Abstract
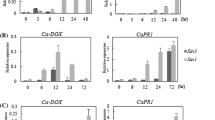
Polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins (PGIPs) are plant cell wall glycoproteins that can inhibit fungal endopolygalacturonases (PGs). The PGIPs directly reduce the aggressive potential of PGs. Here, we isolated and functionally characterized three members of the pepper (Capsicum annuum) PGIP gene family. Each was up-regulated at a different time following stimulation of the pepper leaves by Phytophthora capcisi and abiotic stresses including salicylic acid, methyl jasmonate, abscisic acid, wounding and cold treatment. Purified recombinant proteins individually inhibited activity of PGs produced by Alternaria alternata and Colletotrichum nicotianae, respectively, and virus-induced gene silencing in pepper conferred enhanced susceptibility to P. capsici. Because three PGIP genes acted similarily in conferring resistance to infection by P. capsici, and because individually purified proteins showed consistent inhibition against PG activity of both pathogens, CaPGIP1 was selected for manipulating transgenic tobacco. The crude proteins from transgenic tobacco exhibited distinct enhanced resistance to PG activity of both fungi. Moreover, the transgenic tobacco showed effective resistance to infection and a significant reduction in the number of infection sites, number of lesions and average size of lesions in the leaves. All results suggest that CaPGIPs may be involved in plant defense response and play an important role in a plant’s resistance to disease.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adie BAT, Pérez-Pérez J, Pérez-Pérez MM, Godoy M, Sánchez-Serrano JJ, Schmelz EA, Solano R (2007) ABA is an essential signal for plant resistance to pathogens affecting JA biosynthesis and the activation of defenses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:1665–1681
Afzal AJ, Lightfoot DA (2007) Soybean disease resistance protein RHG1-LRR domain expressed, purified and refolded from Escherichia coli inclusion bodies: preparation for a functional analysis. Pro Exp Pur 53:346–355
Agüero CB, Uratsu SL, Greve C, Powell AT, Labavitch JM, Meredith CP, Dandekar AM (2005) Evaluation of tolerance to Pierce’s disease and Botrytis in transgenic plants of Vitis vinifera L. expressing the pear PGIP gene. Mol Plant Pathol 6:43–51
Albersheim P, Anderson AJ (1971) Proteins from plant cell walls inhibit polygalacturonases secreted by plant pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 68:1815–1819
An SH, Sohn KH, Choi HW, Hwang IS, Lee SC, Hwang BK (2008) Pepper pectin methylesterase inhibitor protein CaPMEI1 is required for antifungal activity, basal disease resistance and abiotic stress tolerance. Planta 228:61–78
Anderson JP, Badruzsaufari E, Schenk PM, Manners JM, Desmond OJ, Ehlert C, Maclean DJ, Ebert PR, Kazan K (2004) Antagonistic interaction between abscisic acid and jasmonate-ethylene signaling pathways modulates defense gene expression and disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:3460–3479
Asselbergh B, Achuo AE, Höfte M, Van Gijsegem F (2008) Abscisic acid de ficiency leads to rapid activation of tomato defence responses upon infection with Erwinia chrysanthemi. Mol Plant Pathol 9:11–24
Audenaert K, De Meyer GB, Höfte MM (2002) Abscisic acid determines basal susceptibility of tomato to Botrytis cinerea and suppresses salicylic acid-dependent signaling mechanisms. Plant Physiol 128:491–501
Bari R, Jones JDG (2009) Role of plant hormones in plant defence responses. Plant Mol Biol 69:473–488
Bergmann CW, Ito Y, Singer D, Albersheim P, Darvill AG, Benhamou N, Nuss L, Salvi G, Cervone F, De Lorenzo G (1994) Polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein accumulates in Phaseolus vulgaris L. in response to wounding, elicitors and fungal infection. Plant J 5:625–634
Bezier A, Lambert B, Baillieul F (2002) Cloning of a grapevine Botrytis-responsive gene that has homology to the tobacco hypersensitivity-related hsr203. J Exp Bot 53:2279–2280
