Abstract
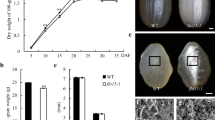
A floury endosperm mutant, osagpl2-3, was isolated from the M2 generation of japonica rice cultivar Nipponbare following ethyl methane sulfonate mutagenesis. The osagpl2-3 mutant produced a white-core endosperm compared to the transparent endosperm of the wild type (WT). The results from scanning electron microscope showed that the osagpl2-3 mutant grains comprised of round and loosely packed starch granules, some of which were compounded. The analysis for cooking and nutrition quality traits indicated that the values of gel consistency, gelatinization temperature, and rapid viscosity analysis profile of osagpl2-3 grains were lower than those of the WT. Besides, the protein content, the contents of nine different amino acids, and the thermodynamic parameters of T p and ΔT 1/2 in osagpl2-3 were also different from those of the WT. Genetic analysis revealed that osagpl2-3 mutation was controlled by a single recessive gene. The osagpl2-3 gene was mapped between InDel markers R1M30 and ID1-12 on rice chromosome 1. In the candidate region of the Nipponbare genome, an annotated gene, LOC_Os01g44220 which encodes a large subunit of putative ADP-glucose pyrophosphrylase named OsAPL2 was considered the optimal candidate. Cloning and sequencing of LOC_Os01g44220 in different plants of the osagpl2-3 mutants revealed a single nucleotide mutation (G→A) in the open reading frame region, which led to a substitution of an acidic amino acid Glu (E) by a basic amino acid Lys (K) accordingly. Furthermore, the mutant site is close to the functional domain which interacts with the ADP-Glc. In brief, these results suggested that the osagpl2-3 is a new mutant of OsAPL2.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Amylose content
- ADPG:
-
ADP-glucose
- AGPase:
-
ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase
- ATP:
-
Adenosine 5′ triphosphate
- GC:
-
Gel consistency
- Glc-1-P:
-
Glucose-1-phosphate
- GT:
-
Gelatinization temperature
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- PC:
-
Protein content
- RVA:
-
Rapid viscosity analysis
- PPDK:
-
Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase
References
Akihiro T, Mizuno K, Fujimura T (2005) Gene expression of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and starch contents in rice cultured cells are cooperatively regulated by sucrose and ABA. Plant Cell Physiol 46(6):937–946. doi:10.1093/pcp/pci101
Bao JS, Kong XL, Xie JK, Xu LJ (2004) Analysis of genotypic and environmental effects on rice starch. 1. Apparent amylose content, pasting viscosity, and gel texture. J Agric Food Chem 52(19):6010–6016
Chen M, Presting G, Barbazuk WB, Goicoechea JL, Blackmon B, Fang FC, Kim H, Frisch D, Yu YS, Sun SH, Higingbottom S, Phimphilai J, Phimphilai D, Thurmond S, Gaudette B, Li P, Liu JD, Hatfield J, Main D, Farrar K, Henderson C, Barnett L, Costa R, Williams B, Walser S, Atkins M, Hall C, Budiman MA, Tomkins JP, Luo MZ, Bancroft I, Salse J, Regad F, Mohapatra T, Singh NK, Tyagi AK, Soderlund C, Dean RA, Wing RA (2002) An integrated physical and genetic map of the rice genome. Plant Cell 14(3):537–545. doi:10.1105/tpc.010485
Comparot-Moss S, Denyer K (2009) The evolution of the starch biosynthetic pathway in cereals and other grasses. J Exp Bot 60(9):2481–2492. doi:10.1093/jxb/erp141
Denyer K, Patron NJ, Greber B, Fahy BE, Laurie DA, Parker ML (2004) The lys5 mutations of barley reveal the nature and importance of plastidial ADP-Glc transporters for starch synthesis in cereal endosperm. Plant Physiol 135(4):2088–2097. doi:10.1104/pp.104.045203
Dickinso DB, Preiss J (1969) Presence of Adp-glucose pyrophosphorylase in shrunken-2 and brittle-2 mutants of maize endosperm. Plant Physiol 44(7):1058–1062
