Abstract
Key message
Enhanced glutathione content improves lateral root development by positively regulating the transcripts of root development genes responsive to glutathione treatment, thereby increasing the overall productivity of rice plants.
Abstract
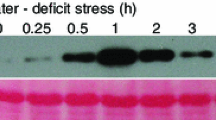
Glutathione is primarily known as a cellular antioxidant molecule, but its role in lateral root development in rice plants has not been elucidated. Here, we have investigated its role in lateral root development of rice Oryza sativa L. Exogenous glutathione (GSH) promoted both the number and length of lateral roots in rice, and the GSH biosynthesis inhibitor buthionine sulfoximine (BSO) significantly reduced these parameters, compared to untreated plants. The inhibition by BSO was reversed with exogenous GSH. Transcript profiling by RNA-seq revealed that expression of the transcription factor genes DREB and ERF and the hormone-related genes AOS, LOX, JAZ, and SAUR were significantly downregulated in the BSO-treated plants and, in contrast, upregulated in plants treated with GSH and with GSH and BSO together. We generated OsGS-overexpressing transgenic plants in which the transgene is controlled by the abiotic-stress-inducible OsRab21 promoter to study the effect of endogenously increased GSH levels. In cold stress, transgenic rice plants enhanced stress tolerance and lateral root development by maintaining redox homeostasis and improving upregulating the expression of transcription factors and hormone-related genes involved in lateral root development. We observed improved root growth of OsGS-overexpressing plants in paddy fields compared to the wild-type controls. These traits may have alleviated transplanting stress during early growth in the field and accounted for the increased productivity. These results provide information and perspectives on the role of GSH in gene expression, lateral root development, and grain yield in rice.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashraf M, Bashir A (2003) Relationship of photosynthetic capacity at the vegetative stage and during grain development with grain yield of two hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars differing in yield. Eur J Agron 19:277–287. https://doi.org/10.1078/0367-2530-00121
Awasthi JP, Saha B, Chowardhara B, Devi SS, Borgohain P, Panda SK (2018) Qualitative analysis of lipid peroxidation in plants under multiple stress through Schiff’s reagent: a histochemical approach. Bio Protoc. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.2807
Bashandy T, Guilleminot J, Vernoux T, Caparros-Ruiz D, Ljung K, Meyer Y, Reichheld JP (2010) Interplay between the NADP-linked thioredoxin and glutathione systems in Arabidopsis auxin signaling. Plant Cell 22:376–391. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.071225
Bengough AG, McKenzie BM, Hallett PD, Valentine TA (2011) Root elongation, water stress, and mechanical impedance: a review of limiting stresses and beneficial root tip traits. J Exp Bot 62:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq350
Cai XT, Xu P, Zhao PX, Liu R, Yu LH, Xiang CB (2014) Arabidopsis ERF109 mediates cross-talk between jasmonic acid and auxin biosynthesis during lateral root formation. Nat Commun 5:5833. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6833
Cheng JC, Seeley KA, Sung ZR (1995) Rml1 and Rml2, Arabidopsis genes required for cell-proliferation at the root-tip. Plant Physiol 107:365–376. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.2.365
Chinnusamy V, Zhu J, Zhu JK (2007) Cold stress regulation of gene expression in plants. Trends Plant Sci 12:444–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2007.07.002
Dempsey RW, Merchant A, Tausz M (2012) Differences in ascorbate and glutathione levels as indicators of resistance and susceptibility in Eucalyptus trees infected with Phytophthora cinnamomi. Tree Physiol 32:1148–1160. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tps076
Diaz-Vivancos P, de Simone A, Kiddie G, Foyer CH (2015) Glutathione—linking cell proliferation to oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 89:1154–1164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.09.023
Dumlao MR, Darehshouri A, Cohu CM, Muller O, Mathias J, Adams III WW, Demmig-Adams B (2012) Low temperature acclimation of photosynthetic capacity and leaf morphology in the context of phloem loading type. Photosynth Res 113:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-012-9762-5
Dunbabin V, Rengel Z, Diggle AJ (2004) Simulating form and function of root systems: efficiency of nitrate uptake is dependent on root system architecture and the spatial and temporal variability of nitrate supply. Funct Ecol 18:204–211. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0269-8463.2004.00827.x
Fattorini L, Falasca G, Kevers C, Rocca LM, Zadra C, Altamura MM (2009) Adventitious rooting is enhanced by methyl jasmonate in tobacco thin cell layers. Planta 231:155–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-009-1035-y
