Abstract
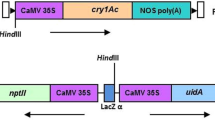
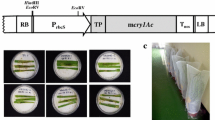
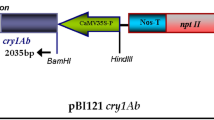
Marker-free transgenic tomato plants harboring a synthetic Bacillus thuringiensis endotoxin gene, cryIAc, were obtained by using a chemically regulated, Cre/loxP-mediated site-specific DNA recombination system, in which the selectable marker neomycin phosphotransferase gene flanked by two directly oriented loxP sites was located between the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter and a promoterless cryIAc. Upon induction by 2 μM β-estradiol, sequences encoding the selectable marker and cre sandwiched by two loxP sites were excised from the tomato genome, leading to activation of the downstream endotoxin gene cryIAc with high expression levels as shown by Northern blot and ELISA assay (250–790 ng g−1 fresh wt) in T1 generation. For transgenic line with single transgenic loci, 15% of T1 progenies were revealed marker-free. This autoexcision strategy provides an effective approach to eliminate a selectable marker gene from transgenic tomato, thus expediting the public acceptance of genetically modified crop.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen P, Wang C, Soong S, To K (2003) Complete sequence of the binary vector pBI121 and its application in cloning T-DNA insertion from transgenic plants. Mol Breed 11:287–293
Coppoolse ER, de Vroomen MJ, Roelofs D, Smit J, van Gennip F, Hersmus BJ, Nijkamp HJ, van Haaren MJ (2003) Cre recombinase expression can result in phenotypic aberrations in plants. Plant Mol Biol 51:263–279
Dale EC, Ow DW (1991) Gene transfer with subsequent removal of the selection gene from the host genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10558–10562
Delannay X, LaVallee BJ, Proksch RK, Fuchs RL, Sims SK, Greenplate JT, Marrone PG, Dodson RB, Augustine JJ, Layton JG, Fischhoff DA (1989) Field performance of transgenic tomato plants expressing Bacillus thuringiensis var kurstaki insect control protein. Biotechnology 7:1265–1269
Goldsbrough AP, Lastrella CN, Yoder JI (1993) Transposition mediated re-positioning and subsequent elimination of marker genes from transgenic tomato. Biotechnology 11:1286–1292
Mor TS, Gomez-Lim MA, Palmer KE (1998) Perspective: edible vaccines—a concept coming of age. Trends Microbiol 6:449–453
Ouyang B, Chen YH, Li HX, Qian CJ, Huang SL, Ye ZB (2005) Transformation of tomato with osmotin and chitinase genes and their resistance to Fusarium wilt. J Hortic Sci Biotech 80:517–522
Sambrook J, Fritsh EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Sreekala C, Wu L, Gu K, Wang D, Tian D, Yin Z (2005) Excision of a selectable marker in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.) using a chemically regulated Cre/loxP system. Plant Cell Rep 24:86–94
Srivastava V, Ow DW (2004) Marker-free site-specific gene integration in plants. Trends Biotechnol 22:627–629
Wang Y, Chen B, Hu Y, Li J, Lin Z (2005) Inducible excision of selectable marker gene from transgenic plants by the Cre/lox site-specific recombination system. Transgenic Res 14:605–614
Wang BM, He ZP, Zhao ZX (1998) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) of Bacillus thuringiensis insect control protein as expressed in transgenic cotton. Acta Gossypii Sin 10:220–221
Zhang YY, Ouyang B, Ye ZB (2004) Recent advances in marker-free transgenic plants. J Agric Biotechnol 12:589–596
Zhang W, Subbarao S, Addae P, Shen A, Armstrong C, Peschke V, Gilbertson L (2003) Cre/lox-mediated marker gene excision in transgenic maize (Zea mays L.) plants. Theor Appl Genet 107:1157–1168
Zuo J, Niu Q, Møller S, Chua N-H (2001) Chemical-regulated, site-specific DNA recombination in transgenic plants. Nature Biotechnol 19:157–161
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr Chua Nam-Hai (Laboratory of Plant Molecular Biology, Rockefeller University, USA), Dr Zhang Qi-Fa (National Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement, Huazhong Agricultural University, China) for the gift of pX6-GFP vector and pUBC vector respectively, and Dr Guo Wen-Wu (National Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement, Huazhong Agricultural University, China) for reading this manuscript. This work was supported by the Hi-Tech Research and Development (863) Program of China (No. 2001AA212221) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30270914).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Li, H., Ouyang, B. et al. Chemical-induced autoexcision of selectable markers in elite tomato plants transformed with a gene conferring resistance to lepidopteran insects. Biotechnol Lett 28, 1247–1253 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9081-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9081-z