Abstract
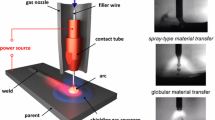
Gas metal arc welding is indispensable in many fields of industry. In this process, various kinds of shielding gas are used, and they significantly affect the behaviors of the arc plasma and metal transfer. In this study, these behaviors with various kinds of shielding gas are numerically investigated. In addition, the influence of the electrical conductivity of the metal vapor is discussed. Simulation results show that with Ar gas, spray transfer occurs at an arc current of more than 240 A, and with CO2 gas, the transfer mode is globular, even at an arc current of 300 A. The calculation results show that the current path near the wire tip critically determines droplet behavior. With Ar gas, the current path is spread out, covering the molten wire, whereas with CO2 gas, the current path is concentrated at the bottom of the molten wire. Therefore, to achieve spray transfer, the current path needs to be spread at the wire tip; however, if the spreading is excessive, the transfer mode becomes streaming transfer. To investigate the influence of the metal vapor, a numerical experiment using pseudo metal vapor was carried out. Even with CO2 gas, the electrical conductivity of the metal vapor was low, and thus the current path was not concentrated at the bottom of the molten wire, allowing spray transfer. The numerical results show that metal transfer phenomena can be regulated by controlling the electrical conductivity of the metal vapor.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruckdeschel WEW (1976) Classification of metal transfer. IIW Doc. XII-636-76
Ludwig HC (1957) Metal transfer characteristics in gas-shielded arc welding. Weld J 36:23s–26s
Needham JC, Cooksey CJ, Milner DR (1960) Metal transfer in inert-gas shielded-arc welding. Br Weld J 7:101–114
Liu S, Siewert TA (1989) Metal transfer in gas metal arc welding: droplet rate. Weld J 68:52s–58s
Lesnewich A (1958) Control of melting rate and metal transfer in gas-shielded metal-arc welding part II—control of metal transfer. Weld J 37:418s–425s
Rhee S, Kannatey-Asibu E Jr (1992) Observation of metal transfer during gas metal arc welding. Weld J 71:381s–386s
Kataoka T, Ikeda R, Ono M, Yasuda K, Hirata Y (2009) Effect of REM addition of wire on CO2 gas shielded arc phenomenon. Weld Int 23:517–522
Valensi F, Pellerin S, Boutaghane A, Dzierzega K, Zielinska S, Pellerin N, Briand F (2010) Plasma diagnostics in gas metal arc welding by optical emission spectroscopy. J Phys D Appl Phys 43:434002
Rouffet ME, Weldt M, Goett G, Kozakov R, Shoepp H, Weltmann KD, Uhrlandt D (2010) Spectroscopy investigation of the high-current phase of a pulsed GMAW process. J Phys D Appl Phys 43:434003
Schnick M, Fuessel U, Hertel M, Haessler M, Spille-Kohoff A, Murphy AB (2010) Modelling of gas–metal arc welding taking into account metal vapour. J Phys D Appl Phys 43:434008
Methong T, Shigeta M, Tanaka M, Ikeda R, Matsushita M, Poopat B (2018) Visualization of gas metal arc welding on globular to spray transition current. Sci Technol Weld Join 23:87–94
Simpson SW, Zhu P (1995) Formation of molten droplet at a consumable anode in an electric welding arc. J Phys D Appl Phys 28:1594–1600
Choi SK, Yoo CD, Kim Y-S (1998) Dynamic simulation of metal transfer in GMAW, part 1: globular and spray transfer modes. Weld J 77:38s–44s
Choi SK, Yoo CD, Kim Y-S (1998) The dynamic analysis of metal transfer in pulsed current gas metal arc welding. J Phys D Appl Phys 31:207–215
Wang G, Huang PG, Zhang YM (2003) Numerical analysis of metal transfer in gas metal arc welding. Metall Mater Trans B 34B:345–353
Kadota K, Hirata Y (2011) Numerical model of metal transfer using an electrically conductive liquid. Weld World 55:50–55
Wang F, Hou WK, Hu SJ, Kannatey-Asibu E, Schultz WW, Wang PC (2003) Modelling and analysis of metal transfer in gas metal arc welding. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:1143–1152
Haidar J, Lowke JJ (1996) Predictions of metal droplet formation in arc welding. J Phys D Appl Phys 29:2951–2960
Hu J, Tsai HL (2007) Heat and mass transfer in gas metal arc welding. Part II: the metal. Int J Heat Mass Transf 50:808–820
Xu G, Hu J, Tsai HL (2009) Three-dimensional modeling of arc plasma and metal transfer in gas metal arc welding. Int J Heat Mass Transf 52:1709–1724
Ogino Y, Hirata Y (2015) Numerical simulation of metal transfer in argon gas-shielded GMAW. Weld World 59:465–473
Hertel M, Spille-Kohoff A, Fuessel U, Schnick M (2013) Numerical simulation of droplet detachment in pulsed gas–metal arc welding including the influence of metal vapour. J Phys D Appl Phys 46:224003
Hertel M, Trautmann M, Jaeckel S, Fuessel U (2017) The role of metal vapour in gas metal arc welding and methods of combined experimental and numerical process analysis. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 37:531–547
Ogino Y, Hirata Y, Murphy AB (2016) Numerical simulation of GMAW process using Ar and an Ar–CO2 gas mixture. Weld World 60:345–353
Wilke CR (1950) A viscosity equation for gas mixtures. J Chem Phys 18:517–519
Hirt CW, Nichols BD (1981) Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries. J Comput Phys 39:201–225
Brackbill JU, Kothe DB, Zamach C (1992) A continuum method for modeling surface tension. J Comput Phys 100:335–354
Murphy AB (1995) Transport coefficients of air, argon–air, nitrogen–air and oxygen–air plasmas. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 15:279–307
Murphy AB, Arundell CJ (1994) Transport coefficients of argon, nitrogen, oxygen, argon–nitrogen and argon–oxygen plasmas. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 14:451–490
Murphy AB (2010) The effect of metal vapour in arc welding. J Phys D Appl Phys 43:434001
Rao ZH, Hu J, Liao SM, Tsai HL (2010) Modeling of the transport phenomena in GMAW using argon–helium mixtures. Part I—the arc. Int J Heat Mass Transf 53:5707–5721
Ushio M, Wu CS (1997) Mathematical modeling of three-dimensional heat and fluid flow in a moving gas metal arc weld pool. Metall Mater Trans B 28B:509–516
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by the Structural Materials for Innovation of the Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP) of the Japan Science and Technology (JST) Agency and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number JP16H06937.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogino, Y., Hirata, Y. & Asai, S. Discussion of the Effect of Shielding Gas and Conductivity of Vapor Core on Metal Transfer Phenomena in Gas Metal Arc Welding by Numerical Simulation. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 40, 1109–1126 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-020-10102-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-020-10102-1