Abstract
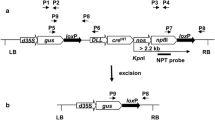
Transgene escape, a major environmental and regulatory concern in transgenic crop cultivation, could be alleviated by removing transgenes from pollen, the most frequent vector for transgene flow. A transgene excision vector containing a codon optimized serine resolvase CinH recombinase (CinH) and its recognition sites RS2 were constructed and transformed into tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum cv. Xanthi). CinH recombinase recognized 119 bp of nucleic acid sequences, RS2, in pollen and excised the transgene flanked by the RS2 sites. In this system, the pollen-specific LAT52 promoter from tomato was employed to control the expression of CinH recombinase. Loss of expression of a green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene under the control of the LAT59 promoter from tomato was used as an indicator of transgene excision. Efficiency of transgene excision from pollen was determined by flow cytometry (FCM)-based pollen screening. While a transgenic event in the absence of CinH recombinase contained about 70% of GFP-synthesizing pollen, three single-copy transgene events contained less than 1% of GFP-synthesizing pollen based on 30,000 pollen grains analyzed per event. This suggests that CinH-RS2 recombination system could be effectively utilized for transgene biocontainment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Ahmad H, Galili S, Gressel J (2004) Tandem constructs to mitigate transgene persistence: tobacco as a model. Mol Ecol 13:697–710
Al-Ahmad H, Dwyer J, Moloney M, Gressel J (2006) Mitigation of establishment of Brassica napus transgenes in volunteers using a tandem construct containing a selectively unfit gene. Plant Biotechnol J 4:7–21
Aono M, Wakiyama S, Nagatsu M, Nakajima N, Tamaoki M, Kubo A, Saji H (2006) Detection of feral transgenic oilseed rape with multiple-herbicide resistance in Japan. Environ Biosafety Res 5:77–87
Beckie HJ, Warwick SI, Nair H, Séguin-Swartz G (2003) Gene flow in commercial fields of herbicide-resistant canola (Brassica napus). Ecol Appl 13:1276–1294
Brown T (2001) Southern blotting. Curr Protocols Mol Biol 2.9.1–2.9.20
Chevre AM, Eber F, Darmency H, Fleury A, Picault H, Letan-neur JC, Renard M (2000) Assessment of interspecific hybridization between transgenic oilseed rape and wild radish under agronomic conditions. Theor Appl Genet 100:1233–1239
Dale EC, Ow DW (1990) Intra- and intermolecular site-specific recombination in plant cells mediated by bacteriophage P1 recombinase. Gene 91:79–85
Daniell H (2002) Molecular strategies for gene containment in transgenic crops. Nature Biotechnol 20:581–586
Daniell H, Datta R, Varma S, Gray S, Lee SB (1998) Containment of herbicide resistance through genetic engineering of the chloroplast genome. Nature Biotechnol 16:345–348
Gray AJ, Raybould AF (1998) Crop genetics—reducing transgene escape routes. Nature 392:653–654
Grindley NDF, Whiteson KL, Rice PA (2006) Mechanisms of site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Biochem 75:567–605
Halfhill MD, Zhu B, Warwick SI, Raymer PL, Millwood RJ, Weissinger AK, Stewart CN Jr (2004) Hybridization and backcrossing between transgenic oilseed rape and two related weed species under field conditions. Environ Biosafety Res 3:73–81
Haygood R, Ives AR, Andow DA (2005) Population genetics of transgene containment. Ecol Lett 7:213–220
Horsh RB, Fry JE, Hoffmann NL, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1985) A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227:1229–1231
Iamtham S, Day A (2000) Removal of antibiotic resistance genes from transgenic tobacco plastids. Nat Biotechnol 18:1172–1176
Ingram J (2000) The separation distance required to ensure cross-pollination is below specified limits in non-seed crops of sugar beet, maize and oilseed rape. Plant Var and Seeds 13:181–199
Kempe K, Rubtsova M, Berger C, Kumlehn I, Schollmeier C, Gils M (2010) Transgene excision from wheat chromosomes by phage phiC31 integrase. Plant Mol Biol 72:673–687
Kholodii G (2001) The shuffling function of resolvases. Gene 269:121–130
Klippell A, Kanaar R, Kahmann R, Cozzarelli NR (1993) Analysis of strand exchange and DNA binding of enhancer-independent Gin recombinase mutants. EMBO J 12:1047–1057
Lloyd AM, Davis RW (1994) Functional expression of the yeast FLP/FRT site-specific recombination system in Nicotina tabacum. Mol Gen Genet 242:653–657
Luo K, Duan H, Zhao D, Zheng X, Deng W, Chen Y, Stewart CN Jr, McAvoy R, Jiang X, Wu Y, He A, Pei Y, Li Y (2007) ‘GM-gene-deletor’: fused loxP-FRT recognition sequences dramatically improve the efficiency of FLP or CRE recombinase on transgene excision from pollen and seed of tobacco plants. Plant Biotechnol J 5:263–274
Lyznik LA, Mitchell JC, Hirayama L, Hodges TK (1993) Activity of yeast FLP recombinase in maize and rice protoplasts. Nucleic Acids Res 21:969–975
Maeser S, Kahmann R (1991) The Gin recombinase of phage Mu can catalyze site-specific recombination in plant protoplasts. Mol Gen Genet 230:170–176
Maliga P (2004) Plastid transformation in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:289–300
Mariani C, DeBeuckeleer M, Trueltner J, Leemans J, Goldberg RB (1990) Induction of male sterility in plants by a chimeric ribonuclease gene. Nature 347:737–741
