Abstract
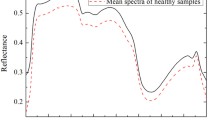
Assessment of crop health status in real time could provide reliable and useful information for making effective and efficient management decisions regarding the appropriate time and method to control crop diseases and insect damage. In this study, hyperspectral reflectance of symptomatic and asymptomatic rice leaves infected by Pyricularia grisea Sacc, Bipolaris oryzae Shoem, Aphelenchoides besseyi Christie and Cnaphalocrocis medinalis Guen was measured in a laboratory within the 350–2 500 nm spectral region. Principal component analysis was performed to obtain the principal component spectra (PCs) of different transformations of the original spectra, including original (R), common logarithm of reciprocal (lg (1/R)), and the first derivative of original and common logarithm of reciprocal spectra (R′ and (lg (1/R))′). A probabilistic neural network classifier was applied to discriminate the symptomatic rice leaves from asymptomatic ones with the front PCs. For identifying symptomatic and asymptomatic rice leaves, the mean overall discrimination accuracies for R, lg (1/R), R′ and (lg (1/R))′ were 91.3, 93.1, 92.3 and 92%, and the mean Kappa coefficients were 0.771, 0.835, 0.829 and 0.82, respectively. To discriminate between disease and insect damage, the overall accuracies for R, lg (1/R), R′ and (lg (1/R))′ were 97.7, 98.1, 100 and 100%, and the Kappa coefficients were 0.962, 0.97, 1 and 1, respectively. These results demonstrated that hyperspectral remote sensing can discriminate between multiple diseases and the insect damage of rice leaves under laboratory conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abalos, P., Daffner, J., & Pinochet, L. (2000). Evaluation of three Brucella soluble antigens used in an indirect Elisa to discriminate S19 vaccinated from naturally infected cattle. Veterinary Microbiology, 71, 161–167.
Albacete, A., Ghanem, M. E., Dodd, I. C., & Pérez-Alfocea, F. (2010). Principal component analysis of hormone profiling data suggests an important role for cytokinins in regulating leaf growth and senescence of salinized tomato. Plant Signal Behavior, 5, 45–48.
Congalton, R. G. (1991). A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 37, 35–46.
Demetriades-Shah, T. H., Steven, M. D., & Clark, J. A. (1990). High-resolution derivative spectra in remote sensing. Remote Sensing of Environment, 33, 55–64.
Fraenkel, G., & Fallil, F. (1981). The spinning (stitching) behavior of the rice leaf folder, Cnaphalocrocis Medinalis. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 29, 138–146.
Fung, T., & Ledrew, E. (1987). Application of principal components analysis to change detection. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 53, 1649–1658.
Ham, F. M., & Kostanic, I. (2001). Principles of neurocomputing for science and engineering (p. 174). New York: McGoriginal-Hill Companies.
Helsel, Z. (1992). Energy and alternatives for fertilizer and pesticides use. In R. C. Fluck (Ed.), Energy in World Agriculture (pp. 177–201). Florida, USA: Elsevier.
Holden, H., & LeDrew, E. (1998). Spectral discrimination of healthy and non-healthy corals based on cluster analysis, principal component analysis, and derivative spectroscopy. Remote Sensing of Environment, 65, 217–224.
Horler, D. N. H., Dockray, M., & Barber, J. (1983). The red edge of plant leaf reflectance. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 4, 273–288.
Horst, G. L., Engelke, M. C., & Meyers, W. (1984). Assessment of visual evaluation techniques. Agronomy Journal, 76, 619–622.
Huang, J. R., Sun, J. Y., Liao, H. J., & Liu, X. D. (2015). Detection of brown planthopper infestation based on SPAD and spectral data from rice under different rates of nitrogen fertilizer. Precision Agriculture, 16, 148–163.
IRRI (International Rice Research Institute). (2014). World rice statistics online query facility. Retrieved March 19, 2018 from http://ricestat.irri.org:8080/wrsv3/entrypoint.htm.
Jackson, R. D. (1986). Remote sensing of biotic and abiotic plant stress. Annual review of Phytopathology, 24, 265–287.
