Abstract
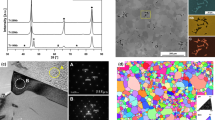
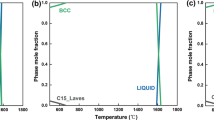
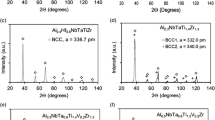
The structure of Ti-Nb-B alloys that are cast and annealed at subsolidus temperatures and at 1400°C is experimentally analyzed (x-ray diffraction, metallography, and electron probe microanalysis), and so are temperatures of their phase transformations (differential thermal analysis and pyrometry). No ternary phases are found in the alloys. Projections of solidus and liquidus surfaces, an isothermal section at 1400°C, and a vertical section at 7.5 at.% B are constructed. A reaction scheme is proposed for alloy crystallization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Lampman, “Wrought titanium and titanium alloys,” in: Metals Handbook, Tenth Edition, Vol. 2, Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials, ASM, Metals Park, Ohio (1990), pp. 592–633.
S. Tamirisakandala, R. B. Bhat, J. S. Tiley, and D. B. Miracle, “Grain refinement of cast titanium alloys via trace boron addition,” Scr. Mater., 53, 1421–1426 (2005).
A. B. Godfrey and M. H. Loretto, “The nature of complex precipitates associated with the addition of boron to a γ-based titanium aluminide,” Intermetallics, 4, No. 1, 47–53 (1996).
D. J. Larson, C. T. Liu, and M. B. Miller, “Boron solubility and boride compositions in α2 + γ titanium aluminides,” Intermetallics, 5, No. 6, 411–414 (1997).
T. T. Cheng, “The mechanism of grain refinement in TiAl alloys by boron addition-an alternative hypothesis,” Intermetallics, 8, No. 1, 29–37 (2000).
M. Beschliesser, A. Chatterjee, A. Lorich, et al., “Designed fully lamellar microstructures in a γ-TiAl based alloy: adjustment and microstructural changes upon long-term isothermal exposure at 700 and 800° C,” Mater. Sci. Engin. A., 329-331, 124–129 (2002).
F. Marino, A. Rebuffo, and F. Sorrentino, “Effects of low-cycle fatigue on bending properties and fracture toughness of un-HIP’ed Ti-47Al-2Cr-2Nb-1B intermetallic,” Int. J. Fatigue, 27, No. 2, 143–153 (2005).
C. R. Feng and D. J. Michel, “Microstructures of Nb-26Ti-48Al + (Nb, Ti)B,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, A152, 202–207 (1992).
F. Tang, S. Emura, and M. Hagiwara, “Reinforcing effect of in-situ grown TiB fibers on Ti-22Al-11Nb-4Mo alloy,” Scripta Mater., 43, 573–578 (2000).
F. Tang, Sh. Nakazawa, and M. Hagiwara, “Effect of boron microalloying on microstructure, tensile properties and creep behavior of Ti-22Al-20Nb-2W alloy,” Material. Sci. Eng. A., A315, Nos. 1–2, 147–152 (2001).
T. Saito, T. Furuta, and T. Yamaguchi, “Development of low cost titanium matrix composite,” in: Recent Advances in Titanium Metal Matrix Composites, TSM, PA, Warrendale (1995), pp. 33–44.
F. W. Grossman and A. S. Yue, “Undirectionally solidified Ti-TiB and Ti-Ti5Si3 eutectic composites,” Metall. Trans., 2, 1545–1555 (1985).
Yu. B. Kuz’ma, “An x-ray structural investigation of the systems niobium-titanium-boron and niobium-molybdenum-boron,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 10, No. 4, 298–300 (1971).
G. A. Yasinskaya and M. S. Groysberg, “Interaction of titanium boride with niobium and tungsten,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 2, No. 6, 457–458 (1963).
T. B. Gorbacheva, Yu. I. Krylov, and N. M. Mikova, “Investigation of high-temperature interaction between refractory metals and borides,” in: O. P. Kolchin (ed.), Collection of Papers on Solid Alloys and Refractory Metals, Metallurgy, Moscow (1973), pp. 239–243.
