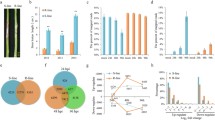
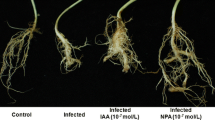
Abstract
Canola (Brassica napus L.) is an agriculturally and economically important crop in Canada, and its growth and yield are frequently influenced by fungal pathogens. Sclerotinia sclerotiorum is among those fungal pathogens and causes stem rot disease in B. napus whereas it has been reported that Brassica carinata is moderately tolerant to S. sclerotiorum. Jasmonic acid/ethylene (JA/ET) and salicylic acid (SA) are phytohormones that are known to be involved in plant disease responses. To investigate the defense signaling cascades involved in the interaction of B. napus and B. carinata with S. sclerotiorum, we examined the expression of five orthologs of B. napus genes involved in JA/ET or SA signaling pathways using quantitative RT-PCR. Our results indicated that there are differences in the timing of JA/ET and SA signaling pathways between B. napus and B. carinata. Our results in these two Brassica species also support previous observations that necrotrophic pathogens trigger JA/ET signaling in response to infection. Finally, we observed that transgenic canola expressing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate-deaminase producing low levels of ET was relatively more susceptible to S. sclerotiorum than its wild-type counterpart, suggesting that ET inhibits S. sclerotiorum-induced symptom development.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal GK, Tamogami S, Han O, Iwahashi H, Rakwal R (2004) Rice octadecanoid pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 317:1–15
Agrios G (1997) Plant pathology, 4th edn. Academic, New York, p 357
Asai T, Stone JM, Heard JE, Kovtun Y, Yorgey P, Sheen J, Ausubel FM (2000) Fumonisin B1-induced cell death in Arabidopsis protoplasts requires jasmonate-, ethylene-, and salicylate-dependent signaling pathways. Plant Cell 12:1823–1835
Bent AF, Innes RW, Ecker JR, Staskawicz BJ (1992) Disease development in ethylene-insensitive Arabidopsis thaliana infected with virulent and avirulent Pseudomonas and Xanthomonas Pathogens. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 5:372–378
Berrocal-Lobo M, Molina A, Solano R (2002) Constitutive expression of ETHYLENE-RESPONSE-FACTOR1 in Arabidopsis confers resistance to several necrotrophic fungi. Plant J 29:23–32
Bleecker AB, Estelle MA, Somerville C, Kende H (1988) Insensitivity to ethylene conferred by a dominant mutation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 241:1086–1089
Bolton MD, Thomma B, Nelson BD (2006) Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary: biology and molecular traits of a cosmopolitan pathogen. Mol Plant Patho 7:1–16
Cao H, Bowling SA, Gordon AS, Dong XN (1994) Characterization of an Arabidopsis mutant that is nonresponsive to inducers of systemic acquired-resistance. Plant Cell 6:1583–1592
Cao H, Glazebrook J, Clarke JD, Volko S, Dong XN (1997) The Arabidopsis NPR1 gene that controls systemic acquired resistance encodes a novel protein containing ankyrin repeats. Cell 88:57–63
Chen JT, Chang WC (2003) 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid enhanced direct somatic embryogenesis from Oncidium leaf cultures. Biol Plant 46:455–458
Chen YF, Etheridge N, Schaller GE (2005) Ethylene signal transduction. Ann Bot 95:901–915
Chern M, Fitzgerald HA, Canlas PE, Navarre DA, Ronald PC (2005) Overexpression of a rice NPR1 homolog leads to constitutive activation of defense response and hypersensitivity to light. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 18:511–520
Clarke JD, Aarts N, Feys BJ, Dong XN, Parker JE (2001) Constitutive disease resistance requires EDS1 in the Arabidopsis mutants cpr1 and cpr6 and is partially EDS1-dependent in cpr5. Plant J 26:409–420
Delaney TP, Uknes S, Vernooij B, Friedrich L, Weymann K, Negrotto D, Gaffney T, Gutrella M, Kessmann H, Ward E, Ryals J (1994) A central role of salicylic-acid in plant-disease resistance. Science 266:1247–1250
Delaney TP, Friedrich L, Ryals JA (1995) Arabidopsis signal-transduction mutant defective in chemically and biologically induced disease resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6602–6606