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Centis S, Guillas I, Séjalon N, Tugayé MTE, Dumas B (1997) Endopolygalacturonase genes from Colletotrichum lindemuthianum: cloning of CLPG2 and comparison of its expression to that of CLPG1 during saprophytic and parasitic growth of the fungus. Mol Plant Microb Interact 10(6):769–775
Cheng Q, Cao YZH, Pan HX, Wang MX, Huang MR (2008) Isolation and characterization of two genes encoding polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein from Populus deltoides. J Genet Genomics 35(10):631–638
Cheong YH, Chang HS, Gupta R, Wang X, Zhu T, Luan S (2002) Transcriptional profiling reveals novel interactions between wounding, pathogen, abiotic stress, and hormonal responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 129(2):661–677
Chinnusamy V, Gong ZZ, Zhu JK (2008) Abscisic acid-mediated epigenetic processes in plant development and stress responses. J Integr Plant Biol 50:1187–1195
Chisholm ST, Coaker G, Day B, Staskawicz BJ (2006) Host-microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 124(4):803–814
Chung E, Seong E, Kim YC, Chung EJ, Oh SK, Lee S, Park JM, Joung YH, Choi D (2004) A method of high frequency virus-induced gene silencing in chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L. cv. Bukang). Mol Cell 17(2):377–380
Cook BJ, Clay RP, Bergmann CW, Albersheim P, Darvil AG (1999) Fungal polygalacturonase exhibit different substrate degradation patterns and differ in their susceptibilities to polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins. Mol Plant Microb Interact 12(8):703–711
Darvill A, Bergmann C, Cervone F, De Lorenzo G, Ham KS, Spiro MD, York WS, Albersheim P (1994) Oligosaccharins involved in plant growth and host-pathogen interactions. Biochem Soc Symp 60:89–94
D’Ovidio R, Anderson OD (1994) Purification and molecular characterization of a soybean polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein. Theor App Genet 88:759–763
D’Ovidio R, Raiola A, Capodicasa C, Devoto A, Pontiggia D, Roberti S, Galletti R, Conti E, O’Sullivan D, De Lorenzo G (2004) Characterization of the complex locus of bean encoding polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins reveals subfunctionalization for defense against fungi and insects. Plant Physiol 135(4):2424–2435
D’Ovidio R, Roberti S, Di Giovanni M, Capodicasa C, Melaragni M, Sella L, Tosi P, Favaron F (2006) The characterization of the soybean polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins (PGIP) gene family reveals that a single member is responsible for the activity detected in soybean tissues. Planta 224(3):633–645
de Bruxelles GL, Roberts MR (2001) Signals regulating multiple responses to wounding and herbivores. Crit Rev Plant Sci 20:487–521
De Lorenzo G, Ferrari S (2002) Polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins in defense against phytopathogenic fungi. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5(4):295–299
De Lorenzo G, Castoria R, Bellincampi D, Cervone F (1997) Fungal invasion enzymes and their inhibition. In: Carroll G, Tudzynski P (eds) The mycota. Springer, Berlin, pp 61–83
De Lorenzo G, Cervone F, Bellincampi D, Caprari C, Clark AJ, Desiderio A, Devoto A, Forrest R, Leckie F, Nuss L, Salvi G (1994) Polygalacturonase, PGIP and oligogalacturonides in cell–cell communication. Biochem Soc Trans 22:396–399
De Lorenzo G, D’Ovidio R, Cervone F (2001) The role of polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins (PGIPS) in defense against pathogenic fungi. Ann Rev Phytopathol 39:313–335
Dempsey DA, Shah J, Klessig D (1999) Salicylic acid and disease resistance in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 18:547–575
Desiderio A, Aracri B, Leckie F, Mattei B, Salvi G, Tigelaar H, van Roekel JS, Baulcombe DC, Melchers LS, De Lorenzo G, Cervone F (1997) Polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins (PGIPs) with different specificities are expressed in Phaseolus vulgaris. Mol Plant Microb Interact 10(7):852–860
Devoto A, Clark AJ, Nuss L, Cervone F, De Lorenzo G (1997) Developmental and pathogen-induced accumulation of transcripts of polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Planta 202(3):284–292
