Abstract
Soybean seed hardness is an important quality character in soybean food processing. Both vegetable soybean and natto require soft seeds to achieve a desirable sensory experience and for effective processing. In this study, we used a texture analyzer to measure the seed hardness of Chinese mini core collection via two indexes over 4 years and found significant correlations among the seed hardness, seed oil content, and germplasm eco-region. Based on 1514 SNPs, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) were conducted using a mixed linear model (MLM). Seventeen SNPs were identified to be associated with seed hardness in at least two environments. Among them, one locus, designated Q-15-0087770, was associated with two indexes, and 13 putative genes were confirmed based on their annotations in SoyBase. This research provides new insights into advanced marker-assisted selections for breeding soybeans for seed hardness and oil content.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alqsous S, Carpentier E, Kleineude D, Burel C, Mareck A, Dauchel H, Gomord V, Balange A (2004) Identification and isolation of a pectin methylesterase isoform that could be involved in flax cell wall stiffening. Planta 219(2):369-378
Argel P, Paton C (1999) Overcoming legume hardseededness. In: Loch DS, Ferguson JE (eds) Forage seed production: tropical andsubtropical species, vol 2. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 247–265
Bordes J, Ravel C, Le Gouis J, Lapierre A, Charmet G, Balfourier F (2011) Use of a global wheat core collection for association analysis of flour and dough quality traits. J Cereal Sci 54:137–147
Brummell DA, Dal CV, Crisosto CH, Labavitch JM (2004) Cell wall metabolism during maturation, ripening and senescence of peach fruit. J Exp Bot 55:2029–2039
Calero E, West S, Hinson K (1981) Water absorption of soybean seeds ans associated causal factors 1. Crop Sci 21(6):926–933
Catoire L, Pierron M, Morvan C, Penhoat CHD, Goldberg R (1998) Investigation of the action patterns of pectinmethylesterase isoforms through kinetic analyses and NMR spectroscopy. Implications in cell wall expansion. J Biol Chem 273:33150–33156
Chen P, Buss G (1993) Diehl K Physical and chemical characteristics associated with hardness of small-seeded soybean for natto. In: ASACSSA-SSSA International Annual Meetings
Clemente TE, Cahoon EB (2009) Soybean oil: genetic approaches for modification of functionality and total content. Plant Physiol 151:1030–1040
Crookes PR, Grierson D (1983) Ultrastructure of tomato fruit ripening and the role of polygalacturonase isoenzymes in cell wall degradation. Plant Physiol 72:1088–1093
Ferrándiz C (2002) Regulation of fruit dehiscence in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 53:2031–2038
Flintgarcia SA, Thornsberry JM, Buckler ES IV (2003) Structure of linkage disequilibrium in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:357–374
Fraczek J, Hebda T, Slipek Z, Kurpaska S (2005) Effect of seed coat thickness on seed hardness Canadian biosystems engineering= Le genie des biosystemes au Canada: La revue de la societe canadienne de genie agroalimentaire et biologique
Frankel O, Brown A (1984) Current plant genetic resources—a critical appraisal. In: Genetics: new frontiers: proceedings of the XV International Congress of Genetics/editors, VL Chopra...[et al.], 1984. New Delhi: Oxford & IBH Publishing Co
Hirata K, Masuda R, Tsubokura Y, Yasui T, Yamada T, Takahashi K, Nagaya T, Sayama T, Ishimoto M, Hajika M (2014) Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with boiled seed hardness in soybean. Breed Sci 64:362–370. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.64.362