Dong X (1998) SA, JA, ethylene, and disease resistance in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:316–323
Ellis C, Karafyllidis L, Turner JG (2002) Constitutive activation of jasmonate signaling in an Arabidopsis mutant correlates with enhanced resistance to Erysiphe cichoracearum, Pseudomonas syringae, and Myzus persicae. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:1025–1030
Feys BJ, Parker JE (2000) Interplay of signaling pathways in plant disease resistance. Trends Genet 16:449–455
Friedrich L, Vernooij B, Gaffney T, Morse A, Ryals J (1995) Characterization of tobacco plants expressing a bacterial salicylate hydroxylase gene. Plant Mol Biol 29:959–968
Fujimoto SY, Ohta M, Usui A, Shinshi H, Ohme-Takagi M (2000) Arabidopsis ethylene-responsive element binding factors act as transcriptional activators or repressors of GCC box-mediated gene expression. Plant Cell 12:393–404
Glazebrook J (2005) Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Ann Rev Phytopathol 43:205–227
Glazebrook J, Rogers EE, Ausubel FM (1996) Isolation of Arabidopsis mutants with enhanced disease susceptibility by direct screening. Genetics 143:973–982
Glick BR (1995) The enhancement of plant-growth by free-living Bacteria. Can J Microbiol 41:109–117
Glick BR, Penrose DM, Li JP (1998) A model for the lowering of plant ethylene concentrations by plant growth-promoting bacteria. J Theor Biol 190:63–68
Glick BR, Patten CL, Holguin G, Penrose DM (1999) Biochemical and genetic mechanisms used by plant growth promoting Bacteria. Imperial College Press, London, pp 45–53
Grbic V, Bleecker AB (1995) Ethylene regulates the timing of leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant J 8:595–602
Greenberg JT, Silverman FP, Liang H (2000) Uncoupling salicylic acid-dependent cell death and defense-related responses from disease resistance in the Arabidopsis mutant acd5. Genetics 156:341–350
Hammer O, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: palaeontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electronica 4(1):9
Hegedus DD, Li RG, Buchwaldt L, Parkin I, Whitwill S, Coutu C, Bekkaoui D, Rimmer SR (2008) Brassica napus possesses an expanded set of polygalacturonase inhibitor protein genes that are differentially regulated in response to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum infection, wounding and defense hormone treatment. Planta 228:241–253
Heitz T, Bergey DR, Ryan CA (1997) A gene encoding a chloroplast-targeted lipoxygenase in tomato leaves is transiently induced by wounding, systemin, and methyl jasmonate. Plant Physiol 114:1085–1093
Hoffman T, Schmidt JS, Zheng X, Bent AF (1999) Isolation of ethylene-insensitive soybean mutants that are altered in pathogen susceptibility and gene-for-gene disease resistance. Plant Physiol 119:935–949
Honma M, Shimomura T (1978) Metabolism of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid. Agric Biol Chem 42:1825–1831
Ishiguro S, Kawai-Oda A, Ueda J, Nishida I, Okada K (2001) The DEFECTIVE IN ANTHER DEHISCENCE1 gene encodes a novel phospholipase A1 catalyzing the initial step of jasmonic acid biosynthesis, which synchronizes pollen maturation, anther dehiscence, and flower opening in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 13:2191–2209
Jacobson CB, Pasternak JJ, Glick BR (1994) Partial purification and characterization of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase from the plant growth promoting rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida GR12–2. Can J Microbiol 40:1019–1025
Jing HC, Schippers JHM, Hille J, Dijkwei PP (2005) Ethylene-induced leaf senescence depends on age-related changes and OLD genes in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 56:2915–2923
Kachroo A, Kachroo P (2007) Salicylic acid-, jasmonic acid- and ethylene-mediated regulation of plant defense signaling. Genet Eng (N Y) 28:55–83
Kesarwani M, Yoo JM, Dong XN (2007) Genetic interactions of TGA transcription factors in the regulation of pathogenesis-related genes and disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 144:336–346
Knoester M, van Loon LC, van den Heuvel J, Hennug J, Bol JF, Linthorst HJM (1998) Ethylene insensitive tobacco lacks nonhost resistance against soil-borne fungi. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1933–1937