Di Matteo A, Federici L, Mattei B, Salvi G, Johnson KA, Savino C, De Lorenzo G, Tsernoglou D, Cervone F (2003) The crystal structure of polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein (PGIP), a leucine-rich repeat protein involved in plant defense. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(17):10124–10128
Di Matteo A, Bonivento D, Tsernoglou D, Federici L, Cervone F (2006) Polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein (PGIP) in plant defence: a structural view. Phytochemistry 67(6):528–533
Di C, Zhang M, Xu S, Cheng T, An L (2006) Role of polygalacturonase inhibiting protein in plant defense. Crit Rev Microbiol 32(2):91–100
Di C, Li M, Long F, Bai M, Liu YJ, Zheng XL, Xu SJ, Xiang Y, Sun Z, An LZH (2009) Molecular cloning, functional analysis and localization of a novel gene encoding polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein in Chorispora bungeana. Planta 231(1):169–178
Dong X (1998) SA, JA, ethylene, and disease resistance in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:316–323
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Fang BH, Zhang GM, Chi CF, Liu P (2004) The dynamic effects of Colletotrichum capsici f. nicotianae toxin on MDA content and some protective enzymes in tobacco. Aata Phytopathologica Sinica 34(4):27–31
Favaron F, D’Ovidio R, Porceddu E, Alghisi P (1994) Purification and molecular characterization of a soybean polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein. Planta 195(1):80–87
Favaron F, Castiglioni C, D’Ovidio R, Alghisi P (1997) Polygalacturonase inhibiting proteins from Allium porrum L. and their role in plant tissue against fungal endo-polygalacturonases. Physiol Mol. Plant Pathol 50(6):403–417
Federici L, Di Matteo A, Fernandez-Recio J, Tsernoglou D, Cervone F (2006) Polygalacturonase inhibiting proteins: players in plant innate immunity. Trends Plant Sci 11(2):65–70
Feng JL, Wang K, Liu X, Chen SN, Chen JS (2009) The quantification of tomato microRNAs response to viral infection by stem-loop real-time RT-PCR. Gene 437(1–2):14–21
Ferrari S, Vairo D, Ausubel FM, Cervone F, de Lorenzo G (2003) Tandemly duplicated Arabidopsis genes that encode polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins are regulated coordinately by different signal transduction pathways in response to fungal infection. Plant Cell 15:93–106
Ferrari S, Galletti R, Vairo D, de Cervone F, Lorenzo G (2006) Antisense expression of the Arabidopsis thaliana AtPGIP1 gene reduces polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein accumulation and enhances susceptibility to Botrytis cinerea. Mol Plant Microb Interact 19(8):931–936
Flors V, Ton J, Jakab G, Mauch-Mani B (2005) Abscisic acid and callose: team players in defence against pathogens? J Phytopathol 153:377–383
Frediani M, Cremonini R, Salvi G, Caprari C, Desiderio A (1993) Cytological localization of the PGIP genes in the embryo suspensor cells of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Theor Appl Genet 87(3):369–373
Gomathi V, Gayathri S, Anupama B, Silva JAT, Gnanamanickam SS (2006) Molecular aspects of polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins (PGIPs) in plant defense. In: Silva JAT (ed) Floriculture, ornamental and plant biotechnology, vol 3. Global Science Books, London, pp 373–379
Grüner R, Strompen G, Pfitzner AJP, Pfitzner UM (2003) Salicylic acid and the hypersensitive response initiate distinct signal transduction pathways in tobacco that converge on the as-1-like element of the PR-1a promoter. Euro J Biochem 270(24):4876–4886
Hegedus DD, Li R, Buchwaldt L, Parkin I, Whitwill S, Coutu C, Bekkaoui D, Rimmer SR (2008) Brassica napus possesses an expanded set of polygalacturonase inhibitor protein genes that are differentially regulated in response to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum infection, wounding and defense hormone treatment. Planta 228(2):241–253
Hu CG, Honda C, Kita M, Zhang Z, Tsuda T, Moriguchi TA (2002) Simple protocol for RNA isolation from fruit trees containing high levels of polysaccharides and polyphenol compounds. Plant Mol Bio Report 20(1):69
