Abstract
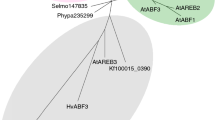
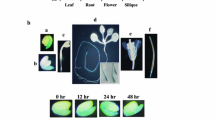
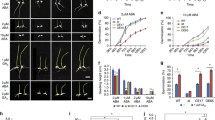
To investigate the crosstalk of abscisic acid (ABA) and gibberellin (GA) signaling in wheat (Triticum aestivum), we have focused on the transcription factor TaABF1. TaABF1 (a member of the ABA response element binding factor family) physically interacts with PKABA1, a signaling component in the ABA-suppression of GA-induced gene expression in cereal grains. Constitutive expression of TaABF1 in aleurone cells of imbibing grains completely eliminated GA-induced expression from the Amy32b promoter. In addition to its effect on Amy32b, TaABF1 strongly stimulated expression from the ABA-inducible HVA1 and HVA22 promoters. Overexpression of TaABF1 fully substituted for exogenous ABA in the induction of these two promoters. The introduction of a construct directing RNA inhibition (RNAi) of TaABF1 did not prevent either ABA-mediated or PKABA1-mediated suppression of Amy32b expression. Similarly, the RNAi construct did not prevent ABA-induction of HVA1. These results suggest that another protein may act redundantly with TaABF1 during cereal imbibition. Although TaABF1 mRNA was downregulated during imbibition of afterripened grains, transcript levels were not significantly altered by exogenous GA or ABA, suggesting that upregulation of TaABF1 at the mRNA level is not required for its role in ABA signaling. We propose a model in which TaABF1 is involved in two separate branches of ABA signaling. In this model, TaABF1 acts downstream of PKABA1 in ABA-suppression of GA-induced gene expression, and participates (independently of PKABA1) in the stimulation of ABA-induced genes.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- ABF:
-
Abscisic acid response element binding factor
- ABRE:
-
Abscisic acid response element
- ABRC:
-
Abscisic acid response complex
- GA:
-
Gibberellin
- nt:
-
Nucleotide
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative (real time) reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
- RNAi:
-
RNA inhibition
- SnRK2:
-
Snf1-Related kinase 2
References
Altshul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, et al (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402. doi:10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Bensmihen S, Rippa S, Lambert G, Jublot D, Pautot V, Granier F, et al (2002) The homologous ABI5 and EEL transcription factors function antagonistically to fine-tune gene expression during late embryogenesis. Plant Cell 14:1391–1403. doi:10.1105/tpc.000869
Bensmihen S, Giraudat J, Parcy F (2005) Characterization of three homologous basic leucine zipper transcription factors (bZIP) of the ABI5 family during Arabidopsis thaliana embryo maturation. J Exp Bot 412:597–603. doi:10.1093/jxb/eri050
Casaretto J, Ho T-HD (2003) The transcription factors HvABI5 and HvVP1 are required for the abscisic acid induction of gene expression in barley aleurone cells. Plant Cell 15:271–284. doi:10.1105/tpc.007096
Casaretto JA, Ho T-HD (2005) Transcriptional regulation by abscisic acid in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seeds involves autoregulation of the transcription factor HvABI5. Plant Mol Biol 57:21–34. doi:10.1007/s11103-004-6520-x
Chae M-J, Lee J-S, Nam M-H, Cho K, Hong J-Y, Yi S-A et al (2007) A rice dehydration-inducible SNF1-related protein kinase 2 phosphorylates an abscisic acid responsive element-binding factor and associates with ABA signaling. Plant Mol Biol 63:151–169. doi:10.1007/s11103-006-9079-x
Choi H, Hong J, Ha J, Kang J, Kim SK (2000) ABFs, a family of ABA-responsive element binding factors. J Biol Chem 275:1723–1730. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.3.1723
Christensen AH, Quail PH (1996) Ubiquitin promoter-based vectors for high-level expression of selectable and/or screenable marker genes in monocotyledonous plants. Transgenic Res 5:213–218. doi:10.1007/BF01969712
Diaz I, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Abraham Z, Martínez M, Moneda II-L, Carbonero P (2002) The GAMYB protein from barley interacts with the DOF transcription factor BPBF and activates endosperm-specific genes during seed development. Plant J 29:453–464. doi:10.1046/j.0960-7412.2001.01230.x