Hobson G (1965) The Firmness of Tomato Fruit in Relation to Polygalacturonase Activity. J Hort Sci 40(1):66-72
Hu M, Yu D, Meng X (1990) The effect of different ecogeographic environment on the seed quality of soybeans in China. Soybean Sci 9:39–49
Hu Z, Zhang H, Kan G, Ma D, Zhang D, Shi G, Hong D, Zhang G, Yu D (2013) Determination of the genetic architecture of seed size and shape via linkage and association analysis in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Genetica 141:247–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-013-9723-8
Huang J, Guo N, Li Y, Sun J, Hu G, Zhang H, Li Y, Zhang X, Zhao J, Xing H, Qiu L (2016) Phenotypic evaluation and genetic dissection of resistance to Phytophthora sojae in the Chinese soybean mini core collection. BMC Genet 17:85. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-016-0383-4
Hwang EY, Song Q, Jia G, Specht JE, Hyten DL, Costa J, Cregan PB (2014) A genome-wide association study of seed protein and oil content in soybean. BMC Genomics 15:1
Jiang P, Zhang P P, Zhang X, Ma H (2017) Genetic Diversity and Association Analysis for Solvent Retention Capacity in the Accessions Derived from Soft Wheat Ningmai 9. INT J GENOMICS 2017(9):2413150
Jun TH, Van K, Kim MY, Lee SH, Walker DR (2008) Association analysis using SSR markers to find QTL for seed protein content in soybean. Euphytica 162:179–191
Keim P, Diers BW, Shoemaker RC (1990) Genetic analysis of soybean hard seededness with molecular markers. TAG Theor Appl Genet 79:465–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226154
Lee G, Boerma H, Villagarcia M, Zhou X, Carter T, Li Z, Gibbs M (2004) A major QTL conditioning salt tolerance in S-100 soybean and descendent cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 109:1610–1619
Leng JT, Chen YZ, Wang Y, Wu CX (2007) Character analysis of newly-developed soybean varieties and breeding objectives in different regions of China. Soybean Sci 26:293
Li YH, Li W, Zhang C, Yang L, Chang RZ, Gaut BS, Qiu LJ (2010) Genetic diversity in domesticated soybean (Glycine max) and its wild progenitor (Glycine soja) for simple sequence repeat and single-nucleotide polymorphism loci. New Phytol 188:242–253
Li Q, Fan C, Zhang X, Wang X, Wu F, Hu R, Fu Y (2014) Identification of a soybean MOTHER OF FT AND TFL1 homolog involved in regulation of seed germination. PLoS One 9:e99642
Li YH, Reif JC, Ma YS, Hong HL, Liu ZX, Chang RZ, Qiu LJ (2015) Targeted association mapping demonstrating the complex molecular genetics of fatty acid formation in soybean. BMC Genomics 16:841
Li L, Guo N, Niu J, Wang Z, Cui X, Sun J, Zhao T, Xing H (2016) Loci and candidate gene identification for resistance to Phytophthora sojae via association analysis in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. Mol Gen Genomics 291:1095–1103
Li YH, Reif JC, Hong HL, Li HH, Liu ZX, Ma YS, Li J, Tian Y, Li YF, Li WB, Qiu LJ (2018) Genome-wide association mapping of QTL underlying seed oil and protein contents of a diverse panel of soybean accessions. Plant Sci 266:95–101
Liu B, Fujita T, Yan ZH, Sakamoto S, Xu D, Abe J (2007) QTL mapping of domestication-related traits in soybean (Glycine max). Ann Bot 100:1027–1038. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcm149
Micheli F (2001) Pectin methylesterases: cell wall enzymes with important roles in plant physiology. Trends Plant Sci 6:414–419
Moustacas AM, Nari J, Borel M, Noat G, Ricard J (1991) Pectin methylesterase, metal ions and plant cell-wall extension. The role of metal ions in plant cell-wall extension. Biochem J 279:351–354
Mullin WJ, Xu W (2001) Study of soybean seed coat components and their relationship to water absorption. J Agric Food Chem 49:5331–5335