Dickinson DB, Preiss J (1969) Presence of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase in shrunken-2 and brittle-2 mutants of maize endosperm. Plant Physiol 44(7):1058–1062
Fitzgerald MA, Lisle AJ, Martin M (2000) Chalky and translucent rice grains differ in starch composition and structure and cooking properties. Cereal Chem 77(5):627–632
Fitzgerald MA, McCouch SR, Hall RD (2009) Not just a grain of rice: the quest for quality. Trends Plant Sci 14(3):133–139. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2008.12.004
Furlong CE, Preiss J (1969) Biosynthesis of bacterial glycogen. VII. Purification and properties of the adenosine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase of Rhodospirillium rubrum. J Biol Chem 244(10):2539–2548
Giroux MJ, Smidansky ED, Martin JM, Hannah LC, Fischer AM (2003) Seed yield and plant biomass increases in rice are conferred by deregulation of endosperm ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. Planta 216(4):656–664. doi:10.1007/s00425-002-0897-z
Han X, Wang Y, Liu X, Jiang L, Ren Y, Liu F, Peng C, Li J, Jin X, Wu F, Wang J, Guo X, Zhang X, Cheng Z, Wan J (2011) The failure to express a protein disulphide isomerase-like protein results in a floury endosperm and an endoplasmic reticulum stress response in rice. J Exp Bot. doi:10.1093/jxb/err262
Hannah LC, Greene TW (1998) Maize seed weight is dependent on the amount of endosperm ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. J Plant Physiol 152(6):649–652
Haugen TH, Ishaque A, Preiss J (1976) Biosynthesis of bacterial glycogen. Characterization of the subunit structure of Escherichia coli B glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase (EC 2.7.7.27). J Biol Chem 251(24):7880–7885
James MG, Denyer K, Myers AM (2003) Starch synthesis in the cereal endosperm. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6(3):215–222. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(03)00042-6
Jeon JS, Ryoo N, Hahn TR, Walia H, Nakamura Y (2010) Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperm. Plant Physiol Biochem 48(6):383–392. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.03.006
Jin X, Ballicora MA, Preiss J, Geiger JH (2005) Crystal structure of potato tuber ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. EMBO J 24(4):694–704. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600551
Kang HG, Park S, Matsuoka M, An G (2005) White-core endosperm floury endosperm-4 in rice is generated by knockout mutations in the C-type pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase gene (OsPPDKB). Plant J 42(6):901–911. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02423.x
Kato H, Xie GS, Sato Y, Imai R (2010) Isolation of anther-specific gene promoters suitable for transgene expression in rice. Plant Mol Biol Rep 28(3):381–387. doi:10.1007/s11105-009-0162-8
Kumamaru T, Sato H, Satoh H (1997) High-lysine mutants of rice, Oryza sativa L. Plant Breed 116(3):245–249
Lee SK, Hwang SK, Han M, Eom JS, Kang HG, Han Y, Choi SB, Cho MH, Bhoo SH, An G, Hahn TR, Okita TW, Jeon JS (2007) Identification of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase isoforms essential for starch synthesis in the leaf and seed endosperm of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 65(4):531–546. doi:10.1007/s11103-007-9153-z
Li W, Wu J, Weng S, Zhang D, Zhang Y, Shi C (2010) Characterization and fine mapping of the glabrous leaf and hull mutants (gl1) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep 29(6):617–627. doi:10.1007/s00299-010-0848-2
Li N, Zhang S, Zhao Y, Li B, Zhang J (2011) Over-expression of AGPase genes enhances seed weight and starch content in transgenic maize. Planta 233(2):241–250. doi:10.1007/s00425-010-1296-5
