisphosphate-carboxylation and electron-transport capacities. Planta 167:351–358. doi:10.1007/BF00391338
Evans JR (1989) Photosynthesis and nitrogen relationships in leaves of C3 plants. Oecologia 78:9–19. doi:10.1007/BF00377192
Feng L, Wang K, Li Y, Tan Y, Kong J, Li H, Li Y, Zhu Y (2007) Overexpression of SBPase enhances photosynthesis against high temperature stress in transgenic rice plants. Plant Cell Rep 26:1635–1646. doi:10.1007/s00299-006-0299-y
Feng L, Li H, Jiao J, Li D, Zhou L, Wan J, Li Y (2009) Reduction in SBPase activity by antisense RNA in transgenic rice plants: effect on photosynthesis, growth, and biomass allocation at different nitrogen levels. J Plant Biol 52:382–394. doi:10.1007/s12374-009-9049-3
Harris GC, Königer M (1997) The ‘high’ concentrations of enzymes within the chloroplast. Photosynth Res 54:5–23. doi:10.1023/A:1005895213775
Harrison EP, Willingham NM, Lloyd JC, Raines CA (1998) Reduced sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase levels in transgenic tobacco lead to decreased photosynthetic capacity and altered carbohydrate accumulation. Planta 204:27–36. doi:10.1007/s004250050226
Harrison EP, Olcer H, Lloyd JC, Long SP, Raines CA (2001) Small decreases in SBPase cause a linear decline in the apparent RuBP regeneration rate, but do not affect Rubisco carboxylation capacity. J Exp Bot 52:1779–1784. doi:10.1093/jexbot/52.362.1779
Heldt HW, Piechulla B (eds) (2011) Photosynthetic CO2 assimilation by the Calvin cycle. In: Plant biochemistry. Academic Press, London, pp 163–191
Henkes S, Sonnewald U, Badur R, Flachmann R, Stitt M (2001) A small decrease of plastid transketolase activity in antisense tobacco transformants has dramatic effects on photosynthesis and phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell 13:535–551. doi:10.1105/tpc.13.3.535
Hudson GS, Evans JR, von Cammerer S, Arvidsson YBC, Andrews TJ (1992) Reduction of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase content by antisense RNA reduces photosynthesis in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Physiol 98:294–302. doi:10.1104/pp.98.1.294
Izumi M, Tsunoda H, Suzuki Y, Makino A, Ishida H (2012) RBCS1A and RBCS3B, two major members within the Arabidopsis RBCS multigene family, function to yield sufficient Rubisco content for leaf photosynthetic capacity. J Exp Bot 63:2159–2170. doi:10.1093/jxb/err434
Kawahara Y, Bastide M et al (2013) Improvement of the Oryza sativa Nipponbare reference genome using next generation sequence and optical map data. Rice 6:4. doi:10.1186/1939-8433-6-4
Khozaei M, Fisk S, Lawson T, Gibon Y, Sulpice R, Stitt M, Lefebvre SC, Raines CA (2015) Overexpression of plastid transketolase in tobacco results in a thiamine auxotrophic phenotype. Plant Cell 27:432–447. doi:10.1105/tpc.114.131011
Lauerer M, Saftic D, Quick WP, Labate C, Fichtner K, Schulze ED, Rodermel SR, Bogorad L, Stitt M (1993) Decreased ribulose-l,5-bisphosphate carboxylase–oxygenase in transgenic tobacco transformed with ‘antisense’ rbcS. VI. Effect on photosynthesis in plants grown at different irradiance. Planta 190:332–345. doi:10.1007/BF00196962
Lawson T, Bryant B, Lefebvre S, Lloyd JC, Raines CS (2006) Decreased SBPase activity alters growth and development in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Cell Environ 29:48–58. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01399.x
Lefebvre S, Lawson T, Zakhleniuk OV, Lloyd JC, Raines CA, Fryer M (2005) Increased sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase activity in transgenic tobacco plants stimulates photosynthesis and growth from an early stage in development. Plant Physiol 138:451–460. doi:10.1104/pp.104.055046
Makino A, Sage RF (2007) Temperature response of photosynthesis in transgenic rice transformed with ‘sense’ or ‘antisense’ rbcS. Plant Cell Physiol 48:1472–1483. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcm118
Makino A, Mae T, Ohira K (1985) Enzymic properties of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase purified from rice leaves. Plant Physiol 79:57–61. doi:10.1104/pp.79.1.57
Makino A, Mae T, Ohira K (1988) Differences between wheat and rice in the enzyme properties of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase and their relationship to photosynthetic gas exchange. Planta 174:30–38. doi:10.1007/BF00394870
Makino A, Sakashita H, Hidema J, Mae T, Ojima K, Osmond B (1992) Distinctive responses of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and carbonic anhydrase in wheat leaves to nitrogen nutrition and their possible relationships to CO2 transfer resistance. Plant Physiol 100:1737–1743. doi:10.1104/pp.100.4.1737
Makino A, Shimada T, Takumi S, Kaneko K, Matsuoka M, Shimamoto K, Nakano H, Miyao-Tokutomi M, Mae T, Yamamoto N (1997) Does decrease in ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by antisense RbcS lead to a higher N-use efficiency of photosynthesis under conditions of saturating CO2 and light in rice plants? Plant Physiol 114:483–491. doi:10.1104/pp.114.2.483