Garcia-Gimenez JL, Markovic J, Dasi F, Queval G, Schnaubelt D, Foyer CH, Pallardo FV (2013) Nuclear glutathione. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830:3304–3316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.10.005
Gewin V (2010) Food: an underground revolution. Nature 466:552–553. https://doi.org/10.1038/466552a
Goh T, Kasahara H, Mimura T, Kamiya Y, Fukaki H (2012) Multiple AUX/IAA-ARF modules regulate lateral root formation: the role of Arabidopsis SHY2/IAA3-mediated auxin signalling. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367:1461–1468. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2011.0232
Guarise M, Borgonovo G, Bassoli A, Ferrante A (2019) Evaluation of two wild populations of hedge mustard (Sisymbrium officinale (L.) Scop.) as a potential leafy vegetable. Horticulturae. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae5010013
Gueta-Dahan Y, Yaniv Z, Zilinskas BA, Ben-Hayyim G (1997) Salt and oxidative stress: similar and specific responses and their relation to salt tolerance in Citrus. Planta 203:460–469
Gutterson N, Reuber TL (2004) Regulation of disease resistance pathway by AP2/ERF transcription factors. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:465–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2004.04.007
Han Y, Mhamdi A, Chaouch S, Noctor G (2013) Regulation of basal and oxidative stress-triggered jasmonic acid-related gene expression by glutathione. Plant Cell Environ 36:1135–1146. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12048
Hao YJ et al (2011) Soybean NAC transcription factors promote abiotic stress tolerance and lateral root formation in transgenic plants. Plant J 68:302–313. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04687.x
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Anee TI, Fujita M (2017) Glutathione in plants: biosynthesis and physiological role in environmental stress tolerance. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23:249–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-017-0422-2
He XJ, Mu RL, Cao WH, Zhang ZG, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2005) AtNAC2, a transcription factor downstream of ethylene and auxin signaling pathways, is involved in salt stress response and lateral root development. Plant J 44:903–916. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02575.x
Hermans C, Smeyers M, Rodriguez RM, Eyletters M, Strasser RJ, Delhaye JP (2003) Quality assessment of urban trees: a comparative study of physiological characterisation, airborne imaging and on site fluorescence monitoring by the OJIP-test. J Plant Physiol 160:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-00917
Hernandez LE, Sobrino-Plata J, Montero-Palmero MB, Carrasco-Gil S, Flores-Caceres ML, Ortega-Villasante C, Escobar C (2015) Contribution of glutathione to the control of cellular redox homeostasis under toxic metal and metalloid stress. J Exp Bot 66:2901–2911. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv063
Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T (1994) Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J 6:271–282. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1994.6020271.x
Hodges DM, DeLong JM, Forney CF, Prange RK (1999) Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta 207:604–611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250050524
Hsu CH, Hsu YT (2019) Biochemical responses of rice roots to cold stress. Bot Stud 60:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40529-019-0262-1
Hsu YY, Chao YY, Kao CH (2013) Methyl jasmonate-induced lateral root formation in rice: the role of heme oxygenase and calcium. J Plant Physiol 170:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2012.08.015
Huang M, Shan SL, Zhou XF, Chen JN, Cao FB, Jiang LG, Zou YB (2016) Leaf photosynthetic performance related to higher radiation use efficiency and grain yield in hybrid rice. Field Crops Res 193:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2016.03.009
Jahn TP et al (2004) Aquaporin homologues in plants and mammals transport ammonia. FEBS Lett 574:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2004.08.004
Jang IC, Choi WB, Lee KH, Song SI, Nahm BH, Kim JK (2002) High-level and ubiquitous expression of the rice cytochrome c gene OsCc1 and its promoter activity in transgenic plants provides a useful promoter for transgenesis of monocots. Plant Physiol 129:1473–1481. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.002261
Jung H, Chung PJ, Park SH, Redillas MCFR, Kim YS, Suh JW, Kim JK (2017) Overexpression of OsERF48 causes regulation of OsCML16, a calmodulin-like protein gene that enhances root growth and drought tolerance. Plant Biotechnol J 15:1295–1308. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12716
Kaur N, Sharma I, Kirat K, Pati PK (2016) Detection of reactive oxygen species in Oryza sativa L. (rice). Bio Protoc. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.2061
Kocsy G, Galiba G, Brunold C (2001) Role of glutathione in adaptation and signalling during chilling and cold acclimation in plants. Physiol Plant 113:158–164