H. R. Z. Sandim, C. A. Nunes, and A. S. Ramos, “Sintering of P/M Nb-TiB2 alloys,” Mater. Sci. Forum, 416-418, 251–256 (2003).
G. V. Samsonov and V. S. Neshpor, “Investigation of the mutual diffusion of titanium and niobium borides,” Dokl. AN SSSR, 101, No. 5, 899–900 (1955).
G. V. Samsonov and V. S. Neshpor, “Research into the formation of isomorphous boride alloys,” Zh. Fiz. Khim., 29, No. 5, 839–845 (1955).
J. L. Murray, P. K. Liao, and K. E. Spear, “The B-Ti (boron-titanium) system,” Bul. Alloy Phase Equilib., 7, No. 6, 550–555 (1986).
J. L. Murray, P. K. Liao, and K. E. Spear, “The B-Ti (boron-titanium) system,” in: J. L. Murray (ed.), Phase Diagrams of Binary Titanium Alloys, ASM, Metals Park, Ohio (1987), pp. 33–38.
T. B. Massalski, P. R. Subramanian, H. Okomoto, and L. Kasprzak (eds.), Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, ASM, Metals Park, Ohio (1990), p. 3589.
N. P. Lyakishev (ed.), Phase Diagrams for Binary Systems, Vol. 1, Mashinostroyenie, Moscow (1996), p. 245.
X. Ma, Ch. Li, Zh. Du, and W. Zhang, “Thermodynamic assessment of the Ti-B system,” Alloys Comp., 370, 149–158 (2004).
J. L. Murray, “The Nb-Ti (niobium-titanium) system,” in: J. L. Murray (ed.), Phase Diagrams of Binary Titanium Alloys, ASM, Metals Park, Ohio (1987), pp. 188–194.
V. N. Eremenko and L. A. Tretiachenko, Ternary Systems of Titanium with Transition Metals of Groups IV–VI, Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1987), p. 232.
P. Rogl, “Nb-B-C (niobium-boron-carbon),” in: G. Effenberg (ed.), Phase Diagrams of Metal-Boron-Carbon Ternary Systems, Ohio, ASM-MSI, Metals Park (1998), pp. 202–205.
T. Lunström and L. E. Tergenius, “On the solid solution of copper in β-rhombohedral Boron,” J. Less-Common Met., 47, 23–28 (1976).
A. J. Crespo, L.-E. Tergenius, and T. Lundström, “The solid solution of 4d, 5d, and some p elements in β rhomhedral boron,” J. Less. Common Met., 77, 147–150 (1981).
A. Wittmann, H. Nowotny, and H. Boller, “Ein beitrag zum dreistoff titan-molybdän-bor,” Monatsh. Chem., 91, No. 4, 608–615 (1960).
B. F. Decker and J. S. Kasper, “The crystal structure TiB,” Acta Cryst., 7, 77–80 (1954).
G. V. Samsonov and E. V. Petrash, “Some physical and chemical properties of titanium boride and nitride,” Metalloved. Obrab. Met., No. 4, 19–24 (1955).
M. E. Hyman, C. McCullough, I. I. Valencia, et al., “Microstructure evolution in TiAl alloys with B additions: conventional solidification,” Metall. Trans. A., 20A, 1847–1859 (1989).
E. Rudy, Ternary Phase Equilibria in Transition Metal-Boron-Carbon-Silicon Systems, Wright-Patterson, Air Force Materials Laboratory: Tech. Rep. AFML-TR-65-2, Part V, Compendium of Phase Diagram Data, Ohio (1969), p. 689.
P. Rogl, “The System B-N-Nb,” in: P. Rogl and J. C. Schuster (eds.), Phase Diagrams of Ternary Boron Nitride and Silicon Nitride Systems, ASM, Matals Park, Ohio (1992), pp. 68–72.
V. P. Pshokin, A. M. Zakharov, and I. I. Novikov, “Boron solubility in niobium in solid state,” Izv. Vuzov. Tsvet. Metall., No. 1, 111–114 (1971).