Moon HS, Li Y, Stewart CN Jr (2010) Keeping the genie in the bottle: transgene biocontainment by excision in pollen. Trends Biotechnol 28:3–8
Moon HS, Eda S, Saxton AM, Ow D, Stewart CN Jr (2011) An efficient and rapid transgenic pollen screening and detection method using a flow cytometry. Biotechnol J 6:118–123
Morris WF, Kareiva PM, Raymer PL (1994) Do barren zones and pollen traps reduce gene escape from transgenic crops? Ecol Appl 4:157–165
Nakagawa Y, Machida C, Machida Y, Toriyama K (2001) A system to induce the deletion of genomic sequences using R/RS site-specific recombination and the Ac transposon in transgenic rice plants. Theor Appl Genet 102:1136–1141
Onouchi H, Yokoi K, Machida C, Matsuzaki H, Oshima Y, Matsuoka K, Nakamura K, Machida Y (1991) Operation of an efficient site-specific recombination system of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii in tobacco cells. Nucleic Acids Res 19:6373–6378
Onouchi H, Nishihama R, Kudo M, Machida Y, Machida C (1995) Visualization of site-specific recombination catalyzed by a recombinase from Zygosaccharomyces rouxii in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet 247:653–660
Petolino JF, Worden A, Curlee K, Connell J, Strange Moynahan TL, Larsen C, Russel S (2010) Zinc finger nuclease-mediated transgene deletion. Plant Mol Biol 73:617–628
Piñeyro-Nelson A, Van Heerwaarden J, Perales HR, Serratos-Hernandez JA, Rangel A, Hufford MB, Gepts P, Garay-Arroyo A, Rivera-Bustamante R, Alvarez-Buylla ER (2009) Transgenes in Mexican maize: molecular evidence and methodological considerations for GMO detection in landrace populations. Mol Ecol 18:750–761
Rao MR, Moon HS, Schenk TMH, Becker D, Mazarei M, Stewart CN Jr (2010) FLP/FRT Recombination from yeast: application of a two gene cassette scheme as an inducible system in plants. Sensors 10:8526–8535
Ruf S, Hermann M, Berger IF, Carrer H, Bock R (2001) Stable genetic transformation of tomato plastids- high-level foreign protein expression in fruits. Nature Biotechnol 19:870–875
Sreekala C, Wu L, Gu K, Wang D, Tian D, Yin Z (2005) Excision of a selectable marker in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.) using a chemically regulated Cre/loxP system. Plant Cell Rep 24:86–94
Stewart CN Jr, Via LE (1993) A rapid CTAB DNA isolation technique useful for RAPD fingerprinting and other PCR applications. BioTechniques 14:748–751
Stewart CN Jr, Halfhill MD, Warwick SI (2003) Transgene introgression from genetically modified crops to their wild relatives. Nature Rev Genet 4:806–817
Svab Z, Maliga P (2007) Exceptional transmission of plastids and mitochondria from the transplastomic pollen parent and its impact on transgene containment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:7003–7008
Thomson JG, Ow DW (2006) Site-specific recombination systems for the genetic manipulation of eukaryotic genomes. Genesis 44:465–476
Thomson JG, Yau Y-Y, Blanvillain R, Chinquy D, Thilmony R, Ow DW (2009) ParA resolvase catalyzes site-specific excision of DNA from the Arabidopsis genome. Transgenic Res 18:237–248
Thomson JG, Chan R, Thilmony R, Yau Y-Y, Ow DW (2010) PhiC31 recombination system demonstrates heritable germinal transmission of site-specific excision from the Arabidopsis genome. BMC Biotechnol 10:17
Twell D, Yamaguchi J, McCormick S (1990) Pollen-specific gene expression in transgenic plants: coordinate regulation of two different tomato gene promoters during microsporogenesis. Development 109:705–713
Verweire D, Verleyen K, De Buck S, Claeys M, Angenon G (2007) Marker-free transgenic plants through genetically programmed auto-excision. Plant Physiol 145:1220–1231
Weinthal D, Tovkach A, Zeevi V, Tzfira T (2010) Genome editing in plant cells by zinc finger nucleases. Trends Plant Sci 15:308–321
Whittington M (2006) Underground farming. http://www.associatedcontent.com/article/27102/underground_farming.html?cat=15. Accessed 24 Oct 2010
Woo H-J, Cho H-S, Lim S-H, Shin K-S, Lee S-M, Lee K-J, Kim D-H, Cho Y-G (2009) Auto-excision of selectable marker genes from transgenic tobacco via a stress inducible FLP/FRT site-specific recombination system. Transgenic Res 18:455–465
Zhang Y, Li H, Quyang B, Lu Y, Ye Z (2006) Chemical-induced autoexcision of selectable markers in elite tomato plants transformed with a gene conferring resistance to lepidopteran insects. Biotechnol Lett 28:1247–1253
Zuo J, Niu Q-W, Møller SG, Chua N-H (2001) Chemical-regulated, site-specific DNA excision in transgenic plants. Nature Biotechnol 19:157–161
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Murali R. Rao for helping on statistical analysis and Spencer Wei for his help with vector construction. We thank Patrick Gallois for the gift of pPK100 that was included in our vectors. This research was funded by USDA Biotechnology Risk Assessment Grants to C. N. Stewart, Jr. and D. W. Ow. We especially wish to express our gratitude to collaborator Yi Li, also a co-PI on the above grant, for the extensive help in this line of research and for the many conversations and innovations he and his lab has accomplished.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moon, H.S., Abercrombie, L.L., Eda, S. et al. Transgene excision in pollen using a codon optimized serine resolvase CinH-RS2 site-specific recombination system. Plant Mol Biol 75, 621–631 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9756-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9756-2