Abstract
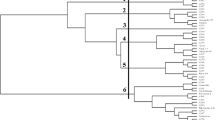
Jatropha curcas (jatropha) is a potential biodiesel crop. A major limitation in production is that jatropha remains wild with low genetic variation. Related species/genera in the Euphorbiaceae can potentially be used for its genetic improvement. In this study, we employed inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSRs) to assess genetic variation among 30 accessions of jatropha, two accessions of bellyache bush (Jatropha gossypifolia), two accessions of spicy jatropha (Jatropha integerrima), two accessions of bottleplant shrub (Jatropha podagrica), and three accessions of castor bean hybrids. Genetic relationships were evaluated using 27 of 86 ISSR markers, yielding 307 polymorphic bands with polymorphism contents ranging from 0.76 to 0.95 for IMPN 1 and UBC 807 markers, respectively. Dice’s genetic similarity coefficient ranged from 0.39 to 0.99, which clearly separated the plant samples into seven groups at the coefficient of 0.48. The first group comprised J. curcas from Mexico, the second group comprised J. curcas from China and Vietnam, the third group comprised J. curcas from Thailand, the fourth group was J. integerrima, the fifth group was J. gossypifolia, the sixth group was J. podagrica, and the last and most distinct group was Ricinus communis. Analysis of molecular variance revealed that 63% of the variability was attributable to variation among groups, while 37% was due to variation within groups. Based on Nei’s genetic distance, the population from G2 (J. curcas from China) and G4 (J. curcas from Vietnam) had the least ISSR variability (0.0668), whereas G8 (R. communis) and Jatropha spp. displayed the highest distance (0.6005–0.7211).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basha SD, Sujatha M (2007) Inter and intra-population variability of Jatropha curcas (L.) characterized by RAPD and ISSR markers and development of population-specific SCAR markers. Euphytica 156(3):375–386
Basha SD, Sujatha M (2009) Genetic analysis of Jatropha species and interspecific hybrids of Jatropha curcas using nuclear and organelle specific markers. Euphytica 168(2):197–214
Basha SD, Francis G, Makkar HPS, Becker K, Sujatha M (2009) A comparative study of biochemical traits and molecular markers for assessment of genetic relationships between Jatropha curcas L. germplasm from different countries. Plant Sci 176:812–823
Bhagyawant SS, Srivastava N (2008) Genetic fingerprinting of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) germplasm using ISSR markers and their relationships. Afr J Biotechnol 7(24):4428–4431
Blair MW, Panaud O, McCouch SR (1999) Inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) amplification for analysis of microsatellite motif frequency and fingerprinting in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 98:780–792
Bostein D, White RL, Sholnick M, David RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphism. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Devappa RK, Swamylingappa B (2008) Biochemical and nutritional evaluation of Jatropha protein isolate prepared by steam injection heating for reduction of toxic and antinutritional factors. J Sci Food Agric 88:911–919
Dice LR (1945) Measures of the amount of ecological association between species. Ecology 26:297–302
Francis G, Edinger R, Becker K (2005) A concept for simultaneous wasteland reclamation, fuel production, and socio-economic development in degraded areas in India: Need, potential and perspectives of Jatropha plantations. Nat Resour Forum 29:12–24
Ganesh Ram S, Parthiban KT, Senthil Kumar R, Thiruvengadam V, Paramathma M (2008) Genetic diversity among Jatropha species as revealed by RAPD markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 55:803–809
Guillemaut P, Maréchal-Drouard L (1992) Isolation of plant DNA: a fast, inexpensive, and reliable method. Plant Mol Biol Report 10(1):60–65
Gupta S, Srivastava M, Mishra GP, Naik PK, Chauhan RS, Tiwari SK, Kumar M, Singh R (2008) Analogy of ISSR and RAPD markers for comparative analysis of genetic diversity among different Jatropha curcas genotypes. Afr J Biotechnol 7(23):4230–4343
Hampl V, Pavlícek A, Flegr J (2001) Construction and bootstrap analysis of DNA fingerprinting-based phylogenetic trees with the freeware program Freetree: application to trichomonad parasites. Int J Syst Ecol Mic 51:731–735
Hashizume T, Shimamoto I, Hirai M (2003) Construction of a linkage map and QTL analysis of horticultural traits for watermelon [Citrullus lanatus (THUNB.) MATSUM & NAKAI] using RAPD, RFLP and ISSR markers. Theor Appl Genet 106:779–785
Heller J (1996) Physic nut, Jatropha curcas L. Promoting the conservation and use of underutilized and neglected crops. 1. Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research, Gartersleben
Joshi-Saha A, Gopalakrishna T (2007) Inheritance and tagging of gene regulating flowering time in the green manure crop Sesbania rostrata (Bremek. & Obrem.). Mol Breed 20:389–399
Kimura I, Crow J (1964) The number of alleles that can be maintained in a finite population. Genetics 49:725–738
King AJ, He W, Cuevas JA, Freudenberger M, Ramiaramanana D, Graham IA (2009) Potential of Jatropha curcas as a source of renewable oil and animal feed. J Exp Bot 13:1–9
Lewontin RC (1972) The apportionment of human diversity. Evol Biol 6:381–398
Li Z, Nelson RL (2002) RAPD marker diversity among cultivated and wild soybean accessions from four Chinese provinces. Crop Sci 42:1737–1744
Makkar HPS, Becker K, Schmook B (1998) Edible provenances of Jatropha curcas from Quintana Roo state of Mexico and effect of roasting on antinutrient and toxic factors in seeds. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 52:31–36
