Abstract
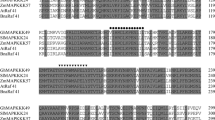
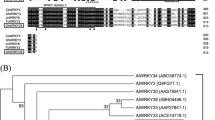
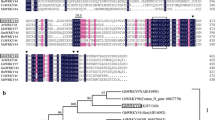
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades play a pivotal role in environmental responses and developmental processes in plants. Previous researches mainly focus on the MAPKs in groups A and B, and little is known on group C. In this study, we isolated and characterized GhMPK7, which is a novel gene from cotton belonging to the group C MAPK. RNA blot analysis indicated that GhMPK7 transcript was induced by pathogen infection and multiple defense-related signal molecules. Transgenic Nicotina benthamiana overexpressing GhMPK7 displayed significant resistance to fungus Colletotrichum nicotianae and virus PVY, and the transcript levels of SA pathway genes were more rapidly and strongly induced. Furthermore, the transgenic N. benthamiana showed reduced ROS-mediated injuries by upregulating expression of oxidative stress-related genes. Interestingly, the transgenic plants germinated earlier and grew faster in comparison to wild-type plants. β-glucuronidase activity driven by the GhMPK7 promoter was detected in the apical meristem at the vegetative stage, and it was enhanced by treatments with signal molecules and phytohormones. These results suggest that GhMPK7 might play an important role in SA-regulated broad-spectrum resistance to pathogen infection, and that it is also involved in regulation of plant growth and development.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal GK, Jwa NS, Rakwal R, Agrawal VP (2001) Signaling molecules and blast pathogen attack activates rice OsPR1a and OsPR1b genes: a model illustrating components participating during defense/stress response. Plant Physiol Biochem 39:1095–1103
Alvarez ME, Pennell RI, Meijer PJ, Ishikawa A, Dixon RA, Lamb C (1998) Reactive oxygen intermediates mediate a systemic signal network in the establishment of plant immunity. Cell 92:773–784
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Phytopathol 55:373–399
Baumann K, De Paolis A, Costantino P, Gualberti G (1999) The DNA binding site of the Dof protein NtBBF1 is essential for tissue-specific and auxin-regulated expression of the rolB oncogene in plants. Plant Cell 11:323–333
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brodersen P, Petersen M, Bjorn Nielsen H, Zhu S, Newman MA, Shokat KM, Rietz S, Parker J, Mundy J (2006) Arabidopsis MAP kinase 4 regulates salicylic acid- and jasmonic acid/ethylene-dependent responses via EDS1 and PAD4. Plant J 47:532–546
Calderini O, Glab N, Bergounioux C, Heberle-Bors E, Wilson C (2001) A novel tobacco mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase, NtMEK1, activates the cell cycle-regulated p43Ntf6 MAP kinase. J Biol Chem 276:18139–18145
Chen PW, Chiang CM, Tseng TH, Yu SM (2006) Interaction between rice MYBGA and the gibberellin response element controls tissue-specific sugar sensitivity of alpha-amylase genes. Plant Cell 18:2326–2340
Cheong YH, Moon BC, Kim JK, Kim CY, Kim MC, Kim IH, Park CY, Kim JC, Park BO, Koo SC, Yoon HW, Chung WS, Lim CO, Lee SY, Cho MJ (2003) BWMK1, a rice mitogen-activated protein kinase, locates in the nucleus and mediates pathogenesis-related gene expression by activation of a transcription factor. Plant Physiol 132:1961–1972
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Coca MA, Damsz B, Yun DJ, Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Narasimhan ML (2000) Heterotrimeric G-proteins of a filamentous fungus regulate cell wall composition and susceptibility to a plant PR-5 protein. Plant J 22:61–69
Colcombet J, Hirt H (2008) Arabidopsis MAPKs: a complex signalling network involved in multiple biological processes. Biochem J 413:217–226
Dangl JL, Jones JD (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411:826–833
Djamei A, Pitzschke A, Nakagami H, Rajh I, Hirt H (2007) Trojan horse strategy in Agrobacterium transformation: abusing MAPK defense signaling. Science 318:453–456
Doczi R, Brader G, Pettko-Szandtner A, Rajh I, Djamei A, Pitzschke A, Teige M, Hirt H (2007) The Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase MKK3 is upstream of group C mitogen-activated protein kinases and participates in pathogen signaling. Plant Cell 19:3266–3279
Durrant WE, Dong X (2004) Systemic acquired resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 42:185–209
Fritig B, Heitz T, Legrand M (1998) Antimicrobial proteins in induced plant defense. Curr Opin Immunol 10:16–22