Kong Y et al (2013) Tissue-specific expression of SMALL AUXIN UP RNA41 differentially regulates cell expansion and root meristem patterning in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 54:609–621. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pct028
Koprivova A, Mugford ST, Kopriva S (2010) Arabidopsis root growth dependence on glutathione is linked to auxin transport. Plant Cell Rep 29:1157–1167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-010-0902-0
Kwon SY, Jeong YJ, Lee HS, Kim JS, Cho KY, Allen RD, Kwak SS (2002) Enhanced tolerances of transgenic tobacco plants expressing both superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase in chloroplasts against methyl viologen-mediated oxidative stress. Plant Cell Environ 25:873–882. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.2002.00870.x
Lee DH, Lee CB (2000) Chilling stress-induced changes of antioxidant enzymes in the leaves of cucumber: in gel enzyme activity assays. Plant Sci 159:75–85
Li X, Zeng R, Liao H (2016) Improving crop nutrient efficiency through root architecture modifications. J Integr Plant Biol 58:193–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12434
Lim H et al (2016) A simple, rapid and systematic method for the developed GM rice analysis. Plant Biotechnol Rep 10:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-015-0384-1
Lin ZF, Liu N, Lin GZ, Peng CL (2009) In situ localisation of superoxide generated in leaves of Alocasia macrorrhiza (L.) Shott under various stresses. J Plant Biol 52:340–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-009-9044-8
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Loque D, Ludewig U, Yuan L, von Wiren N (2005) Tonoplast intrinsic proteins AtTIP2;1 and AtTIP2;3 facilitate NH3 transport into the vacuole. Plant Physiol 137:671–680. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.051268
Marquez-Garcia B, Njo M, Beeckman T, Goormachtig S, Foyer CH (2014) A new role for glutathione in the regulation of root architecture linked to strigolactones. Plant Cell Environ 37:488–498. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12172
Maurel C, Verdoucq L, Luu DT, Santoni V (2008) Plant aquaporins: membrane channels with multiple integrated functions. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:595–624. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092734
McGrath KC et al (2005) Repressor- and activator-type ethylene response factors functioning in jasmonate signaling and disease resistance identified via a genome-wide screen of Arabidopsis transcription factor gene expression. Plant Physiol 139:949–959. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.068544
Mellander PE, Bishop K, Lundmark T (2004) The influence of soil temperature on transpiration: a plot scale manipulation in a young Scots pine stand. Forest Ecol Manag 195:15–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2004.02.051
Mhamdi A, Han Y, Noctor G (2013) Glutathione-dependent phytohormone responses: teasing apart signaling and antioxidant functions. Plant Signal Behav 8:e24181. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.24181
Nagel KA, Kastenholz B, Jahnke S, van Dusschoten D, Aach T, Mühlich M, Truhn D, Scharr H, Terjung S, Walter A, Schurr U (2009) Temperature responses of roots: impact on growth, root system architecture and implications for phenotyping. Funct Plant Biol 36:947–959. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP09184
Nie J et al (2018) The AP2/ERF transcription factor CmERF053 of chrysanthemum positively regulates shoot branching, lateral root, and drought tolerance. Plant Cell Rep 37:1049–1060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-018-2290-9
Pandurangaiah M et al (2014) Overexpression of horsegram (Macrotyloma uniflorum Lam. Verdc.) NAC transcriptional factor (MuNAC4) in groundnut confers enhanced drought tolerance. Mol Biotechnol 56:758–769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-014-9754-0
Parry G (2015) The plant nuclear envelope and regulation of gene expression. J Exp Bot 66:1673–1685. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv023
Peret B et al (2009) Arabidopsis lateral root development: an emerging story. Trends Plant Sci 14:399–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2009.05.002
Rahman I, Kode A, Biswas SK (2006) Assay for quantitative determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide levels using enzymatic recycling method. Nat Protoc 1:3159–3165. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.378
Rai M, He C, Wu R (2009) Comparative functional analysis of three abiotic stress-inducible promoters in transgenic rice. Transgenic Res 18:787–799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-009-9263-2
Ranathunge K, El-Kereamy A, Gidda S, Bi YM, Rothstein SJ (2014) AMT1;1 transgenic rice plants with enhanced NH4+ permeability show superior growth and higher yield under optimal and suboptimal NH4+ conditions. J Exp Bot 65:965–979. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert458
Rausch T, Gromes R, Liedschulte V, Muller I, Bogs J, Galovic V, Wachter A (2007) Novel insight into the regulation of GSH biosynthesis in higher plants. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 9:565–572. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-965580