Niu Y, Xu Y, Liu XF, Yang SX, Wei SP, Xie FT, Zhang YM (2013) Association mapping for seed size and shape traits in soybean cultivars. Mol Breed 31:785–794
Nordborg M (2000) Linkage disequilibrium, gene trees and selfing: an ancestral recombination graph with partial self-fertilization. Genetics 154:923–929
Orazaly M, Chen P, Zeng A, Zhang B (2015) Identification and confirmation of quantitative trait loci associated with soybean seed hardness. Crop Sci 55:688–694
Pelloux J, Rusterucci C, Mellerowicz EJ (2007) New insights into pectin methylesterase structure and function. Trends Plant Sci 12:267–277
Prabha T, Bhagyalakshmi N (1998) Carbohydrate metabolism in ripening banana fruit. Phytochemistry 48:915–919
Prtichard J, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945
R Development Core Team (2011) R: a language and environment for statistical computing, Vol.1. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Ragus L (1987) Role of water absorbing capacity in soybean germination and seedling vigour. Seed Sci Technol 15:285-296
Rolletschek H, Borisjuk L (2005) Photosynthesis in seeds: localisation, features and role in storage. Recent Res. Dev. Plant Sci 3:25–45
Saito G, Chang Y, Walling L, Thomson W (1989) A correlation in plastid development and cytoplasmic ultrastructure with nuclear gene expression during seed ripening in soybean. New Phytol 113:459–469
Sonah H, O'Donoughue L, Cober E, Rajcan I, Belzile F (2015) Identification of loci governing eight agronomic traits using a GBS-GWAS approach and validation by QTL mapping in soya bean. Plant Biotechnol J 13:211–221
Song JY, An GH, Kim CJ (2003) Color, texture, nutrient contents, and sensory values of vegetable soybeans [Glycine max (L) Merrill] as affected by blanching. Food Chemistry 83:69–74
Sterling JD, Quigley HF, Orellana A, Mohnen D (2001) The catalytic site of the pectin biosynthetic enzyme α-1,4-galacturonosyltransferase is located in the lumen of the Golgi. Plant Physiol 127:360–371
Sun J, Guo N, Lei J, Li LH, Hu GJ, Xing H (2014) Association mapping for partial resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). J Genet 93(2):355–363
Sun L, Miao Z, Cai C, Zhang D, Zhao M, Wu Y, Zhang X, Swarm SA, Zhou L, Zhang ZJ, Nelson RL, Ma J (2015) GmHs1-1, encoding a calcineurin-like protein, controls hard-seededness in soybean. Nat Genet 47:939–943. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3339
Sved J (1971) Linkage disequilibrium and homozygosity of chromosome segments in finite populations. Theor Popul Biol 2:125–141
Taira H (1990) Quality of soybeans for processed foods in Japan. Jpn Agric Res Q 24(3):224-230
Toda K, Hirata K, Masuda R, Yasui T, Yamada T, Takahashi K, Nagaya T, Hajika M (2015) Relationship between mutations of the pectin methylesterase gene in soybean and the hardness of cooked beans. J Agric Food Chem 63:8870–8878. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b02896
Wang L, Guan Y, Guan R, Li Y, Ma Y, Dong Z, Liu X, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Chang R, Xu H, Li L, Lin F, Luan W, Yan Z, Ning X, Zhu L, Cui Y, Piao R, Liu Y, Chen P, Qiu L (2006) Establishment of Chinese soybean Glycine max core collections with agronomic traits and SSR markers. Euphytica 151:215–223
Watanabe S, Tajuddin T, Yamanaka N, Hayashi M, Harada K (2004) Analysis of QTLs for reproductive development and seed quality traits in soybean using recombinant inbred lines. Breed Sci 54:399–407
Yaklich R, Wergin W, Vigil E (1986) Special secretory cells in the soybean seed coat. Protoplasma 134:78–87
Yano K, Yamamoto E, Aya K, Takeuchi H, Lo PC, Hu L, Yamasaki M, Yoshida S, Kitano H, Hirano K, Matsuoka M (2016) Genome-wide association study using whole-genome sequencing rapidly identifies new genes influencing agronomic traits in rice. Nat Genet 48:927–934