Fusada N, Masuda T, Kuroda H, Shimada H, Ohta H, Takamiya K (2005) Identification of a novel cis-element exhibiting cytokinin-dependent protein binding in vitro in the 5′-region of NADPH-protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase gene in cucumber. Plant Mol Biol 59:631–645
Group MAPK (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: a new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci 7:301–308
Gu YQ, Wildermuth MC, Chakravarthy S, Loh YT, Yang C, He X, Han Y, Martin GB (2002) Tomato transcription factors pti4, pti5, and pti6 activate defense responses when expressed in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 14:817–831
Hamel LP, Nicole MC, Sritubtim S, Morency MJ, Ellis M, Ehlting J, Beaudoin N, Barbazuk B, Klessig D, Lee J, Martin G, Mundy J, Ohashi Y, Scheel D, Sheen J, Xing T, Zhang SQ, Seguin A, Ellis BE (2006) Ancient signals: comparative genomics of plant MAPK and MAPKK gene families. Trends Plant Sci 11:192–198
Horsch RB, Fry JE, HoVmann NL, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1985) A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227:1229–1231
Hwang SH, Lee IA, Yie SW, Hwang DJ (2008) Identification of an OsPR10a promoter region responsive to salicylic acid. Planta 227:1141–1150
Ichimura K, Casais C, Peck SC, Shinozaki K, Shirasu K (2006) MEKK1 is required for MPK4 activation and regulates tissue-specific and temperature-dependent cell death in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 281:36969–36976
Inukai Y, Sakamoto T, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Shibata Y, Gomi K, Umemura I, Hasegawa Y, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2005) Crown rootless1, which is essential for crown root formation in rice, is a target of an AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR in auxin signaling. Plant Cell 17:1387–1396
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5:387–405
Jeong MJ, Lee SK, Kim BJ, Kwon TR, Cho WS, Park YT, Lee JO, Kwon HB, Byun MO, Park SC (2006) A rice (Oryza stativa L.) MAP kinase gene, OsMAPK44, is involved in response to abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 85:151–160
Jin H, Liu Y, Yang KY, Kim CY, Baker B, Zhang S (2003) Function of a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in N gene-mediated resistance in tobacco. Plant J 33:719–731
Jonak C, Okresz L, Bogre L, Hirt H (2002) Complexity, cross talk and integration of plant MAP kinase signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:415–424
Jones JD, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444:323–329
Joo S, Liu Y, Lueth A, Zhang S (2008) MAPK phosphorylation-induced stabilization of ACS6 protein is mediated by the non-catalytic C-terminal domain, which also contains the cis-determinant for rapid degradation by the 26 S proteasome pathway. Plant J 54:129–140
Kunkel BN, Brooks DM (2002) Cross talk between signaling pathways in pathogen defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:325–331
Lee JS, Wang S, Sritubtim S, Chen JG, Ellis BE (2009) Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinase MPK12 interacts with the MAPK phosphatase IBR5 and regulates auxin signaling. Plant J 57:975–985
Liu Q, Xue Q (2007) Computational identification and phylogenetic analysis of the MAPK gene family in Oryza sativa. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:6–14
Liu Y, Jin H, Yang KY, Kim CY, Baker B, Zhang S (2003) Interaction between two mitogen-activated protein kinases during tobacco defense signaling. Plant J 34:149–160
Martin GB, Bogdanove AJ, Sessa G (2003) Understanding the functions of plant disease resistance proteins. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:23–61
Nakagami H, Pitzschke A, Hirt H (2005) Emerging MAP kinase pathways in plant stress signalling. Trends Plant Sci 10:339–346
Nakagami H, Soukupová H, Schikora A, Zárský V, Hirt H (2006) A mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase mediates reactive oxygen species homeostasis in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 281:38697–38704
Orozco-Cardenas M, Ryan CA (1999) Hydrogen peroxide is generated systemically in plant leaves by wounding and systemin via the octadecanoid pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:6553–6557
Ortiz-Masia D, Perez-Amador MA, Carbonell J, Marcote MJ (2007) Diverse stress signals activate the C1 subgroup MAP kinases of Arabidopsis. FEBS Lett 581:1834–1840
Ortiz-Masia D, Perez-Amador MA, Carbonell P, Aniento F, Carbonell J, Marcote MJ (2008) Characterization of PsMPK2, the first C1 subgroup MAP kinase from pea (Pisum sativum L.). Planta 227:1333–1342