Hwang BH, Bae H, Lim HS, Kim KB, Kim SJ, Im MH, Park BS, Kim DS, Kim J (2010) Overexpression of polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein 2 (PGIP2) of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis) increased resistance to the bacterial pathogen Pectobacterium carotovorum ssp. Carotovorum. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 103(3):293–305
Isshiki A, Akimitsu K, Yamamoto M, Yamamoto H (2001) Endopolygalacturonase is essential for citrus black rot caused by Alternaria citri but Not Brown Spot Caused by Alternaria alternata. Mol Plant Microb Interact 14(6):749–757
Janni M, Di Giovanni M, Roberti S, Capodicasa C, D’Ovidio R (2006) Characterization of expressed PGIP genes in rice and wheat reveals similar extent of sequence variation to dicto PGIPs and identifies an active PGIP lacking an entire LRR repeat. Theor Appl Genet 113(7):1233–1245
Janni M, Sella L, Favaron F, Blechl AE, Lorenzo GD, D’Ovido R (2008) The Expression of a bean PGIP in transgenic wheat confers increased resistance to the fungal pathogen Bipolaris sorokiniana. Mol Plant Microb Interact 21(2):171–177
Johnson C, Boden E, Arias J (2003) Salicylic acid and NPR1 induce the recruitment of trans-activating TGA factors to a defense gene promoter in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:1846–1858
Johnston DJ, Ramanathan V, Williamson B (1993) A protein from immature raspberry fruits which inhibits endopolygalacturonases from Botrytis cinerea and other micro-organisms. J Exp Bot 44(5):971–976
Jones JDG (2001) Putting knowledge of plant disease resistance genes towork. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:281–287
Jones DA, Jones JDG (1997) The roles of leucine-rich repeat proteins in plant defences. Adv Bot Res 24:89–167
Jones AL, Hamilton AJ, Voinnet O, Thomas CL, Maule AJ, Baulcombe DC (1999) RNA-DNA interactions and DNA methylation in post-transcriptional gene silencing. Plant Cell 11(12):2291–2302
Joubert DA, Slaughter AR, Kemp G, Becker VWJ, Krooshof GH, Bergmann C, Benen J, Pretorius IS, Vivier MA (2006) The grapevine polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein (VvPGIP1) reduces Botrytis cinerea susceptibility in transgenic tobacco and differentially inhibits fungal polygalacturonases. Transgenic Res 15(6):687–702
Joubert DA, Kars I, Wagemakers L, Bergmann C, Kemp G, Vivier MA, van Kan JA (2007) A polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein from grapevine reduces the symptoms of the endopolygalacturonase BcPG2 from Botrytis cinerea in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves without any evidence for in vitro interaction. Mol Plant Microb Interact 20(4):392–402
Karr AL, Albersheim P (1970) Polysaccharide-degrading enzymes are unable to attack plant cell walls without prior action by a “all-modifying enzyme”. Plant Physiol 46:69–80
Kars I, Krooshof GH, Wagemakers L, Joosten R, Benen JA, van Kan JA (2005) Necrotizing activity of five Botrytis cinerea endopolygalacturonases produced in Pichia pastoris. Plant J 43(2):213–225
Kemp G, Stanton L, Bergmann CW, Clay RP, Albersheim P, Darvill A (2004) Polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins can function as activators of polygalacturonase. Mol Plant Microb Interact 17:888–894
Kim ES, Hwang BK (1992) Virulence to Korean pepper cultivars of isolates of Phytophthora capsici from different geographic areas. Plant Dis 76:486–489
Kobe B, Deisenhofer JZ (1994) The leucine-rich repeat: a versatile binding motif. Trends Biochem Sci 19(10):415–421
Komatsu K, Hashimoto M, Ozeki J, Yamaji Y, Maejima K, Senshu H, Himeno M, Kagiwada S, Okano Y, Namba S (2010) Viral-induced systemic necrosis in plants involves both programmed cell death and the inhibition of viral multiplication, which are regulated by independent pathways. Mol Plant Microb Interact 23(3):283–293
Kothari H, Kumar P, Singh N (2006) Prokaryotic expression, purification, and polyclonal antibody production against a novel drug resistance gene of Leishmania donovani clinical isolate. Protein Expr Purif 45:15–21
