Abstract
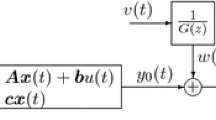
This paper discusses iterative identification problems for a class of output nonlinear systems (i.e., Wiener nonlinear systems) with moving average noises from input–output measurement data, based on the Newton iterative method. The basic idea is to decompose a nonlinear system into two subsystems, to replace the unknown variables in the information vectors with their corresponding estimates at the previous iteration, and to present a Newton iterative identification method using the hierarchical identification principle. The numerical simulation results indicate that the proposed algorithms are effective.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ding, F.: System Identification—New Theory and Methods. Science Press, Beijing (2013)
Shi, Y., Yu, B.: Output feedback stabilization of networked control systems with random delays modeled by Markov chains. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 54(7), 1668–1674 (2009)
Shi, Y., Yu, B.: Robust mixed H-2/H-infinity control of networked control systems with random time delays in both forward and backward communication links. Automatica 47(4), 754–760 (2011)
Li, H., Shi, Y.: Robust H-infty filtering for nonlinear stochastic systems with uncertainties and random delays modeled by Markov chains. Automatica 48(1), 159–166 (2012)
Zhang, Q.J., Luo, J., Wan, L.: Parameter identification and synchronization of uncertain general complex networks via adaptive-impulsive control. Nonlinear Dyn. 71(1–2), 353–359 (2013)
Qin, P., Nishii, R., Yang, Z.J.: Selection of NARX models estimated using weighted least squares method via GIC-based method and l1-norm regularization methods. Nonlinear Dyn. 70(3), 1831–1846 (2012)
Olson, C.C., Nichols, J.M., Virgin, L.N.: Parameter estimation for chaotic systems using a geometric approach: theory and experiment. Nonlinear Dyn. 70(1), 381–391 (2012)
Hizir, N.B., Phan, M.Q., Betti, R., Longman, R.W.: Identification of discrete-time bilinear systems through equivalent linear models. Nonlinear Dyn. 69(4), 2065–2078 (2012)
Ding, F., Chen, T.: Identification of Hammerstein nonlinear ARMAX systems. Automatica 41(9), 1479–1489 (2005)
Ding, F., Shi, Y., Chen, T.: Gradient-based identification methods for Hammerstein nonlinear ARMAX models. Nonlinear Dyn. 45(1–2), 31–43 (2006)
Bai, E.W.: A blind approach to the Hammerstein–Wiener model identification. Automatica 38(6), 967–979 (2002)
Wang, D.Q., Ding, F.: Extended stochastic gradient identification algorithms for Hammerstein–Wiener ARMAX systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 56(12), 3157–3164 (2008)
Wang, D.Q., Ding, F.: Hierarchical least squares estimation algorithm for Hammerstein–Wiener systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 19(12), 825–828 (2012)
Wang, D.Q., Ding, F.: Least squares based and gradient based iterative identification for Wiener nonlinear systems. Signal Process. 91(5), 1182–1189 (2011)
Li, J.H., Ding, F.: Maximum likelihood stochastic gradient estimation for Hammerstein systems with colored noise based on the key term separation technique. Comput. Math. Appl. 62(11), 4170–4177 (2011)
Li, J.H., Ding, F., Yang, G.W.: Maximum likelihood least squares identification method for input nonlinear finite impulse response moving average systems. Math. Comput. Model. 55(3–4), 442–450 (2012)
Wang, W., Ding, F., Dai, J.Y.: Maximum likelihood least squares identification for systems with autoregressive moving average noise. Appl. Math. Model. 36(5), 1842–1853 (2012)
Dehghan, M., Hajarian, M.: An iterative method for solving the generalized coupled Sylvester matrix equations over generalized bisymmetric matrices. Appl. Math. Model. 34(3), 639–654 (2010)
Dehghan, M., Hajarian, M.: Analysis of an iterative algorithm to solve the generalized coupled Sylvester matrix equations. Appl. Math. Model. 35(7), 3285–3300 (2011)
Wu, A.G., Li, B., Zhang, Y., Duan, G.R.: Finite iterative solutions to coupled Sylvester-conjugate matrix equations. Appl. Math. Model. 35(3), 1065–1080 (2011)
Liu, X.G., Lu, J.: Least squares based iterative identification for a class of multirate systems. Automatica 46(3), 549–554 (2010)
Ding, F., Liu, Y.J., Bao, B.: Gradient based and least squares based iterative estimation algorithms for multi-input multi-output systems. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part I, J. Syst. Control Eng. 226(1), 43–55 (2012)
Lorentzen, R.J., Naevdal, G.: An iterative ensemble Kalman filter. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 56(8), 1990–1995 (2011)
Ding, F., Liu, X.P., Liu, G.: Gradient based and least-squares based iterative identification methods for OE and OEMA systems. Digit. Signal Process. 20(3), 664–677 (2010)
Wang, D.Q., Yang, G.W., Ding, R.F.: Gradient-based iterative parameter estimation for Box–Jenkins systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 60(5), 1200–1208 (2010)
Xie, L., Yang, H.Z.: Gradient based iterative identification for non-uniform sampling output error systems. J. Vib. Control 17(3), 471–478 (2011)
Sun, Z., Zeng, J.P., Xu, H.R.: Generalized Newton-iterative method for semismooth equations. Numer. Algorithms 58(3), 333–349 (2011)
Arnal, J., Migallón, V., Penadés, J.: Parallel Newton two-stage multisplitting iterative methods for nonlinear systems. BIT Numer. Math. 43(5), 849–861 (2003)
Xiong, W.L., Ma, J.X., Ding, R.F.: An iterative numerical algorithm for modeling a class of Wiener nonlinear systems. Appl. Math. Lett. 26(4), 487–493 (2013)