Finkelstein R, Gampala SSL, Lynch TJ, Thomas TL, Rock CD (2005) Redundant and distinct functions of the ABA response loci ABA-INSENSITIVE(ABI)5 and ABRE-BINDING FACTOR(ABF)3. Plant Mol Biol 59:253–267. doi:10.1007/s11103-005-8767-2
Fujii H, Verslues PE, Zhu J-K (2007) Identification of two protein kinases required for abscisic acid regulation of seed germination, root growth, and gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:485–494. doi:10.1105/tpc.106.048538
Fujita Y, Fujita M, Satoh R, Maruyama K, Parvez MM, Seki M, HIratsu K, Ohme-Takagi M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2005) AREB1 is a transcription activator of novel AREB-dependent ABA signaling that enhances drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:3470–3488. doi:10.1105/tpc.105.035659
Furihata T, Maruyama K, Umezawa T, Yoshida R, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2006) Abscisic acid-dependent multisite phosphorylation regulates the activity of a transcription activator AREB1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:1988–1993. doi:10.1073/pnas.0505667103
Gómez-Cadenas A, Verhey SD, Hollapa LD, Shen Q, Ho T-HD, Walker-Simmons MK (1999) An abscisic acid-induced protein kinase, PKABA1, mediates abscisic-acid suppressed gene expression in barley aleurone layers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:1767–1772. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.4.1767
Gómez-Cadenas A, Zentella R, Walker-Simmons MK, Ho T-HD (2001) Gibberellin/abscisic acid antagonism in barley aleurone cells: site of action of the protein kinase PKABA1 in relation to gibberellin signaling molecules. Plant Cell 13:667–679
Gubler F, Raventos D, Keys M, Watts R, Mundy J, Jacobsen JV (1999) Target genes and regulatory domains of the GAMYB transcription activator in cereal aleurone. Plant J 17:1–9. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00346.x
Guo H-S, Fei J-F, Xie Q, Chua N-H (2003) A chemical-regulated inducible RNAi system in plants. Plant J 34:383–392. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01723.x
Hirayama T, Shinozaki K (2007) Perception and transduction of abscisic acid signals: keys to the function of the versatile plant hormone ABA. Trends Plant Sci 12:1360–1385. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2007.06.013
Hobo T, Kowyama Y, Hattori T (1999) A bZIP factor, TRAB1, interacts with VP1 and mediates abscisic acid-induced transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:15348–15353. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.26.15348
Holappa LD, Walker-Simmons MK (1995) The wheat abscisic acid-responsive protein kinase mRNA PKABA1, is up-regulated by dehydration, cold, temperature, and osmotic stress. Plant Physiol 108:1203–1209
Jakoby M, Weisshaar B, Droge-Laser W, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Tiedemann J, Kroj T, Parcy F (2002) bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 7:106–111
Johnson RR (2003) Seed development: germination. In: Thomas B, Murphy D, Murray B (eds) Encyclopedia of applied plant sciences. Academic Press, pp 1298–1304
Johnson RR, Wagner RL, Verhey SD, Walker-Simmons MK (2002) The abscisic acid-responsive kinase PKABA1 interacts with a seed-specific abscisic acid response element-binding factor, TaABF, and phosphorylates TaABF peptide sequences. Plant Physiol 130:837–846. doi:10.1104/pp.001354
Kim SY, Ma J, Perret P, Li Z, Thomas TL (2002) Arabidopsis ABI5 subfamily members have distinct DNA-binding and transcriptional activities. Plant Physiol 130:688–697. doi:10.1104/pp.003566
Kim SK, Kang J-Y, Cho D-I, Park JH, Kim SY (2004) ABF2, an ABRE-binding bZIP factor, is an essential component of glucose signaling and its over expresssion affects multiple stress tolerance. Plant J 40:75–87 doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02192.x
Kobayashi Y, Murata M, Minami H, Yamamoto S, Kagaya Y, Hobo T et al (2005) Abscisic acid-activated SNRK2 protein kinases function in the gene-regulation pathway of ABA signal transduction by phosphorylating ABA response element-binding factors. Plant J 44:939–949. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02583.x
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163 doi:10.1093/bib/5.2.150
Lanahan MB, Ho T-HD, Rogers SW, Rogers JC (1992) A gibberellin response complex in cereal alpha-amylase gene promoters. Plant Cell 4:203–211
