Abstract
Aims
The combined effects of nitrogen (N) deposition and management practices on fine root decomposition remain unknown. The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of the two factors on fine root decay in Moso bamboo plantations.
Methods
This study was performed over a three-year period and included three nitrogen treatments (30, 60, and 90 kg N ha−1 yr.−1) and two management practices (conventional and intensive).
Results
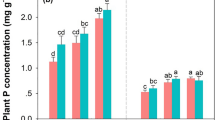
Fine root decomposition was significantly affected by N inputs and management practices both separately and in combination (P < 0.01). N inputs had a stronger effect than management practices. The low-N input (30 kg N ha−1 yr.−1) accelerated fine root decomposition and nutrient release, whereas high-N inputs (≥ 60 kg N ha−1 yr.−1) inhibited decomposition and nutrient release. Moreover, intensive management practices strengthened the inhibitory effects of the high-N inputs.
Conclusions
Moderate N deposition (< 60 kg N ha−1 yr.−1) may decrease soil carbon storage but increase Moso bamboo productivity, while excessive N deposition (≥ 90 kg N ha−1 yr.−1) may have opposing effects. The combined effects of management practices and nitrogen amendment should be considered when estimating the effects of increasing atmospheric N deposition on plantation ecosystems.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson M, Kjøller A, Struwe S (2004) Microbial enzyme activities in leaf litter, humus and mineral soil layers of European forests. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1527–1537
Austin AT, Ballaré CL (2010) Dual role of lignin in plant litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. Proc Natl AcadSci USA 107:4618–4622
Axelsson G, Berg B (1988) Fixation of ammonia (15N) to scots pine needle litter in different stages of decomposition. Scand J For Res 3:273–279
Balesdent J, Besnard E, Arrouays D, Chenu C (1998) The dynamics of carbon in particle-size fractions of soil in a forest-cultivation sequence. Plant Soil 201:49–57
Berg B, McClaugherty C (2008) Plant litter: Decomposition, humus formation, carbon sequestration, 2nd edn. Springer, Heidelberg
Berg B, McClaugherty C, Santo AVD, Johnson D (2001) Humusbuildup in boreal forests: effects of litter fall and its Nconcentration. Can JFor Res 31:988–998
Bloomfield J, Vogt KA, Vogt DJ (1993) Decay rate and substrate quality of fine roots and foliage of two tropical tree species in the Luquillo experimental forest, Puerto Rico. Plant Soil 150:233–245
Brandt LA, King JY, Hobbie SE, Milchunas DG, Sinsabaugh RL (2010) The role of photodegradation in surface litter decomposition across a grassland ecosystem precipitation gradient. Ecosystems 13:1–17
Carreiro MM, Sinsabaugh RL, Repert DA, Parkhurst DF (2000) Microbial enzyme shifts explain litter decay responses to simulated nitrogen deposition. Ecology 81:2359–2365
Cui J, Zhou J, Peng Y, He Y, Yang H, Mao J, Zhang M, Wang Y, Wang S (2014) Atmospheric wet deposition of nitrogen and sulfur in the agroecosystem in developing and developed areas of southeastern China. Atmos Environ 89:102–108
Fang H, Mo J, Peng S, Li Z, Wang H (2007) Cumulative effects of nitrogen additions on litter decomposition in three tropical forests in southern China. Plant Soil 297:233–242
Fog K (1988) The effect of added nitrogen on the rate of decomposition of organic matter. Biol Rev 63:433–462
Galloway JN, Townsend AR, Erisman JW, Bekunda M, Cai Z, Freney JR, Martinelli L, Seitzinger SP, Sutton MA (2008) Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 320:889–892
Gosz JR, Likens GE, Bormann FH (1973) Nutrient release from decomposing leaf and branch litter in the Hubbard brook Forest, New Hampshire. Ecol Monogr 43:173–191
Hobbie SE (2008) Nitrogen effects on decomposition: a five-year experiment in eight temperate sites. Ecology 89:2633–2644
Hobbie SE, Eddy WC, Buyarski CR, Adair EC, Ogdahl ML, Weisenhorn P (2012) Response of decomposing litter and its microbial community to multiple forms of nitrogen enrichment. Ecol Monogr 82:389–405
Jackson RB, Mooney HA, Schulze ED (1997) A global budget for fine root biomass, surface area, and nutrient contents. Proc Natl AcadSci USA 94:7362–7366