Petersen M, Brodersen P, Naested H, Andreasson E, Lindhart U, Johansen B, Nielsen HB, Lacy M, Austin MJ, Parker JE, Sharma SB, Klessig DF, Martienssen R, Mattsson O, Jensen AB, Mundy J (2000) Arabidopsis map kinase 4 negatively regulates systemic acquired resistance. Cell 103:1111–1120
Ron M, Avni A (2004) The receptor for the fungal elicitor ethylene-inducing xylanase is a member of a resistance-like gene family in tomato. Plant Cell 16:1604–1615
Singh K, Foley RC, Oñate-Sánchez L (2002) Transcription factors in plant defense and stress responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:430–436
Sohn KH, Lee SC, Jung HW, Hong JK, Hwang BK (2006) Overexpression of the pepper CARAV1 pathogen-induced gene encoding a RAV transcription factor induces pathogenesis-related genes and enhances resistance to bacterial pathogen in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 61:897–915
Somssich IE (1997) MAP kinases and plant defence. Trends Plant Sci 2:406–408
Stone JM, Walker JC (1995) Plant protein kinase families and signal transduction. Plant Physiol 108:451–457
Sutoh K, Yamauchi D (2003) Two cis-acting elements necessary and sufficient for gibberellin-upregulated proteinase expression in rice seeds. Plant J 34:635–645
Trewavas A, Gilroy S (1991) Signal transduction in plant cells. Trends Genet 7:356–361
Ulmasov T, Hagen G, Guilfoyle TJ (1999) Dimerization and DNA binding of auxin response factors. Plant J 19:309–319
Walia A, Lee JS, Wasteneys G, Ellis B (2009) Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinase MPK18 mediates cortical microtubule functions in plant cells. Plant J 59:565–575
Wang H, Ngwenyama N, Liu Y, Walker JC, Zhang S (2007a) Stomatal development and patterning are regulated by environmentally responsive mitogen-activated protein kinases in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:63–73
Wang MM, Zhang Y, Wang J, Wu XL, Guo XQ (2007b) A novel MAP Kinase gene in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.), GhMAPK, is involved in response to diverse environmental stresses. J Biochem Mol Biol 40:325–332
Wang H, Liu Y, Bruffett K, Lee J, Hause G, Walker JC, Zhang S (2008) Haplo-insufficiency of MPK3 in MPK6 mutant background uncovers a novel function of these two MAPKs in Arabidopsis ovule development. Plant Cell 20:602–613
Widmann C, Gibson S, Jarpe MB, Johnson GL (1999) Mitogen-activated protein kinase: conservation of a three-kinase module from yeast to human. Physiol Rev 79:143–180
Yamamoto S, Nakano T, Suzuki K, Shinshi H (2004) Elicitor-induced activation of transcription via W box-related cis-acting elements from a basic chitinase gene by WRKY transcription factors in tobacco. Biochim Biophys Acta 1679:279–287
Yang KY, Liu Y, Zhang S (2001) Activation of a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is involved in disease resistance in tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:741–746
Yoo SD, Cho YH, Tena G, Xiong Y, Sheen J (2008) Dual control of nuclear EIN3 by bifurcate MAPK cascades in C2H4 signalling. Nature 451:789–795
Yoshioka H, Numata N, Nakajima K, Katou S, Kawakita K, Rowland O, Jones JD, Doke N (2003) Nicotiana benthamiana gp91phox homologs NbrbohA and NbrbohB participate in H2O2 accumulation and resistance to Phytophthora infestans. Plant Cell 15:706–718
Zhang S, Klessig DF (1998) Resistance gene N-mediated de novo synthesis and activation of a tobacco mitogen-activated protein kinase by tobacco mosaic virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:7433–7438
Zhang S, Klessig DF (2001) MAPK cascades in plant defense signaling. Trends Plant Sci 6:520–527
Zong XJ, Li DP, Gu LK, Li DQ, Liu LX, Hu XL (2009) Abscisic acid and hydrogen peroxide induce a novel maize group C MAP kinase gene, ZmMPK7, which is responsible for the removal of reactive oxygen species. Planta 229:485–495
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30571215) and China National Transgenic Plant Research and Commercialization Project (Grant No. 2009ZX08009-113B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.


Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, J., An, HL., Zhang, L. et al. GhMPK7, a novel multiple stress-responsive cotton group C MAPK gene, has a role in broad spectrum disease resistance and plant development. Plant Mol Biol 74, 1–17 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-010-9661-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-010-9661-0