Lopez-Molina L, Mongrand S, Chua N-H (2001) A postgermination developmental arrest checkpoint is mediated by abscisic acid and requires the ABI5 transcription factor in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:4782–4787. doi:10.1073/pnas.081594298
Lopez-Molina L, Mongrand S, Kinoshita N, Chua N-H (2003) AFP is a novel negative regulator of ABA signaling that promotes ABI5 protein degradation. Genes Dev 17:410–418. doi:10.1101/gad.1055803
Lovegrove A, Hooley R (2000) Gibberellin and abscisic acid signaling in aleurone. Trends Plant Sci 5:102–110. doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(00)01571-5
Moreno-Risueño MÁ, Díaz I, Carrillo L, Fuentes R, Carbonero P (2007) The HvDOF19 transcription factor mediates the abscisic acid-dependent repression of hydrolase genes in germinating barley aleurone. Plant J 51:352–365. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03146.x
Nakamura S, Lynch TJ, Finkelstein RR (2001) Physical interactions between ABA response loci of Arabidopsis. Plant J 26:627–635. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01069.x
Nakamura S, Komatsuda T, Miura H (2007) Mapping diploid wheat homologues of Arabidopsis seed ABA signaling genes and QTLs for seed dormancy. Theor Appl Genet 114:1129–1139. doi:10.1007/s00122-007-0502-8
Oh S-J, Song SI, Kim YS, Jang H-J, Kim SY, Kim M et al (2005) Arabidopsis CBF3/DREB1A and ABF3 in transgenic rice increased tolerance to abiotic stress without stunting growth. Plant Physiol 138:341–351. doi:10.1104/pp.104.059147
Shen Q, Uknes SJ, Ho T-HD (1993) Hormone response complex in a novel abscisic acid and cycloheximide-inducible barley gene. J Biol Chem 268:23652–23660
Shen Q, Zhang P, Ho T-HD (1996) Modular nature of abscisic acid (ABA) response complexes; composite promoter units that are necessary and sufficient for ABA induction of gene expression. Plant Cell 8:1107–1119
Shen Q, Casaretto J, Zhang P, Ho T-HD (2004) Functional definition of ABA-response complexes: the promoter units necessary and sufficient for ABA induction of gene expression in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Mol Biol 54:111–124. doi:10.1023/B:PLAN.0000028773.94595.e8
Shoonheim PJ, Sinnige MP, Casaretto JA, Veiga H, Bunney TD, Quatrano RS et al (2007) 14-3-3 adaptor proteins are intermediates in ABA signal transduction during barely seed germination. Plant J 49:289–301. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02955.x
Uno Y, Furihata T, Abe H, Yoshida R, Shinozaki K (2000) Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper transcription factors involved in an abscisic acid-dependent signal transduction pathway under drought and high-salinity conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11632–11637. doi:10.1073/pnas.190309197
Yamauchi D, Zentella R, Ho T-HD (2002) Molecular analysis of the barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) gene encoding the protein kinase PKABA1 capable of suppressing gibberellin action in aleurone layers. Planta 215:319–326. doi:10.1007/s00425-002-0740-6
Zentella R, Yamauchi D, Ho T-HD (2002) Molecular dissection of the gibberellin/abscisic acid signaling pathways by transiently expressed RNA interference in barley aleurone cells. Plant Cell 14:2289–2301. doi:10.1105/tpc.003376
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Xialou Zou and Angi Zhang for their help with particle bombardment. They also thank Peter Quail for providing plasmid pAHC17, Nam-Hai Chua for providing plasmid pSKint, and Camille Steber for providing Brevor wheat grains. This work was supported in part by a grant from the US National Science Foundation (IOB-0443676), by a US National Institutes of Health Grant (P20-RR-016463) from the INBRE program of the National Center for Research Resources, and by a Colby College Natural Sciences Division Research Grant. We also thank the Wattis Dumke Foundation for funding the purchase of a real time thermal cycler to facilitate qRT-PCR experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, R.R., Shin, M. & Shen, J.Q. The wheat PKABA1-interacting factor TaABF1 mediates both abscisic acid-suppressed and abscisic acid-induced gene expression in bombarded aleurone cells. Plant Mol Biol 68, 93–103 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9354-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9354-0