Jia Y, Yu G, He N, Zhan X, Fang H, Sheng W, Zuo Y, Zhang D, Wang Q (2014) Spatial and decadal variations in inorganic nitrogen wet deposition in China induced by human activity. Sci Rep 4:3763
Jiang P, Wang H, Wu J, Xu Q, Zhou G (2009) Winter mulch increases soil CO2 efflux under Phyllostachys Praecox stands. J Soils Sediments 9:511–514
Keeler BL, Hobbie SE, Kellogg L (2009) Effects of long-term nitrogen additions on soil and litter microbial enzyme activity in eight forested and grassland sites–implications for litter and SOM decomposition. Ecosystems 12:1–15
Knorr M, Frey SD, Curtio PS (2005) Nitrogen additions and litter decomposition: a meta-analysis. Ecology 86:3252–3257
Li H, Lei Y (2010) Estimation and evaluation of forest biomass carbon storage in China. Chinese Forestry Press, Beijing
Li R, Werger MJA, de Kroon H, During HJ, Zhong Z (2000) Interactions between shoot age structure, nutrient availability and physiological integration in the giant bamboo Phyllostachys pubescens. Plant boil 2:437–446
Li Q, Song X, Gu H, Gao F (2016) Nitrogen deposition and management practices increase soil microbial biomass carbon but decrease diversity in Moso bamboo plantations. Sci Rep 6:28235
Lin C, Yang Y, Guo J, Chen G, Xie J (2011) Fine root decomposition of evergreen broadleaved and coniferous tree species in mid-subtropical China: dynamics of dry mass, nutrient and organic fractions. Plant Soil 338:311–327
Liu X, Zhang Y, Han W, Tang A, Shen J, Cui Z, Vitousek P, Erisman JW, Goulding K, Christie P, Fangmeier A, Zhang F (2013) Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 494:459–462
Liu L, Zhang X, Wang S, Lu X, Ouyang X (2016) A review of spatial variation of inorganic nitrogen (N) wet deposition in China. PLoSONE11:e0146051
Manning P, Saunders M, Bardgett RD, Bonkowski M, Bradford MA, Ellis RJ, Kandeler E, Marhan S, Tscherko D (2008) Direct and indirect effects of nitrogen deposition on litter decomposition. Soil Biol Biochem 40:688–698
Manzoni S, Jackson RB, Trofymow JA, Porporato A (2008) The global stoichiometry of litter nitrogen mineralization. Science 321:684–686
Manzoni S, Trofymow JA, Jackson RB, Porporato A (2010) Stoichiometric controls on carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus dynamics in decomposing litter. Ecol Monogr 80:89–106
Mary B, Recous S, Darwis D, Robin D (1996) Interactions between decomposition of plant residues and nitrogen cycling in soil. Plant Soil 181:71–82
Matson PA, McDowell WH, Townsend AR, Vitousek PM (1999) Theglobalization of N deposition: ecosystem consequences in tropical environments. Biogeochemistry 46:67–83
Mo J, Brown S, Xue J, Fang Y, Li Z, Li D, Dong S (2007) Response of nutrient dynamics of decomposing pine (Pinusmassoniana) needles to simulated N deposition in a disturbed and a rehabilitated forest in tropical China. Ecol Res 22:649–658
Nadelhoffer KJ, Raich JW (1992) Fine root production estimates and belowground carbon allocation in forest ecosystems. Ecology 73:1139–1147
Olson JS (1963) Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposition in ecological system. Ecology 44:322–331
Ostertag R, Hobbie SE (1999) Early stages of root and leaf decomposition in Hawaiian forest: effect of nutrient availability. Oecologia 121:564–573
Parton W, Silver WL, Burke IC, Grassens L, Harmon ME, Currie WS, King JY, Adair EC, Brand LA, Hart SC (2007) Global-scale similarities in nitrogen release patterns during long-term decomposition. Science 315:361–364
Reay DS, Dentener F, Smith P, Grace J, Feely RA (2008) Global nitrogen deposition and carbon sinks. Nat Geosci 1:430–437
Silver WL, Miya RK (2001) Global patterns in root decomposition: comparisons of climate and litter quality effects. Oecologia 129:407–419
Sinsabaugh RL (2010) Phenol oxidase, peroxidase and organic matter dynamics of soil. Soil Biol Biochem 42:391–404
Song X, Zhou G, Jiang H, Yu S, Fu J, Li W, Wang W, Ma Z, Peng C (2011) Carbon sequestration by Chinese bamboo forests, and their ecological benefits: assessment of potential, problems, and future challenges. Environ Rev 19:418–428
Song X, Jiang H, Zhang Z, Zhou G, Zhang S, Peng C (2014) Interactive effects of elevated UV-B radiation and N deposition on Moso bamboo litter decomposition. Soil Biol Biochem 69:11–16
Song X, Zhou G, Gu H, Qi L (2015) Management practices amplify the effects of N deposition on leaf litter decomposition of the Moso bamboo forest. Plant Soil 395:391–400