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis—a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(21):9828–9832
Ministry of Agriculture PRC (1988) Standard of Ministry of Agriculture, P. R. China.NY147-88. Method for rice quality measurement, vol NY147-88. Standard Press of China, Beijing
Nagai YS, Sakulsingharoj C, Edwards GE, Satoh H, Greene TW, Blakeslee B, Okita TW (2009) Control of starch synthesis in cereals: metabolite analysis of transgenic rice expressing an up-regulated cytoplasmic ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase in developing seeds. Plant Cell Physiol 50(3):635–643. doi:10.1093/Pcp/Pcp021
Ng PC, Henikoff S (2003) SIFT: predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3812–3814
Ng PC, Henikoff S (2006) Predicting the effects of amino acid substitutions on protein function. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 7:61–80. doi:10.1146/annurev.genom.7.080505.115630
Nishio T, Iida S (1993) Mutants Having a Low Content of 16-Kda Allergenic Protein in Rice (Oryza-Sativa L). Theor Appl Genet 86(2–3):317–321
Ohdan T, Francisco PB Jr, Sawada T, Hirose T, Terao T, Satoh H, Nakamura Y (2005) Expression profiling of genes involved in starch synthesis in sink and source organs of rice. J Exp Bot 56(422):3229–3244. doi:10.1093/jxb/eri292
Okita TW, Nakata PA, Anderson JM, Sowokinos J, Morell M, Preiss J (1990) The subunit structure of potato tuber ADPglucose pyrophosphorylase. Plant Physiol 93(2):785–790
Preiss J, Greenberg E, Sabraw A (1975) Biosynthesis of bacterial glycogen—kinetic studies of a glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase (Ec 2.7.7.27) from a glycogen-deficient mutant of Escherichia coli B. J Biol Chem 250(19):7631–7638
Qiao Y, Lee SI, Piao R, Jiang W, Ham TH, Chin JH, Piao Z, Han L, Kang SY, Koh HJ (2010) Fine mapping and candidate gene analysis of the floury endosperm gene, FLO(a), in rice. Mol Cells 29(2):167–174. doi:10.1007/s10059-010-0010-6
Ryoo N, Yu C, Park CS, Baik MY, Park IM, Cho MH, Bhoo SH, An G, Hahn TR, Jeon JS (2007) Knockout of a starch synthase gene OsSSIIIa/Flo5 causes white-core floury endosperm in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep 26(7):1083–1095. doi:10.1007/s00299-007-0309-8
Satoh H, Omura T (1981) New endosperm mutations induced by chemical mutagens in rice, Oryza sativa L. Jpn J Breed 31(3):316–326
She KC, Kusano H, Koizumi K, Yamakawa H, Hakata M, Imamura T, Fukuda M, Naito N, Tsurumaki Y, Yaeshima M, Tsuge T, Matsumoto K, Kudoh M, Itoh E, Kikuchi S, Kishimoto N, Yazaki J, Ando T, Yano M, Aoyama T, Sasaki T, Satoh H, Shimada H (2010) A novel factor FLOURY ENDOSPERM2 is involved in regulation of rice grain size and starch quality. Plant Cell 22(10):3280–3294. doi:10.1105/tpc.109.070821
Shen YJ, Jiang H, Jin JP, Zhang ZB, Xi B, He YY, Wang G, Wang C, Qian L, Li X, Yu QB, Liu HJ, Chen DH, Gao JH, Huang H, Shi TL, Yang ZN (2004) Development of genome-wide DNA polymorphism database for map-based cloning of rice genes. Plant Physiol 135(3):1198–1205. doi:10.1104/pp.103.038463135/3/1198
Singh R, Juliano BO (1977) Free sugars in relation to starch accumulation in developing rice grain. Plant Physiol 59(3):417–421
Sui JM, Guo BT, Wang JS, Qiao LX, Zhou Y, Zhang HG, Gu MH, Liang GH (2012) A new GA-insensitive semidwarf mutant of rice (Oryza sativa L.) with a missense mutation in the SDG gene. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30(1):187–194. doi:10.1007/s11105-011-0321-6
Supervision tSBoQaT (1999) The National Standard of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T17891-1999. High Quality Paddy vol GB/T17891-1999. Beijing
Thang NB, Wu JG, Zhou WH, Shi CH (2010) The screening of mutants and construction of mutant library for Oryza sativa cv. Nipponbare via ethyl methane sulphonate inducing. Biologia 65(4):660–669. doi:10.2478/s11756-010-0059-x