A. M. Zakharov, V. N. Pshokin, and E. I. Ivanova, “Niobium angle of the Nb-B-C system, Izv. AN SSSR, Metally, No. 5, 193–196 (1985).
A. M. Zakharov and V. N. Pshokin, “Niobium angle of the Nb-Hf-B system,” Izv. AN SSSR, Metally, No. 6, 195–196 (1985).
L. A. Borges, G. C. Coelho, C. A. Nunes, and P. A. Suzuki, “New data on phase equilibria in the Nb-rich region of the Nb-B system,” J. Phase Equilibria, 24, No. 3, 140–146 (2003).
H. Nowotny, F. Benesovsky, and R. Kieffer, “Beitrag zum aufbau systeme Niob-Bor und Tantal-Bor,” Z. Metallkd., 50, No. 7, 417–423 (1959).
H. Bolmgren and T. A. Lundström, “New binary boride, Nb5B6,” J. Less-Common Met., 159, L25–L27 (1990).
C. A. Nunes, B. B. de Lima, G. C. Coelho, et al., “On the stability of the V5B6-phase,” J. Alloys Comp., 370, 164–168 (2004).
S. Okada, K. Hamano, T. Lundström, and I. Higashi, “Crystal growth of the new compound Nb2B3, and the borides NbB, Nb5B6, Nb3B4, and NbB2 using the copper-flux method,” in: D. Emin, T. L. Aselage, A. C. Switendick, et al. (eds.), AIP Conf. Proc. 231 “Boron-Rich Solid” (10th Int. Symp. on Boron, Borides, and Related Compounds, 1990, Albuquergue, NM, USA), AIP, New York (1991), pp. 456–459.
Ju. A. Kocherzhinsky, “Differential thermocouple up to 2450°C and thermographic investigations of refractory silicides,” in: Thermal Analysis Proceeding of Third ICTA (Davos), Vol. 1, Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel (1971), pp. 549–559.
Yu. A. Kocherzhinskii, E. A. Shishkin, and V. I. Vasilenko, “DTA apparatus with a thermocouple sensor up to 2200°C,” in: Phase Diagrams of Metal Systems [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1971), pp. 245–249.
M. Pirani and H. Altertum, “Uber eine Methode zur Schmelzpunktbestimmung an Hochschmelzenden Metallen,” Z. Elektrochem., 29, No. 1–2, 5–8 (1923).
E. Rudy and J. Progulski, “A Pirani furnace for the precision determination of the melting temperatures of refractory metallic substances,” Planseeber. Pulvermet., 15, No. 1, 13–45 (1967).
A. A. Bondar, V. A. Maslyuk, T. Ya. Velikanova, and A. V. Grytsiv, “Phase equilibria in the Cr-Ni-C system and their use in developing physical and chemical basis for chromium carbide-based solid solutions,” Poroshk. Metall., No. 5–6, 13–24 (1997).
T. Ya. Velikanova, A. A, Bondar, and A. V. Grytsiv, “The chromium-nickel-carbon phase diagram,” J. Phase Equilibria, 20, No. 2, 125–147 (1999).
A. V. Dobromyslov and V. A. Elkin, “Martensitic transformation and metastable β-phase in binary titanium alloys with d-metals of 4–6 periods,” Scr. Mater., 44, 905–910 (2001).
L. V. Artyukh, D. B. Borysov, A. A. Bondar, et al., “Titanium-boride eutectic materials: Phase equilibria and constitution of alloys in the Ti-rich portion of the Ti-V-B system,” High Temp. Mat. Pr.-Isr., 25, No. 1–2, 75–82 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
__________
Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 46, No. 1–2(453), pp. 72–87, 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borisov, D.B., Artyukh, L.V., Bondar, A.A. et al. Titanium-boride eutectic materials. Structure of the Ti-Nb-B alloys and phase equilibria. Powder Metall Met Ceram 46, 58–71 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-007-0011-y
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-007-0011-y