Song X, Gu H, Wang M, Zhou G, Li Q (2016) Management practices regulate the response of Moso bamboo foliar stoichiometry to nitrogen deposition. Sci Rep 6:24107
Sun T, Mao Z, Han Y (2013) Slow decomposition of very fine roots and some factors controlling the process: a 4-year experiment in four temperate tree species. Plant Soil 372:445–458
Thirukkumaran CM, Parkinson D (2000) Microbial respiration, biomass, metabolic quotient and litter decomposition in a lodgepole pine forest floor amended with nitrogen and phosphorous fertilizers. Soil Biol Biochem 32:59–66
Tian H, Chen G, Lu C, Xu X, Ren W, Zhang B, Banger K, Tao B, Pan S, Liu M, Zhang C, Bruhwiler L, Wofsy S (2015) Global methane and nitrous oxide emissions from terrestrial ecosystems due to multiple environmental changes. Ecosyst Health Sustain 1:4
Tu L, Peng Y, Chen G, Hu H, Xiao Y, Hu T (2015) Direct and indirect effects of nitrogen additions on fine root decomposition in a subtropical bamboo forest. Plant Soil 389:273–288
Van Groenigen KJ, Six J, Hungate BA, de Graaff MA, van Breemen N, van Kessel C (2006) Element interactions limit soil carbon storage. Proc Natl AcadSci USA 103:6571–6574
Xie Y, Zhang S, Zhao X, Xiong Z, Xing G (2008) Seasonal variation patterns of NH4 +-N/NO3 −-N ratio and δ15 NH4 + value in rainwater in Yangtze river delta. Chinese. J Appl Ecol 19:2035–2041
Xu R (2013) Amelioration principles and technologies for acidified red soils. Science Press, Beijing
Xu X, Hirata E (2005) Decomposition patterns of leaf litter of seven common canopy species in a subtropical forest: N and P dynamics. Plant Soil 273:279–289
Xu Q, Liu L, Hong Y (1998) Analysis on enzyme activities of high-yield and low-yield Phyllostachys pubescens stands. J Bamboo Res 17:37–40
Xu Q, Jiang P, Xu Z (2008) Soil microbial functional diversity under intensively managed bamboo plantations in southern China. J Soils Sediments 8:177–183
Yang Y, Chen G, Guo J, Lin P (2004) Decomposition dynamic of fine roots in a mixed forest of Cunninghamialanceolataand Tsoongiodendronodorumin midsubtropics. Ann ForSci61:65–72
Zhang D, Hui D, Luo Y, Zhou G (2008) Rates of litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems: global patterns and controlling factors. J Plant Ecol 1:85–93
Zhou B, Fu M (2004) Review on bamboo’s underground rhizome-root system research. For Res 17:533–540
Zhou B, Fu M (2008) Fine root production and turnover of Phyllostachys pubescens stands in Miaoshanwu nature reserve. Acta Agri UnivJiangxiensis 2:239–245
Zhou G, Jiang P (2004) Density, storage and spatial distribution of carbon in Phyllostachy pubescens forest. SciSilvaeSinicae 40:20–24
Zhou G, Xu J, Jiang P (2006) Effect of management practices on seasonal dynamics of organic carbon in soils under bamboo plantations. Pedosphere 16:525–531
Zhou G, Jiang P, Xu Q (2010) Carbon fixing and transition in the ecosystem of bamboo stands. Science Press, Beijing
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the “948” Project of the State Forestry Bureau of China (Grant No. 2013-4-55), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31270517, 31470529), and the Pandeng Project for Young & Middle-aged Discipline Leaders of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. pd2013234).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no competing financial interests. All of the authors have contributed substantially to the manuscript and approved the final submission. All previous work cited in the manuscript has been fully acknowledged.
This study did not involve human participants, specimens or tissue samples, or vertebrate animals, embryos or tissues.
This manuscript has not been submitted elsewhere in whole or in part and is not currently under consideration for publication in any other journal before a decision has been made by Plant and Soil.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Alfonso Escudero.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Li, Q. & Gu, H. Effect of nitrogen deposition and management practices on fine root decomposition in Moso bamboo plantations. Plant Soil 410, 207–215 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2997-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2997-8