Raya-Gonzalez J, Pelagio-Flores R, Lopez-Bucio J (2012) The jasmonate receptor COI1 plays a role in jasmonate-induced lateral root formation and lateral root positioning in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Physiol 169:1348–1358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2012.05.002
Schnaubelt D et al (2015) Low glutathione regulates gene expression and the redox potentials of the nucleus and cytosol in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 38:266–279. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12252
Sudhakar C, Lakshmi A, Giridarakumar S (2001) Changes in the antioxidant enzyme efficacy in two high yielding genotypes of mulberry (Morus alba L.) under NaCl salinity. Plant Sci 161:613–619
Sun JQ et al (2009) Arabidopsis ASA1 is important for jasmonate-mediated regulation of auxin biosynthesis and transport during lateral root formation. Plant Cell 21:1495–1511. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.064303
Sun S et al (2012) A constitutive expressed phosphate transporter, OsPht1;1, modulates phosphate uptake and translocation in phosphate-replete rice. Plant Physiol 159:1571–1581. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.196345
Sun B, Liu GL, Phan TT, Yang LT, Li YR, Xing YX (2017) Effects of cold stress on root growth and physiological metabolisms in seedlings of different sugarcane varieties. Sugar Tech 19:165–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-016-0452-z
Toro FJ, Martin-Closas L, Pelacho AM (2003) Jasmonates promote cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var Capitata L.) root and shoot development. Plant Soil 255:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026104210974
Trupiano D, Yordanov Y, Regan S, Meilan R, Tschaplinski T, Scippa GS, Busov V (2013) Identification, characterization of an AP2/ERF transcription factor that promotes adventitious, lateral root formation in Populus. Planta 238:271–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1890-4
Vernoux T et al (2000) The ROOT MERISTEMLESS1/CADMIUM SENSITIVE2 gene defines a glutathione-dependent pathway involved in initiation and maintenance of cell division during postembryonic root development. Plant Cell 12:97–110. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.12.1.97
Vivancos PD et al (2010) Recruitment of glutathione into the nucleus during cell proliferation adjusts whole-cell redox homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana and lowers the oxidative defence shield. Plant J 64:825–838. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04371.x
Wang SC, Ichii M, Taketa S, Xu LL, Xia K, Zhou X (2002) Lateral root formation in rice (Oryza sativa): promotion effect of jasmonic acid. J Plant Physiol 159:827–832. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-00825
Wang L, Yang L, Yang F, Li X, Song Y, Wang X, Hu X (2010) Involvements of H2O2 and metallothionein in NO-mediated tomato tolerance to copper toxicity. J Plant Physiol 167:1298–1306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2010.04.007
Yu ZX, Li JX, Yang CQ, Hu WL, Wang LJ, Chen XY (2012) The jasmonate-responsive AP2/ERF transcription factors AaERF1 and AaERF2 positively regulate artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. Mol Plant 5:353–365. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr087
Zhang F et al (2015) Involvement of OsPht1;4 in phosphate acquisition and mobilization facilitates embryo development in rice. Plant J 82:556–569. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12804
Zhu J et al (2015) Low temperature inhibits root growth by reducing auxin accumulation via ARR1/12. Plant Cell Physiol 56:727–736. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcu217
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (No. PJ01366701), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea, and the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), which is funded by the Ministry of Education (2016R1A6A1A05011910), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S-IP, Y-SK, and H-SY conceived the research and wrote the article. S-IP performed most of the experiments and analyzed data, J-JK assisted in phenotypic analyses, H-SK assisted with the GSH assay, and H-SY supervised the research.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11103_2020_1093_MOESM7_ESM.docx
Table S6. Location and copy number of the recombinant DNA that was insert into OsRab21::OsGS transgenic (TR 1, 2, 3) lines according to flanking DNA sequencing (DOCX 30 kb)
11103_2020_1093_MOESM8_ESM.docx
Table S7. Agronomic traits of OsGS-overexpressing transgenic plants (TR 1, 2, 3) grown in paddy fields in 2015-2018 (DOCX 84 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, SI., Kim, JJ., Kim, HS. et al. Enhanced glutathione content improves lateral root development and grain yield in rice plants. Plant Mol Biol 105, 365–383 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-020-01093-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-020-01093-w