Liu, M.M., Xiao, Y.S., Ding, R.F.: Iterative identification algorithm for Wiener nonlinear systems using the Newton method. Appl. Math. Model. 37(9), 6584–6591 (2013)
Ding, F., Chen, T.: Hierarchical gradient-based identification of multivariable discrete-time systems. Automatica 41(2), 315–325 (2005)
Ding, F., Chen, T.: Hierarchical least squares identification methods for multivariable systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 50(3), 397–402 (2005)
Ding, F., Chen, T.: Hierarchical identification of lifted state-space models for general dual-rate systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I, Regul. Pap. 52(6), 1179–1187 (2005)
Ding, J., Ding, F., Liu, X.P., Liu, G.: Hierarchical least squares identification for linear SISO systems with dual-rate sampled-data. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 56(11), 2677–2683 (2011)
Liu, Y.J., Ding, F., Shi, Y.: Least squares estimation for a class of non-uniformly sampled systems based on the hierarchical identification principle. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 31(6), 1985–2000 (2012)
Wang, D.Q., Ding, R., Dong, X.Z.: Iterative parameter estimation for a class of multivariable systems based on the hierarchical identification principle and the gradient search. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 31(6), 2167–2177 (2012)
Ding, F., Shi, Y., Chen, T.: Auxiliary model based least-squares identification methods for Hammerstein output-error systems. Syst. Control Lett. 56(5), 373–380 (2007)
Han, H.Q., Xie, L., Ding, F., Liu, X.: Hierarchical least squares based iterative identification for multivariable systems with moving average noises. Math. Comput. Model. 51(9–10), 1213–1220 (2010)
Zhang, Z.N., Ding, F., Liu, X.G.: Hierarchical gradient based iterative parameter estimation algorithm for multivariable output error moving average systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 61(3), 672–682 (2011)
Ding, F.: Hierarchical multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for Hammerstein nonlinear system modeling. Appl. Math. Model. 37(4), 1694–1704 (2013)
Ding, F., Liu, X.P., Liu, G.: Identification methods for Hammerstein nonlinear systems. Digit. Signal Process. 21(2), 215–238 (2011)
Ding, F., Liu, X.G., Chu, J.: Gradient-based and least-squares-based iterative algorithms for Hammerstein systems using the hierarchical identification principle. IET Control Theory Appl. 7(2), 176–184 (2013)
Zhang, Y.: Unbiased identification of a class of multi-input single-output systems with correlated disturbances using bias compensation methods. Math. Comput. Model. 53(9–10), 1810–1819 (2011)
Ding, F., Liu, G., Liu, X.P.: Parameter estimation with scarce measurements. Automatica 47(8), 1646–1655 (2011)
Ding, F.: Two-stage least squares based iterative estimation algorithm for CARARMA system modeling. Appl. Math. Model. 37(7), 4798–4808 (2013)
Liu, Y.J., Xiao, Y.S., Zhao, X.L.: Multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for multiple-input single-output systems using the auxiliary model. Appl. Math. Comput. 215(4), 1477–1483 (2009)
Liu, Y.J., Sheng, J., Ding, R.F.: Convergence of stochastic gradient estimation algorithm for multivariable ARX-like systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 59(8), 2615–2627 (2010)
Ding, F.: Coupled-least-squares identification for multivariable systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 7(1), 68–79 (2013)
Ding, F.: Decomposition based fast least squares algorithm for output error systems. Signal Process. 93(5), 1235–1242 (2013)
Wang, D.Q.: Least squares-based recursive and iterative estimation for output error moving average systems using data filtering. IET Control Theory Appl. 5(14), 1648–1657 (2011)
Li, J.H., Ding, R.F., Yang, Y.: Iterative parameter identification methods for nonlinear functions. Appl. Math. Model. 36(6), 2739–2750 (2012)
Ding, L., Han, L.L., Chen, X.M.: Time series AR modeling with missing observations based on the polynomial transformation. Math. Comput. Model. 51(5–6), 527–536 (2010)
Chen, J., Zhang, Y., Ding, R.F.: Auxiliary model based multi-innovation algorithms for multivariable nonlinear systems. Math. Comput. Model. 52(9–10), 1428–1434 (2010)
Chen, J., Wang, X.P., Ding, R.F.: Gradient based estimation algorithm for Hammerstein systems with saturation and dead-zone nonlinearities. Appl. Math. Model. 36(1), 238–243 (2012)
Chen, J., Lv, L.X., Ding, R.F.: Multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithms for dual-rate sampled systems with preload nonlinearity. Appl. Math. Lett. 26(1), 124–129 (2013)
Li, J.H.: Parameter estimation for Hammerstein CARARMA systems based on the Newton iteration. Appl. Math. Lett. 26(1), 91–96 (2013)
Hu, P.P., Ding, F.: Multistage least squares based iterative estimation for feedback nonlinear systems with moving average noises using the hierarchical identification principle. Nonlinear Dyn. 73(1–2), 583–592 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61273194, 61203111), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (China, BK2012549), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions and the 111 Project (B12018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, F., Ma, J. & Xiao, Y. Newton iterative identification for a class of output nonlinear systems with moving average noises. Nonlinear Dyn 74, 21–30 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-013-0943-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-013-0943-3