Martins-Lopes P, Lima-Brito J, Gomes S, Meirinhos J, Santos L, Guedes-Pinto H (2007) RAPD and ISSR molecular markers in Olea europaea L.: genetic variability and molecular cultivar identification. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:117–128
McDermott JM, McDonald BA (1993) Gene flow in plant pathosystems. Annu Rev Phytopathol 31:353–373
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3321–3323
Nei M (1978) Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 89:583–590
Openshaw K (2000) A review of Jatropha curcas: an oil plant of unfulfilled promise. Biomass Bioenergy 19(1):1–15
Parthiban KT, Kumar RS, Thiyagarajan P, Subbulakshmi V, Vennila S, Rao MG (2009) Hybrid progenies in jatropha—a new development. Curr Sci 96(6):815–823
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) GenAIEx 6: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Notes 6:288–295
Prabakaran AJ, Sujatha M (1999) Jatropha tanjorensis Ellis & Saroja, a natural interspecific hybrid occurring in Tamil Nadu, India. Genet Resour Crop Evol 46:213–218
Qi X, Pittaway TS, Lindup S, Liu H, Waterman E, Padi FK, Hash CT, Zhu J, Gale MD, Devos KM (2004) An integrated genetic map and a new set of simple sequence repeat markers for pearl millet, Pennisetum glaucum. Theor Appl Genet 109:1485–1493
Ranade SA, Srivastava AP, Rana TS, Srivastava J, Tuli R (2008) Easy assessment of diversity in Jatropha curcas L. plants using two single-primer amplification reaction (SPAR) methods. Biomass Bioenergy 32:533–540
Ratha Krishnan P, Paramathma M (2009) Potentials and Jatropha species wealth of India. Curr Sci 97(7):1000–1004
Reddy MP, Sarlan N, Siddiq EA (2002) Inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) polymorphism and its application in plant breeding. Euphytica 128:9–17
Rohlf FJ (1998) On applications of geometric morphometrics to studies of ontogeny and phylogeny. Syst Biol 47:147–158
Rohlf FJ, Sokal RR (1981) Comparing numerical taxonomic studies. Syst Zool 30:459–490
Sankar AA, Moore GA (2001) Evaluation of inter-simple sequence repeat analysis for mapping in citrus and extension of the genetic linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 102:206–214
Sehgal D, Rajpal VR, Raina SN, Sasanuma T, Sasakuma T (2009) Assaying polymorphism at DNA sequence level for new and novel genetic diversity diagnostics of the safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) world germplasm resources. Genetica 135(3):457–470
Semagn K, Bjørnstad Å, Ndjiondjop MN (2006) An overview of molecular marker methods for plants. Afr J Biotechnol 5(25):2540–2568
Senthil Kumar R, Parthiban KT, Govinda Rao M (2009) Molecular characterization of Jatropha genetic resources through inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers. Mol Biol Rep 36:1951–1956
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana
Sokal RR, Michener CD (1958) Statistical method for evaluating systematic relationships. Univ Kans Sci Bull 38:1409–1438
Sokal RR, Sneath PHA (1963) Principle of numerical taxonomy. Freeman, San Francisco
Sudheer Pamidimarri DVN, Pandya N, Reddy MP, Radhakrishnan T (2009a) Comparative study of interspecific genetic divergence and phylogenic analysis of genus Jatropha by RAPD and AFLP. Mol Biol Rep 36:901–907
Sudheer Pamidimarri DVN, Singh S, Mastan SG, Patel J, Reddy MP (2009b) Molecular characterization and identification of markers for toxic and non-toxic varieties of Jatropha curcas L. using RAPD, AFLP and SSR markers. Mol Biol Rep 36:1357–1364
Sujatha M, Prabakaran AJ (2003) New ornamental Jatropha hybrids through interspecific hybridization. Genet Resour Crop Evol 50:75–82
Tatikonda L, Wani SP, Kannan S, Beerelli N, Sreedevi TK, Hoisington DA, Devi P, Varshney RK (2009) AFLP-based molecular characterization of an elite germplasm collection of Jatropha curcas L., a biofuel plant. Plant Sci 176:505–513
Van der Nest MA, Steenkamp ET, Wingfield BD, Wingfield MJ (2000) Development of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers in Eucalyptus from amplified inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSR). Plant Breed 119:433–436
Venkateswarlu M, Raje Urs S, Surendra Nath B, Shashidhar HE, Maheswaran M, Veeraiah TM, Sabitha MG (2006) A first genetic linkage map of mulberry (Morus spp.) using RAPD, ISSR, and SSR markers and pseudotestcross mapping. Tree Genetics & Genomes 3:15–24
Vijayan K, Srivatsava PP, Nair CN, Awasthi AK, Tikader A, Sreenivasa B, Urs SR (2006) Molecular characterization and identification of markers associated with yield traits in mulberry using ISSR markers. Plant Breed 125:298–301
Wang A, Yu Z, Ding Y (2009) Genetic diversity analysis of wild close relatives of barley from Tibet and the Middle East by ISSR and SSR markers. C R Biologies 332:393–403
Yeh FC, Yang RC, Boyle T (1999) POPGENE Version 1.31, Microsoft Window-based freeware for population genetic analysis. University of Alberta and Centre for International Forestry Research
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Protector Nutrition Co., Ltd. Thailand and Center for Advanced Studies in Agriculture and Food, Institute for Advanced Studies, Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand for financially supporting this work. We also thank Center for Agricultural Biotechnology, Kasetsart University for lab facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanya, P., Taeprayoon, P., Hadkam, Y. et al. Genetic Diversity Among Jatropha and Jatropha-Related Species Based on ISSR Markers. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29, 252–264 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-010-0220-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-010-0220-2