Wan JM, Wang JK, Wan XY, Li HH, Pfeiffer WH, Crouch J (2007) Application of identified QTL-marker associations in rice quality improvement through a design-breeding approach. Theor Appl Genet 115(1):87–100. doi:10.1007/s00122-007-0545-x
Wang E, Wang J, Zhu X, Hao W, Wang L, Li Q, Zhang L, He W, Lu B, Lin H, Ma H, Zhang G, He Z (2008) Control of rice grain-filling and yield by a gene with a potential signature of domestication. Nat Genet 40(11):1370–1374. doi:10.1038/ng.220
Wang BB, Zhu CX, Liu X, Wang WY, Ding HF, Jiang MS, Li GX, Liu W, Yao FY (2011) Fine mapping of qHD4-1, a QTL controlling the heading date, to a 20.7-kb DNA fragment in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol Rep 29(3):702–713. doi:10.1007/s11105-010-0278-x
Wu JG, Shi CH, Zhang XM (2002) Estimating the amino acid composition in milled rice by near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Field Crops Res 75(1):1–7
Xu LJ, Xie JK, Kong XL, Bao JS (2004) Analysis of genotypic and environmental effects on rice starch. 2. Thermal and retrogradation properties. J Agric Food Chem 52(19)):6017–6022. doi:10.1021/jf049235a
Yamakawa H, Hirose T, Kuroda M, Yamaguchi T (2007) Comprehensive expression profiling of rice grain filling-related genes under high temperature using DNA microarray. Plant Physiol 144(1):258–277. doi:10.1104/pp.107.098665
Yamakawa H, Ebitani T, Terao T (2008) Comparison between locations of QTLs for grain chalkiness and genes responsive to high temperature during grain filling on the rice chromosome map. Breed Sci 58(3):337–343
Zhao F, Cai ZJ, Hu TZ, Yao HG, Wang L, Dong N, Wang B, Ru ZG, Zhai WX (2010) Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of a novel gene conferring resistance to rice stripe virus. Plant Mol Biol Rep 28(3):512–518. doi:10.1007/s11105-009-0178-0
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (no. Y3080217), the Science and Technology Office of Zhejiang Province (no. 2010C32002 and no. 2007C12902), the Program for Innovative Research Team in University(IRT1185), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities" after 2007C12902), and 151 Foundation for Talents of Zhejiang Province of China. We thank Mr. Bin Zhang and Kemin Wang for the assistance of getting some data during the project. We also thank Dr. Wenqiang Li and Alfred Quampah in the English revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dapeng Zhang and Jianguo Wu contributed equally to this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
Sequencing primers of candidate gene LOC_Os01g44220. (DOCX 24 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Putative genes in candidate region. (DOCX 31 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
Physical-chemical parameters of protein transcript of LOC_Os01g44220 of WT and flo6. (DOCX 24 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
Secondary structure parameter of protein transcript of LOC_Os01g44220 of WT and flo6. (DOCX 24 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 1
Tertiary structures of protein transcript of LOC_Os01g44220 of WT and flo6 a and b Prediction tertiary of LOC_Os01g44220.1~6 from WT (a) and flo6 (b). c and d Prediction tertiary of LOC_Os01g44220.7 from WT (c) and flo6 (d). White arrows indicated the changes of secondary structure of protein between WT and flo6. (DOCX 604 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Wu, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Phenotypic and Candidate Gene Analysis of a New Floury Endosperm Mutant (osagpl2-3) in Rice. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30, 1303–1312 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-012-0435-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-012-0435-5