Kusaba M, Tsuge T (1994) Nuclear ribosomal DNA variation and pathogenic specialization in Alternaria fungi known to produce host-specific toxins. Appl Environ Microbiol 60(9):3055–3062
Leckie F, Mattei B, Capodicasa C, Hemmings A, Nuss L, Aracri B, De Lorenzo G, Cervone F (1999) The specificity of polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein (PGIP): a single amino acid substitution in the solvent-exposed β-strand/β-turn region of the leucine-rich repeats (LRRs) confers a new recognition capability. Eur Mol Biol Organ 18(9):2352–2363
Li R, Rimmer R, Yu M, Sharpe AG, Seguin-Swartz G, Lydiate D, Hegedus DD (2003) Two Brassica napus polygalacturonase inhibitory protein genes are expressed at different levels in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Planta 217(2):299–308
Liang FS, Zhang KCH, Zhou ChJ, Kong FN, Li J, Wang B (2005) Cloning, characterization and expression of the gene encoding polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins (PGIPs) of peach (Prunus persica L.). Plant Sci 168:481–486
Liu YG, Whittier RF (1995) Thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR: automatable amplification and sequencing of insert end fragments from P1 and YAC clones for chromosome walking. Genomics 25(3):674–681
Liu Y, Schi VM, Dinesh-Kumar SP (2002) Virus-induced gene silencing in tomato. Plant J 31(6):777–786
Machinandiarena MF, Olivieri FP, Daleo GR, Oliva CR (2001) Isolation and characterization of a polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein from potato leaves: accumulation in response to salicylic acid, wounding and infection. Plant Physiol Biochem 39:129–136
Manfredini C, Sicilia F, Ferrari S, Pontiggia D, Salvi G, Caprai C, Lorito M, De Lorenzo G (2006) Polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein 2 of Phaseolus vulgaris inhibits BcPG1, a polygalacturonase of Botrytis cinerea important for pathogenicity, and protects transgenic plants from infection. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 67:108–115
Mariotti L, Casasoli M, Migheli Q, Balmas V, Caprari C, De Lorenzo G (2008) Reclassification of Fusarium verticillioides (syn. F. moniliforme) strain FC-10 as F. phyllophilum. Mycol Res 112(9):1010–1011
Mattei B, Bernalda MS, Federici L, Roepstorff P, Cervone F, Boffi A (2001) Secondary structure and post-translational modifications of the leucine-rich repeat protein PGIP (polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein) from Phaseolus vulgaris. Biochemistry 40(2):569–576
Mauch-Mani B, Mauch F (2005) The role of abscisic acid in plant-pathogen interactions. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:409–414
Mehli L, Kjellsen TD, Dewey FM, Hietala AM (2005) A case study from the interaction of strawberry and Botrytis cinerea highlights the beneWts of comonitoring both partners at genomic and mRNA level. New Phytol 168(2):465–474
Morris PC, Kumar A, Bowles DJ, Cuming AC (1990) Osmotic stress and abscisic acid regulate the expression of the Em gene of wheat. Eur J Biochem 190:625–630
Nishimura S, Kohmoto K (1983) Host-specific toxins and chemical structures from Alternaria species. Annu Rev Phytopathol 21(1):87–116
Nothnagel EA, McNeil M, Albersheim P, Dell A (1983) Hostpathogen interactions. XXII. A galacturonic acid oligosaccharide from plant cell walls elicits phytoalexins. Plant Physiol 71(4):916–926
Nuss L, Mah A, Clark AJ, Grisvard J, Dron M (1996) Differential accumulation of polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein (PGIP) mRNA in two near-isogenic lines of Phaseolus vulgaris L. upon infection with Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Physiol Mol Plant Patho 48(2):83–89
Oeser B, Heidrich PM, Muller U, Tudzynski P, Tenberge KB (2002) Polygalacturonase is a pathogenicity factor in the Claviceps purpurea/rye interaction. Fungal Genet Biol 36(3):176–186
Oke OA (1989) Extracellular enzymes of Colltotrichum nicotianae causing tobacco leaf anthracnose in Nigeria. J Phytopath 127(4):296–304