Makino A, Nakano H, Mae T, Shimamoto T, Yamamoto N (2000) Photosynthesis, plant growth and N allocation in transgenic rice plants with decreased Rubisco under CO2 enrichment. J Exp Bot 51:383–389. doi:10.1093/jexbot/51.suppl_1.383
Murphy DJ, Walker DA (1982) The properties of transketolase from photosynthetic tissue. Planta 155:316–320. doi:10.1007/BF00429458
Ogawa S, Suzuki Y, Yoshizawa R, Kanno K, Makino A (2012) Effect of individual suppression of RBCS multigene family on Rubisco contents in rice leaves. Plant Cell Environ 35:546–553. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02434.x
Olçer H, Lloyd JC, Raines CA (2001) Photosynthetic capacity is differentially affected by reductions in sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase activity during leaf development in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Physiol 125:982–989. doi:10.1104/pp.125.2.982
Price GD, Evans JR, von Caemmerer S, Yu JW, Badger MR (1995) Specific reduction of chloroplast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity by antisense RNA reduces CO2 assimilation via a reduction in ribulose bisphosphate regeneration in transgenic tobacco plants. Planta 195:369–378. doi:10.1007/BF00202594
Prior AF, Tackaberry SE, Aubin AR, Casley LW (2006) Accurate determination of zygosity in transgenic rice by real-time PCR does not require standard curves or efficiency correction. Transgenic Res 15:261–265. doi:10.1007/s11248-005-4024-3
Ruuska SA, Andrews TJ, Badger MR, Price GD, von Caemmerer S (2000) The role of chloroplast electron transport and metabolites in modulating Rubisco activity in tobacco. Insights from transgenic plants with reduced amounts of cytochrome b/f complex or glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Plant Physiol 122:491–504. doi:10.1104/pp.122.2.491
Sharkey TD (1985) Photosynthesis in intact leaves of C3 plants: physics, physiology and rate limitations. Bot Rev 51:53–105. doi:10.1007/BF02861058
Suzuki Y, Makino A (2012) Availability of Rubisco small subunit up-regulates the transcript levels of large subunit for stoichiometric assembly of its holoenzyme in rice. Plant Physiol 160:533–540. doi:10.1104/pp.112.201459
Suzuki Y, Kawazu T, Koyama H (2004) RNA isolation from siliques, dry seeds, and other tissues of Arabidopsis thaliana. Biotechniques 37:542–544
Suzuki Y, Ohkubo M, Hatakeyama H, Ohashi K, Yoshizawa R, Kojima S, Hayakawa T, Yamaya T, Mae T, Makino A (2007) Increased Rubisco content in transgenic rice transformed with the ‘sense’ rbcS gene. Plant Cell Physiol 48:626–637. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcm035
Suzuki Y, Miyamoto T, Yoshizawa R, Mae T, Makino A (2009a) Rubisco content and photosynthesis of leaves at different positions in transgenic rice with an overexpression of RBCS. Plant Cell Environ 32:417–427. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.01937.x
Suzuki Y, Nakabayashi K, Yoshizawa R, Mae T, Makino A (2009b) Differences in expression of the RBCS multigene family and Rubisco protein content in various rice plant tissues at different growth stages. Plant Cell Physiol 50:1851–1855. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcp120
Suzuki Y, Fujimori T, Kanno K, Sasaki A, Ohashi Y, Makino A (2012) Metabolome analysis of photosynthesis and the related primary metabolites in the leaves of transgenic rice plants with increased or decreased Rubisco content. Plant Cell Environ 35:1369–1379. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2012.02494.x
Toki S, Hara N, Ono K, Onodera H, Tagiri A, Oka S, Tanaka H (2006) Early infection of scutellum tissue with Agrobacterium allows high-speed transformation of rice. Plant J 47:969–976. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02836.x
von Caemmerer S, Farquhar GD (1981) Some relationships between the biochemistry of photosynthesis and the gas exchange of leaves. Planta 153:376–387. doi:10.1007/BF00384257
Yamaoka C, Suzuki Y, Makino A (2016) Differential expression of genes of the Calvin–Benson cycle and its related genes during leaf development in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 57:115–124. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcv183
Zhu XG, de Sturler E, Long SP (2007) Optimizing the distribution of resources between enzymes of carbon metabolism can dramatically increase photosynthetic rate: a numerical simulation using an evolutionary algorithm. Plant Physiol 145:513–526. doi:10.1104/pp.107.103713
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (Nos. 26450074 to Y.S. and JP16H02538 to A.M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, Y., Kondo, E. & Makino, A. Effects of co-overexpression of the genes of Rubisco and transketolase on photosynthesis in rice. Photosynth Res 131, 281–289 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-016-0320-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-016-0320-4