Khan, Z. R., Barrion, A. T., Litsinger, J. A., Castilla, N. P., & Joshi, R. C. (1988). A bibliography of rice leaf-folders (Lepidoptera:Pyralidae). Insect Science and its Application, 9, 129–174.
Kitchen, N. R., Sudduth, K. A., Myers, D. B., Drummond, S. T., & Hong, S. Y. (2005). Delineating productivity zones on claypan soil fields using apparent soil electrical conductivity. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 46, 285–308.
Knipling, E. B. (1970). Physical and physiological basis for the reflectance of visible and near-infrared radiation from vegetation. Remote Sensing of Environment, 1, 155–159.
Kobayashi, T., Kanda, E., Kitada, K., Ishiguro, K., & Torigoe, Y. (2001). Detection of rice panicle blast with multispectral radiometer and the potential of using airborne multispectral scanners. Phytopathology, 91, 316–323.
Liang, S. L. (2004). Quantitative remote sensing of land surface (p. 94). New Jersey, USA: Wiley.
Liew, O. W., Chong, P. J., Chong, J., Li, B., & Asundi, A. K. (2008). Signature optical cues: Emerging technologies for monitoring plant health. Sensors, 8, 3205–3239.
Lin, M. S., Ding, X. F., Wang, Z. M., Zhou, F. M., & Lin, N. (2005). Description of Aphelenchoides besseyi from abnormal rice with ‘Small Grains and Erect Panicles’ symptom in China. Rice Science, 12, 289–294.
Liu, Z. Y., Huang, J. F., Shi, J. J., Tao, R. X., Zhou, W., & Zhang, L. L. (2007). Characterizing and estimating rice brown spot disease severity using stepwise regression, principal component regression and partial least-square regression. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science B, 10, 738–744.
Liu, Z. Y., Huang, J. F., Tao, R. X., & Zhang, H. Z. (2008). Estimating rice brown spot disease severity based on principal component analysis and radial basis function neural network. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 28, 2156–2160.
Liu, Z. Y., Shi, J. J., Zhang, L. W., & Huang, J. F. (2010a). Discrimination of rice panicles by hyperspectral reflectance data based on principal components analysis and support vector classification. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science B, 11, 71–78.
Liu, Z. Y., Wu, H. F., & Huang, J. F. (2010b). Application of neural networks to discriminate fungal infection levels in rice panicles using hyperspectral reflectance and principal components analysis. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 72, 99–106.
Lobell, D. B., & Asner, G. P. (2001). Subpixel canopy cover estimation of coniferous forests in Oregon using SWIR imaging spectrometry. Journal of Geophysical Research, 106, 5151–5160.
Malthus, T. J., & Madeira, A. C. (1993). High-resolution spectroradiometry: Spectral reflectance of field beans leaves infected by Botrytis fabae. Remote Sensing of Environment, 45, 107–116.
Mirik, M., Michels, G. J., Jr., Kassymzhanova-Mirik, S., & Elliott, N. C. (2007). Reflectance characteristics of Russian wheat aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) stress and abundance in winter wheat. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 57, 123–134.
Mirik, M., Michels, G. J., Jr., Kassymzhanova-Mirik, S., Elliott, N. C., Catana, V., Jones, D. B., et al. (2006). Using digital image analysis and spectral reflectance data to quantify damage by greenbug (Hemitera: Aphididae) in winter wheat. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 51, 86–98.
Nilsson, H. E. (1995). Remote sensing and image analysis in plant pathology. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 33, 489–527.
Ou, S. H. (1985). Rice Diseases (2nd ed.). Surrey, UK: Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau.
Panda, S. S., Hoogenboom, G., & Paz, J. (2009). Distinguishing blueberry bushes from mixed vegetation land use using high resolution satellite imagery and geospatial techniques. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 67, 51–58.
Pedigo, L. P. (1995). Closing the gap between IPM theory and practice. Journal of Agricultural Entomology, 12, 171–181.
Peñuelas, J., & Filella, I. (1998). Visible and near-infrared reflectance techniques for diagnosing plant physiological status. Trends in Plant Science, 3, 151–156.
Prasannakumar, N. R., Chander, S., & Sahoo, R. N. (2014). Characterization of brown planthopper damage on rice crops through hyperspectral remote sensing under field conditions. Phytoparasitica, 42, 387–395.