Pietro AD, Roncero MIG (1998) Cloning, expression, and role in pathogenicity og pg1 encoding the major extracellular endopolygalacturonase of the vascular wilt pathogen Fusarium oxysporum. Mol Plant Microb Interact 11(1):91–98
Powell AL, Van Kan J, Ten Have A, Visser J, Greve LC, Bennett AB, Labavitch JM (2000) Transgenic expression of pear PGIP in tomato limits fungal colonization. Mol Plant Microb Interact 13:942–950
Ramanathan V, Simpsom C, Thow G, Iannetta P, McNicol R, Williamson B (1997) cDNA cloning and expression of polygalacturonaseinhibiting proteins (PGIPs) from red raspberry (Rubus idaeus). J Exp Bot 48:1185–1193
Ramonel KM, Somerville S (2002) The genomics parade of defense responses: to infinity and beyond. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5(4):291–294
Reymond P, Weber H, Damond M, Farmer EE (2000) Differential gene expression in response to mechanical wounding and insect feeding in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12(5):707–720
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sathiyaraj G, Srinivasan S, Subramanium S, Kim YJ, Kim YJ, Kwon WS, Yang DC (2010) Polygalacturonase inhibiting protein: isolation, developmental regulation and pathogen related expression in Panax ginseng. Mol Biol Rep 37(7):3445–3454
Schaart JG, Mehli L, Schouten HJ (2005) Quantification of allele-specific expression of a gene encoding strawberry polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein (PGIP) using pyrosequencing. Plant J 41(3):493–500
Schenk PM, Kazan K, Wilson I, Anderson JP, Richmond T (2000) Coordinated plant defense responses in Arabidopsis revealed by microarray analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(21):11655–11660
Sella L, Castiglioni C, Roberti S, D’Ovidio R, Favaron F (2004) An endo-polygalacturonase (PG) of Fusarium moniliforme escaping inhibition by plant polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins (PGIPs) provides new insights into the PG–PGIP interaction. FEMS Microbiol Lett 240:117–124
Sessions A, Burke E, Presting G, Aux G, McElver J, Patton D, Dietrich B, Ho P, Bacwaden J, Ko C, Clarke JD, Cotton D, Bullis D, Snell J, Miguel T, Hutchison D, Kimmerly B, Mitzel T, Katagiri F, Glazebrook J, Law M, Goffl SA (2002) A high-throughput Arabidopsis reverse genetics system. Plant Cell 14(12):2985–2994
Sharrock KR, Labavitch JM (1994) Polygalacturonase inhibitors of Bartlett pear fruits: differential effects on Botrytis cinerea polygalacturonase isozymes, and influence on products of fungal hydrolysis of pear cell walls and an ethylene induction in cell culture. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 45(4):305–319
Shieh MT, Brown RL, Whitehead MP, Cary JW, Cotty PJ, Cleveland TE, Dean RA (1997) Molecular genetic evidence for the involvement of a specific polygalacturonase, P2c, in the invasion and spread of Aspergillus flavus in cotton bolls. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(9):3548–3552
Shirano Y, Kachroo P, Shah J, Klessig DF (2002) A gain-of-function mutation in an Arabidopsis toll interleukin1 receptor–nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat type R gene triggers defense responses and results in enhanced disease resistance. Plant Cell 14:3149–3162
Slavov S, Mayama S, Atanassov A (2004) Some aspects of epidemiology of Alternaria alternata tobacco pathotype. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 18(2):28–33
Song WW, Ma XR, Tan H, Zhou JY (2011) Abscisic acid enhances resistance to Alternaria solani in tomato seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 49:693–700
Spadoni S, Zabotina O, Di Matteo A, Mikkelsen JD, Cervone F, De Lorenzo G, Mattei B, Bellincampi D (2006) Polygalacturonase inhibiting protein interacts with pectin through a binding site formed by four clustered residues of arginine and lysine. Plant Physiol 141(2):557–564
Stotz HU, Contos JJA, Powell ALT, Bennett AB, La-bavitch JM (1994) Structure and expression of an inhibitor of fungal polygalacturonases from tomato. Plant Mol Biol 25:607–617
