Abstract
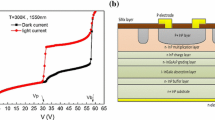
We report on 2D simulations of dark current for InP/In0.53Ga0.47aAs/InP p-i-n photodiode. Our simulation result is in good agreement with experiment confirming that generation-recombination effect is the dominant source of the dark current at low bias. Effects of the thickness and doping concentration of the absorption layer on the dark current are discussed in detail.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrenkiel R.K., Ellingson R., Johnston S., Wanlass M.: Recombination lifetime of In0.53Ga0.47As as a function of doping density. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 3470–3472 (1998). doi:10.1063/1.121669
Chang S.H., Fang Y.K., Ting S.F., Chen S.F., Lin C.Y.: Ultra high performance planar InGaAs PIN photodiodes for high speed optical fiber communication. Sens. Actuators A 133, 9–12 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.sna.2006.04.023
Forrest S.R.: Performance of InxGa1-x,AsyP1-y photodiodes with dark current limited by diffusion, generation recombination, and tunneling. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-17, 217–226 (1981). doi:10.1109/JQE.1981.1071060
Forrest S.R., DiDominico M., Smith R.G., Stocker H.J.: Evidence for tunneling in reverse-biased III-V photodetector diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 36, 580–582 (1980). doi:10.1063/1.91553
Linga K.R., Olsen G.H., Ban V.S., Joshi A.M., Kosonocky W.F.J.: Dark current analysis and characterization of InxGa1-xAs/InAsyP1-y graded photodiodes with x > 0.53 for response to longer wavelengths (>1.7 μm). Lightwave Technol. 10, 1050–1055 (1992). doi:10.1109/50.156844
Makita K., Watanabe I., Tsuji M., Taguchi K.: Dark current and breakdown analysis in In(Al)GaAs/InAlAs superlattice avalanche photodiodes. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 35, 3440–3444 (1996). doi:10.1143/JJAP.35.3440
Onat B.M., Huang W., Masaun N., Lange M., Ettenberg M.H., Dries C.: Ultra low dark current InGaAs technology for focal plane arrays for low-light level visible-shortwave infrared imaging. Proc. of SPIE 6542, 1–9 (2007)
Parks J.W., Smith A.W., Brennan K.F., Tarof L.E.: Theoretical study of device sensitivity and gain saturation of separate absorption, grading, charge, and multiplication InP/InGaAs avalanche photodiodes. IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 43, 2113–2121 (1996). doi:10.1109/16.544382
Shen S.C.: Comparison and competition between MCT and QW structure material for use in IR detectors. Microelectron. J. 25, 713–739 (1994). doi:10.1016/0026-2692(94)90136-8
Synopsys: Synopsys Sentaurus Device user manual, USA 2008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X.D., Hu, W.D., Chen, X.S. et al. Dark current simulation of InP/In0.53Ga0.47As/InP p-i-n photodiode. Opt Quant Electron 40, 1261–1266 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-009-9279-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-009-9279-0