Prather, M., & Ehhalt, D. (2001). Atmospheric chemistry and greenhouse gases. Climate Change 2001: The scientific basis, IPCC third assessment report. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Price, J. C. (1994). How unique is spectral signatures? Remote Sensing of Environment, 49, 181–186.
Qin, Z. H., Zhang, M. H., Christensen, T., Li, W. J., & Tang, H. J. (2003). Remote sensing analysis of rice disease stresses for farm pest management using wide-band airborne data. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 6, 2215–2217.
Richardson, M. D., Karcher, D. E., & Purcell, L. C. (2001). Quantifying turfgrass cover using digital image analysis. Crop Science, 41, 1884–1888.
Shi, J. J., Liu, Z. Y., Zhang, L. L., Zhou, W., & Huang, J. F. (2009). Hyperspectral recognition of rice damaged by rice leaf roller based on support vector machine. Rice Science, 23, 331–334.
Sims, D. A., & Gamon, J. A. (2002). Relationships between leaf pigment concentration and spectral reflectance across a wide range of species, leaf structures and developmental stages. Remote Sensing of Environment, 81, 337–354.
Steddom, K., Bredehoeft, M. W., Khan, M., & Rush, C. M. (2005). Comparison of visual and multispectral radiometric disease evaluations of cercospora leaf spot of sugar beet. Plant Disease, 89, 153–158.
Tang, Y. L., Wang, R. C., & Huang, J. F. (2004). Relations between red edge characteristics and agronomic parameters of crops. Pedosphere, 14, 467–474.
Thenkabail, P. S., Lyon, G. J., & Huete, A. (2011). Hyperspectral Remote Sensing of Vegetation (p. 781). New York, USA: CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group.
Wang, H. W. (1999). Partial least squares regression method and applications (p. 198). Beijing, China: National Defense Industry Press.
Wang, Y., Wang, F. M., Huang, J. F., Wang, X. Z., & Liu, Z. Y. (2009). Validation of artificial neural network techniques in the estimation of nitrogen concentration in rape using canopy hyperspectral reflectance data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 30, 4493–4505.
West, J. S., Bravo, C., Oberit, R., Lemaire, D., Moshou, D., & McCartney, H. A. (2003). The potential of optical canopy measurement for targeted control of field crop diseases. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 41, 593–614.
Wu, S. W., Wang, R. C., Chen, X. B., Shen, Z. Q., & Shi, Z. (2002). Effects of rice leaf blast on spectrum reflectance of rice. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University (Agricultural Science), 20, 73–77.
Xiao, X. M., Boles, S., Frolking, S., Li, C. S., Babu, J. Y., Salas, W., et al. (2006). Mapping paddy rice agriculture in South and Southeast Asia using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sensing of Environment, 100, 95–113.
Yang, Z., Rao, M. N., Elliott, N. C., Kindler, S. D., & Popham, T. W. (2005). Using ground-based multispectral radiometry to detect stress in wheat caused by greenbug (Homoptera: Aphididae) infestation. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 47, 121–135.
Zadoks, J. C., Chang, T. T., & Konzak, C. F. (1974). A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Research, 14, 415–421.
Zhang, W., Pan, L. Q., Tu, K., Zhang, Q., & Liu, M. (2014). Comparison of spectral and image morphological analysis for egg early hatching property detection based on hyperspectral imaging. PLoS ONE, 9, e88659.
Zhao, J. L., Zhao, C. J., Yang, H., Zhang, D. Y., Dong, Y. Y., & Yuan, L. (2013). Identification and characterization of spectral response properties of rice canopy infested by leaf folder. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 15, 694–700.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41301483, 41671437, 31371935, 41201365), the National Basic Research Program (973) of China (2010CB126200), the Agro-Industry R&D Special Fund of China (200903051) and the China Scholarship Council Foundation (201408330029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, ZY., Qi, JG., Wang, NN. et al. Hyperspectral discrimination of foliar biotic damages in rice using principal component analysis and probabilistic neural network. Precision Agric 19, 973–991 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-018-9567-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-018-9567-4