Stotz HU, Powell ALT, Damon SE, Greve LC, Bennett AB, Labavitch JM (1993) Molecular characterization of a polygalacturonase inhibitor from Pyrus communis L. cv. Bartlett. Plant Physiol 102(1):133–138
Stotz HU, Bishop JG, Bergmann CW, Koch M, Albersheim P, Darvill AG, Labavitch JM (2000) Identification of target amino acids that affect interactions of fungal polygalacturonases and their plant inhibitors. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 56:117–139
Sun WX, Jia YJ, Feng BZ, O’Neill NR, Zhu XP, Xie BY, Zhang XG (2009) Functional analysis of Pcipg2 from the straminopilous plant pathogen Phytophthora capsici. Genesis 47(8):535–544
Taipalensuu J, Andreasson E, Eriksson S, Rask L (1997) Regulation of the wound-induced myrosinase-associated protein transcript in Brassica napus plants. Eur J Biochem 247(3):963–971
Taylor RJ, Secor GA (1988) An improved diffusion assay for quantifying the polygalacturonase content of Erwinia culture filtrates. Phytopathology 78(8):1101–1103
ten Have A, Mulder W, Visser J, Van Kam JA (1998) The Endopolygalacturonase gene Bcpg1 is required for full virulence of Botrytis cinerea. Mol Plant Microb Interact 11(10):1009–1016
Thaler JS, Bostock RM (2004) Interactions between abscisic-acid-mediated responses and plant resistance to pathogens and insects. Ecology 85:48–58
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25(24):4876–4882
Ton J, Mauch-Mani B (2004) β-amino-butyric acid-induced resistance against necrotrophic pathogens is based on ABA-dependent priming for callose. Plant J 38:119–130
Torto TA, Rauser L, Kamoun S (2002) The Pipg1 gene of the oomycete Phytophthora infestans encodes a fungal-like endopolygalacturonase. Curr Genet 40(6):385–390
Toubart P, Desiderio A, Salvi G, Cervone F, Daroda L, De Lorenzo G (1992) Cloning and characterization of the gene encoding the endopolygalacturonase-inhibiting protein (PGIP) of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant J 2(3):367–373
Tuskan GA, Difazio S, Jansson S, Bohlmann J, Grigoriev I, Hellsten U, Putnam N, Ralph S, Rombauts S, Salamov A et al (2006) The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray). Science 313(5793):1596–1604
Weurman C (1953) Pectinase inhibitors in pears. Acta Bot Neerl 2:107–121
Wiese J, Kranz T, Schubert S (2004) Induction of pathogen resistance in barley by abiotic stress. Plant Biol 6:529–536
Wu CH, Yan HZ, Liu LF, Liou RF (2008) Functional characterization of a gene family encoding polygalacturonases in Phytophthora parasitica. Mol Plant Microb Interact 21(4):480–489
Yang B, Yajima W, Das D, Suresh MR, Kav NNV (2009) Isolation, expression and characterization of two single-chain variable fragment antibodies against an endo-polygalacturonase secreted by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Pro Exp Pur 64:237–243
Yao C, Conway WS, Ren R, Smith D, Ross GS, Sams CE (1999) Gene encoding polygalacturonase inhibitor in apple fruit is developmentally regulated and activated by wounding and fungal infection. Plant Mol Biol 39:1231–1241
Zhang GM, Wang ZF, Chen RT, Liu YR (1994) On the pathogenicity of the tobacco black death disease. Aata Phytopathol Sinica 24(3):367–371
Zhang R, Yang D, Zhou CH, Cheng K, Liu ZH, Chen L, Fang L, Xie P (2012) β-Actin as a loading control for plasma-based Western blot analysis of major depressive disorder patients. Anal Biochem 427:116–120
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by The Project Graveness Gene of China (2009ZX08009-050B). National Natural Science Foundation of China, NSFC (30871620). We very thank Gary J. Samuels for assisting in revising this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiuju Wang and Xiaoping Zhu contributed equally to the article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Zhu, X., Tooley, P. et al. Cloning and functional analysis of three genes encoding polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins from Capsicum annuum and transgenic CaPGIP1 in tobacco in relation to increased resistance to two fungal pathogens. Plant Mol Biol 81, 379–400 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-013-0007-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-013-0007-6