Abstract
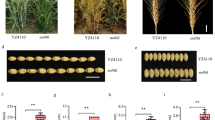
A glabrous, yellow-seeded doubled haploid (DH) line and a hairy, black-seeded DH line in Chinese cabbage (B. rapa) were used as parents to develop a DH line population that segregated for both hairiness and seed coat color traits. The data showed that both traits completely co-segregated each other, suggesting that one Mendelian locus controlled both hairiness and seed coat color in this population. A fine genetic map was constructed and a SNP marker that was located inside a Brassica ortholog of TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA 1 (TTG1) in Arabidopsis showed complete linkage to both the hairiness and seed coat color gene, suggesting that the Brassica TTG1 ortholog shared the same gene function as its Arabidopsis counterpart. Further sequence analysis of the alleles from hairless, yellow-seeded and hairy, black-seeded DH lines in B. rapa showed that a 94-base deletion was found in the hairless, yellow-seeded DH lines. A nonfunctional truncated protein in the hairless, yellow-seeded DH lines in B. rapa was suggested by the coding sequence of the TTG1 ortholog. Both of the TTG1 homologs from the black and yellow seeded B. rapa lines were used to transform an Arabidopsis ttg1 mutant and the results showed that the TTG1 homolog from the black seeded B. rapa recovered the Arabidopsis ttg1 mutant, while the yellow seeded homolog did not, suggesting that the deletion in the Brassica TTG1 homolog had led to the yellow seeded natural mutant. This was the first identified gene in Brassica species that simultaneously controlled both hairiness and seed coat color traits.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agren J, Schemske DW (1992) Artificial selection on trichome number in Brassica rapa. Theor Appl Genet 83:673–678. doi:10.1007/BF00226683
Ahmed SU, Zuberi MI (1971) Inheritance of seed coat color in Brassica campestris L. variety Toria. Crop Sci 11:30
Baudry A, Heim MA, Dubreucq B, Caboche M, Weisshaar B, Lepiniec L (2004) TT2, TT8, and TTG1 synergistically specify the expression of BANYULS and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 39:366–380. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02138.x
Baudry A, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2006) TT8 controls its own expression in a feedback regulation involving TTG1 and homologous MYB and bHLH factors, allowing a strong and cell-specific accumulation of flavonoids in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 46:768–779. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02733.x
Broun P (2005) Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis: a complex network of conserved regulators involved in multiple aspects of differentiation in Arabidopsis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:272–279. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2005.03.006
Chen BY, Jorgensen RB, Cheng BF, Heneen WK (1997) Identification and chromosomal assignment of RAPD marker linked with a gene for seed coat color in a Brassica campestris-alboglabra addition line. Hereditas 126:133–138. doi:10.1111/j.1601-5223.1997.00133.x
Geu-Flores F, Nour-Eldin HH, Nielsen MT, Halkier BA (2007) USER fusion: a rapid and efficient method for simultaneous fusion and cloning of multiple PCR products. Nucleic Acids Res 35(7):e55. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm106
Gruber MY, Wang S, Ethier S, Holowachuk J, Bonham-Smith PC, Soroka J, Lloyd A (2006) “HAIRY CANOLA”—Arabidopsis GL3 induces a dense covering of trichomes on Brassica napus seedlings. Plant Mol Biol 60:679–698. doi:10.1007/s11103-005-5472-0
Haughn G, Chaudhury A (2005) Genetic analysis of seed coat development in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 10(10):472–477. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2005.08.005
Johnson CS, Kolevski B, Smyth DR (2002) TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA2, a trichome and seed coat development gene of Arabidopsis, encodes a WRKY transcription factor. Plant Cell 14:1359–1375. doi:10.1105/tpc.001404
Lander E, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daley M, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(87)90010-3