Yoshioka H, Aoba K, Kashimura Y (1992) Molecular weight and degree of methoxylation in cell wall polyuronide during softening in pear and apple fruit. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 117:600–606
Young G, Mebrahtu T, Johnson J (2000) Acceptability of green soybeans as a vegetable entity. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 55:323–333
Zeng X, Kaplan S (2001) TspO as a modulator of the repressor/antirepressor (PpsR/AppA) regulatory system in Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1. J Bacteriol 183:6355–6364. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.183.21.6355-6364.2001
Zhang B, Chen P, Chen CY, Wang D, Shi A, Hou A, Ishibashi T (2008a) Quantitative trait loci mapping of seed hardness in soybean. Crop Sci 48:1341–1349
Zhang B, Tamura M, BERGER-DOYLE J, Chen P (2008b) Comparison of instrumental methods for measuring seed hardness of food-grade soybean. J Texture Stud 39:28–39
Zhang B, Chen P, Shi A, Hou A, Ishibashi T, Wang D (2009) Putative quantitative trait loci associated with calcium content in soybean seed. J Hered 100:263–269. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/esn096
Zhang H, Hao D, Sitoe HM, Yin Z, Hu Z, Zhang G, Yu D (2015) Genetic dissection of the relationship between plant architecture and yield component traits in soybean (Glycine max) by association analysis across multiple environments. Plant Breed 134:564–572
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31471519), Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System of China (CARS-004-PS10), and Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Modern Crop Production.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have read and approved the manuscript. Han Xing conceived the work. Lijun Qiu, Jinming Zhao, Zhangxiong Liu, Na Guo, and Haitang Wang conducted the planting of soybean materials. Xing Zhang, Yuanpeng Bu, Dong Xue, and Xiangnan Li measured and analyzed the phenotyping data. Xing Zhang, Jinming Zhao, Yuanpeng Bu, and Jing Huang performed genome-wide association studies. Xing Zhang wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Table S1
(DOCX 21 kb)
Table S2
(DOCX 14 kb)
Table S3
(DOCX 14 kb)
Table S4
(DOCX 13 kb)
Table S5
(DOCX 13 kb)
Table S6
(DOCX 13 kb)
Fig. S1
Measurements of Fm and H using a texture analyzer. (PNG 195 kb)
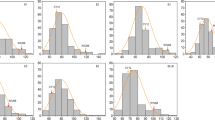
Fig. S2
Frequency distributions of the Fm mean (A) and BLUP (B) and H mean (C) and BLUP (D). (PNG 124 kb)
Fig. S3
The seven eco-regions of the soybean mini core collection in China include: the Northeast spring (NESp), the North spring (NSp), the Huanghuai spring (HSp), the Huanghuai summer (HSu), the South spring (SSp), the South summer (SSu) and the South autumn (SA). (PNG 554 kb)
Fig. S4
Changes in Fm and H over seven eco-regions (A, B) and two subgroups (C, D) over 4 years. (PNG 198 kb)
Fig. S5
Frequency distributions of the mean values of seed protein content (A), moisture (B), and oil content (C) over the three years and oil content in 2012 (D), 2013 (E) and 2014 (F). (PNG 97 kb)
Fig. S6
Changes in seed protein content, oil content and moisture over seven eco-regions (A, B, C) and two subgroups over 3 years (D, E, F). (PNG 202 kb)
Fig. S7
Manhattan plots and QQ plots of Fm (A, B, C, D) and H (E, F, G, H) over 4 years in the MLM model. (PNG 2149 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Zhao, J., Bu, Y. et al. Genome-Wide Association Studies of Soybean Seed Hardness in the Chinese Mini Core Collection. Plant Mol Biol Rep 36, 605–617 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-018-1102-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-018-1102-2