Kunkel BN, Brooks DM (2002) Cross talk between signaling pathways in pathogen defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:325–331
Laudert D, Weiler EW (1998) Allene oxide synthase: a major control point in Arabidopsis thaliana octadecanoid signalling. Plant J 15:675–684
Liang Y, Srivastava S, Rahman MH, Strelkov SE, Kav NN (2008) Proteome changes in leaves of Brassica napus L. as a result of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum challenge. J Agric Food Chem 56:1963–1976
Lund ST, Stall RE, Klee HJ (1998) Ethylene regulates the susceptible response to pathogen infection in tomato. Plant Cell 10:371–382
Martinez C, Blanc F, Le Claire E, Besnard O, Nicole M, Baccou JC (2001) Salicylic acid and ethylene pathways are differentially activated in melon cotyledons by active or heat-denatured cellulase from Trichoderma longibrachiatum. Plant Physiol 127:334–344
McDowell JM, Dangl JL (2000) Signal transduction in the plant immune response. Trends Biochem Sci 25:79–82
Meuwly P, Molders W, Buchala A, Metraux JP (1995) Local and systemic biosynthesis of salicylic-acid in infected Cucumber Plants. Plant Physiol 109:1107–1114
Mussig C, Biesgen C, Lisso J, Uwer U, Weiler EW, Altmann T (2000) A novel stress-inducible 12-oxophytodienoate reductase from Arabidopsis thaliana provides a potential link between Brassinosteroid-action and Jasmonic-acid synthesis. J Plant Physiol 157:143–152
Nakano T, Nishiuchi T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H (2006) Studies on transcriptional regulation of endogenous genes by ERF2 transcription factor in tobacco cells. Plant Cell Physiol 47(4):554–558
Ndamukong I, Abdallat AA, Thurow C, Fode B, Zander M, Weigel R, Gatz C (2007) SA-inducible Arabidopsis glutaredoxin interacts with TGA factors and suppresses JA-responsive PDF1.2 transcription. Plant J 50(1):128–139
Ohtsubo N, Mitsuhara I, Koga M, Seo S, Ohashi Y (1999) Ethylene promotes the necrotic lesion formation and basic PR gene expression in TMV-infected tobacco. Plant Cell Physiol 40:808–817
Penrose DM, Moffatt BA, Glick BR (2001) Determination of 1-aminocycopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) to assess the effects of ACC deaminase-containing bacteria on roots of canola seedlings. Can J Microbiol 47:77–80
Profotova B, Burketova L, Novotna Z, Martinec J, Valentova O (2006) Involvement of phospholipases C and D in early response to SAR and ISR inducers in Brassica napus plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:143–151
Qin J, Zuo KJ, Zhao JY, Ling H, Cao YF, Qiu CX, Li FP, Sun XF, Tang KX (2006) Overexpression of GbERF confers alteration of ethylene-responsive gene expression and enhanced resistance to Pseudomonas syringae in transgenic tobacco. J Biosci 31:255–263
Robison MM, Shah S, Tamot B, Pauls KP, Moffatt BA, Glick BR (2001) Reduced symptoms of Verticillium wilt in transgenic tomato expressing a bacterial ACC deaminase. Mol Plant Pathol J 2:135–145
Ryals J, Weymann K, Lawton K, Friedrich L, Ellis D, Steiner HY, Johnson J, Delaney TP, Jesse T, Vos P, Uknes S (1997) The Arabidopsis NIM1 protein shows homology to the mammalian transcription factor inhibitor I kappa B. Plant Cell 9:425–439
Sasaki Y, Asamizu E, Shibata D, Nakamura Y, Kaneko T, Awai K, Amagai M, Kuwata C, Tsugane T, Masuda T, Shimada H, Takamiya X, Ohta H, Tabata S (2001) Monitoring of methyl jasmonate-responsive genes in Arabidopsis by cDNA macroarray: Self-activation of jasmonic acid biosynthesis and crosstalk with other phytohormone signaling pathways. DNA Res 8:153–161
Schaller F, Zerbe P, Reinbothe S, Reinbothe C, Hofmann E, Pollmann S (2008) The allene oxide cyclase family of Arabidopsis thaliana - localization and cyclization. Febs Journal 275:2428–2441
Sedun FS, Segun GS, Rakow GFW (1989) Genetic variation in reaction to Sclerotinia stem rot in Brassica species. Can J Plant Sci 69:229–232
Seo HS, Song JT, Cheong JJ, Lee YH, Lee YW, Hwang I, Lee JS, Choi YD (2001) Jasmonic acid carboxyl methyltransferase: a key enzyme for jasmonate-regulated plant responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:4788–4793