Li G, Quiros CF (2001) Sequence related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 103:455–461. doi:10.1007/s001220100570
Liu HL (1992) Studies on inheritance of yellow-seeded Brassica napus L. Acta Agron Sin 18:241–249
Liu ZW, Fu TD, Tu JX, Chen BY (2005) Inheritance of seed color and identification of RAPD and AFLP markers linked to the seed color gene in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 110:303–310. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1835-1
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.21.9828
Negi MS, Devic M, Delseny M, Lakshmikumaran M (2000) Identification of AFLP fragments linked to seed coat color in Brassica juncea and conversion to SCAR marker for rapid selection. Theor Appl Genet 101:146–152. doi:10.1007/s001220051463
Nour-Eldin HH, Hansen BG, Nørholm MHH, Jensen JK, Halkier BA (2006) Advancing uracil-excision based cloning towards an ideal technique for cloning PCR fragments. Nucleic Acids Res 34(18):e122. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl635
Nozaki T, Kumazaki A, Koba T, Ishikawa K, Ikehashi H (1997) Linkage analysis among loci for RAPDs, isozymes and some agronomic traits in Brassica campestris L. Euphytica 95:115–123. doi:10.1023/A:1002981208509
Paterson AH, Lan TH, Amasino R, Osborn TC, Quiros CF (2001) Brassica genomics: a complement to, and early beneficiary of, the Arabidopsis sequence. Genome Biol 2:REVIEWS1011.1
Penfield S, Meissner RC, Shoue DA, Carpita NC, Bevan MW (2001) MYB61 is required for mucilage deposition and extrusion in the Arabidopsis seed coat. Plant Cell 13:2777–2791
Rahman MH (2001) Production of yellow-seeded through interspecific crosses. Plant Breed 120:463–472. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0523.2001.00640.x
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Schiefelbein J (2003) Cell-fate specification in the epidermis: a common patterning mechanism in the root and shoot. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:74–78. doi:10.1016/S136952660200002X
Somers DJ, Rakow G, Prabhu VK, Friesen KRD (2001) Identification of a major gene and RAPD markers for yellow seed coat color in B. napus. Genome 44:1077–1082. doi:10.1139/gen-44-6-1077
Song KM, Slocum MK, Osborn TC (1995) Molecular marker analysis of genes controlling morphological variation in Brassica rapa. Theor Appl Genet 90:1–10
Stringam GR (1980) Inheritance of seed color in turnip rape. Can J Plant Sci 60:331–335
Stringam GR, McGregor DI, Pawlowski SH (1974) Chemical and morphological characteristics associated with seed coat color in rapeseed. In: Proceedings of the 4th international rapeseed conference, Giessen, pp 99–108
Tang ZL, Li JN, Zhang XK, Chen L, Wang R (1997) Genetic variation of yellow-seeded rapeseed lines Brassica napus L. from different genetic sources. Plant Breed 116:471–474. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0523.1997.tb01033.x
Teutonico RA, Osborn TC (1994) Mapping of RFLP and quantitative trait loci in Brassica rapa and comparison to the linkage maps of B. napus, B. oleracea and Arabidopsis thaliana. Theor Appl Genet 89:885–894. doi:10.1007/BF00224514
Walker AR, Davison PA, Bolognesi-Winfield AC, James CM, Srinivasan N, Blundell TL, Esch JJ, Marks MD, Gray JC (1999) The TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA1 locus, which regulates trichome differentiation and anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis, encodes a WD40 repeat protein. Plant Cell 11:1337–1350
Woo SS, Jiang J, Gill BS, Paterson AH, Wing RA (1994) Construction and characterization of a bacterial artificial chromosome library of Sorghum bicolor. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4922–4931. doi:10.1093/nar/22.23.4922
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), Bunge Canada and the Manitoba Canola Growers Association in an Industrial Research Chair (IRC) program and partially supported by the Genome Canada/Genome Alberta project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Lu, Y., Yuan, Y. et al. Map-based cloning and characterization of a gene controlling hairiness and seed coat color traits in Brassica rapa . Plant Mol Biol 69, 553–563 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9437-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9437-y