Shah J, Klessig DF (1996) Identification of a salicylic acid-responsive element in the promoter of the tobacco pathogenesis-related beta-1, 3-glucanase gene, PR-2d. Plant J 10:1089–1101
Shah J, Tsui F, Klessig DF (1997) Characterization of a salicylic acid-insensitive mutant (sai1) of Arabidopsis thaliana, identified in a selective screen utilizing the SA-inducible expression of the tms2 gene. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 10:69–78
Shah S, Li JP, Moffatt BA, Glick BR (1998) Isolation and characterization of ACC deaminase genes from two different plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Can J Microbiol 44:833–843
Shivpuri A, Chipa HP, Gupta RBL, Sharma KN (1997) Field evaluation of mustard genotypes against white rust, powdery mildew and stem rot. Annal of Arid Zone 36(4):387–387
Singh MP, Lee FN, Counce PA, Gibbons JH (2004) Mediation of partial resistance to rice blast through anaerobic induction of ethylene. Phytopathology 94:819–825
Stearns JC, Glick BR (2003) Transgenic plants with altered ethylene biosynthesis or perception. Biotechnol Adv 21:193–210
Stenzel I, Hause B, Miersch O, Kurz T, Maucher H, Weichert H, Ziegler J, Feussner I, Wasternack C (2003) Jasmonate biosynthesis and the allene oxide cyclase family of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 51:895–911
Thomma B, Eggermont K, Tierens K, Broekaert WF (1999) Requirement of functional ethylene-insensitive 2 gene for efficient resistance of Arabidopsis to infection by Botrytis cinerea. Plant Physiol 121:1093–1101
van der Fits L, Zhang H, Menke FLH, Deneka M, Memelink J (2000) A Catharanthus roseus BPF-1 homologue interacts with an elicitor-responsive region of the secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene Str and is induced by elicitor via a JA-independent signal transduction pathway. Plant Mol Biol 44:675–685
van Loon LC, Geraats BPJ, Linthorst HJM (2006) Ethylene as a modulator of disease resistance in plants. Trends Plant Sci 11:184–191
Ververidis P, John P (1991) Complete recovery invitro of Ethylene-formaing enzyme-activity. Phytochemistry 30:725–727
Wang KLC, Li H, Ecker JR (2002) Ethylene biosynthesis and signaling networks. Plant Cell 14:S131–S151
Wilkinson JQ, Lanahan MB, Yen HC, Giovannoni JJ, Klee HJ (1995) An ethylene-inducible component of signal-transduction encoded by never-ripe. Science 270:1807–1809
Yang B, Srivastava S, Deyholos MK, Kav NNV (2007) Transcriptional profiling of canola (Brassica napus L.) responses to the fungal pathogen Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Plant Sci 173:156–171
Yuan Y, Zhong S, Li Q, Zhu Z, Lou Y, Wang L, Wang J, Wang M, Li Q, Yang D, He Z (2007) Functional analysis of rice NPR1-like genes reveals that OsNPR1/NH1 is the rice orthologue conferring disease resistance with enhanced herbivore susceptibility. Plant Biotechnol J 5(2):313–324
Zhang YL, Tessaro MJ, Lassner M, Li X (2003) Knockout analysis of Arabidopsis transcription factors TGA2, TGA5, and TGA6 reveals their redundant and essential roles in systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 15:2647–2653
Zhao JW, Wang JL, An LL, Doerge RW, Chen ZJ, Grau CR, Meng JL, Osborn TC (2007) Analysis of gene expression profiles in response to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in Brassica napus. Planta 227:13–24
Acknowledgements
We thank the technical help of Drs. Yuanqing Jiang and Bill Yajima for critical reading of this manuscript. This work was supported by the Alberta Agricultural Research Institute (grant number 2004A001R).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Both Muhammad Rahman and Yue Liang contributed equally.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
Mutiple alignments of cDNA/amino acid sequence of different alleles of genes AOC3, ERF2, and TGA5 by BOXSHADE3.21 (http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/BOX_form.html). (PDF 35 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, B., Rahman, M.H., Liang, Y. et al. Characterization of Defense Signaling Pathways of Brassica napus and Brassica carinata in Response to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum Challenge. Plant Mol Biol Rep 28, 253–263 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-009-0149-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-009-0149-5